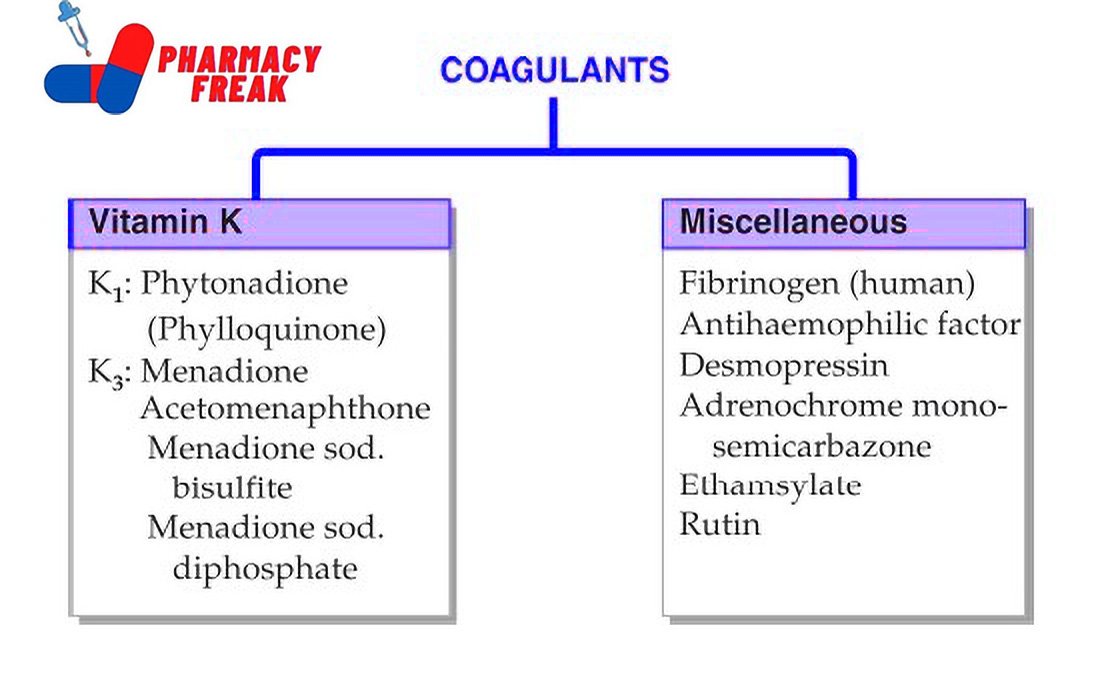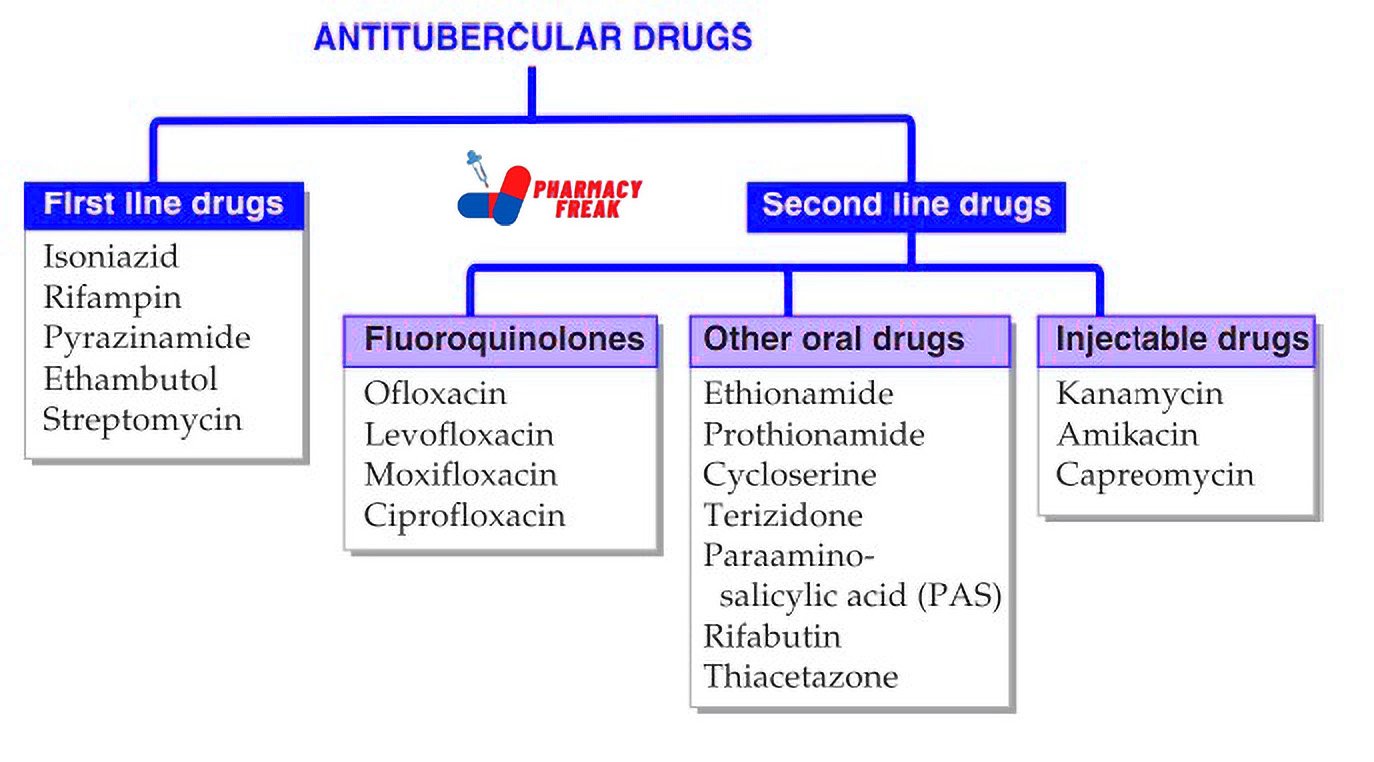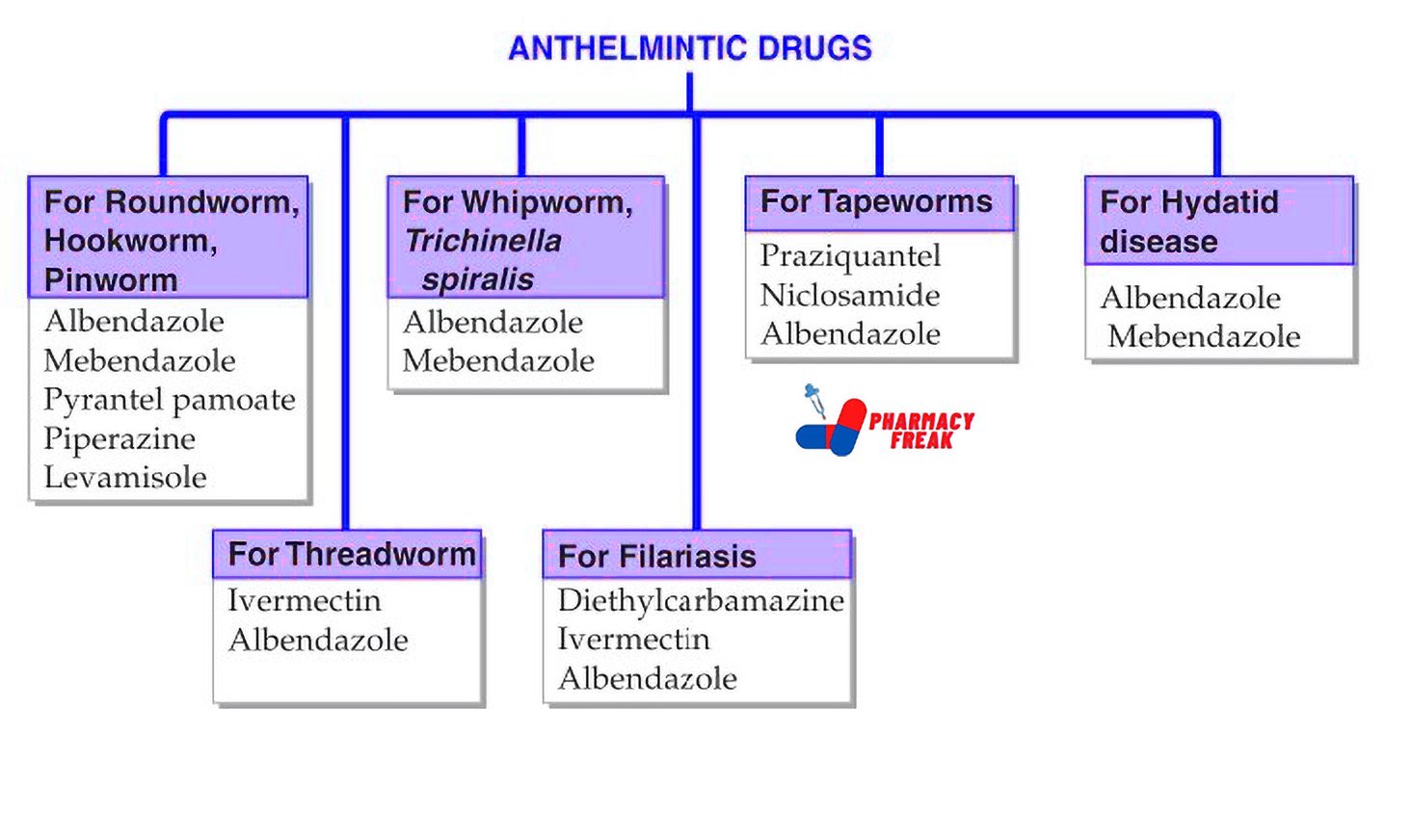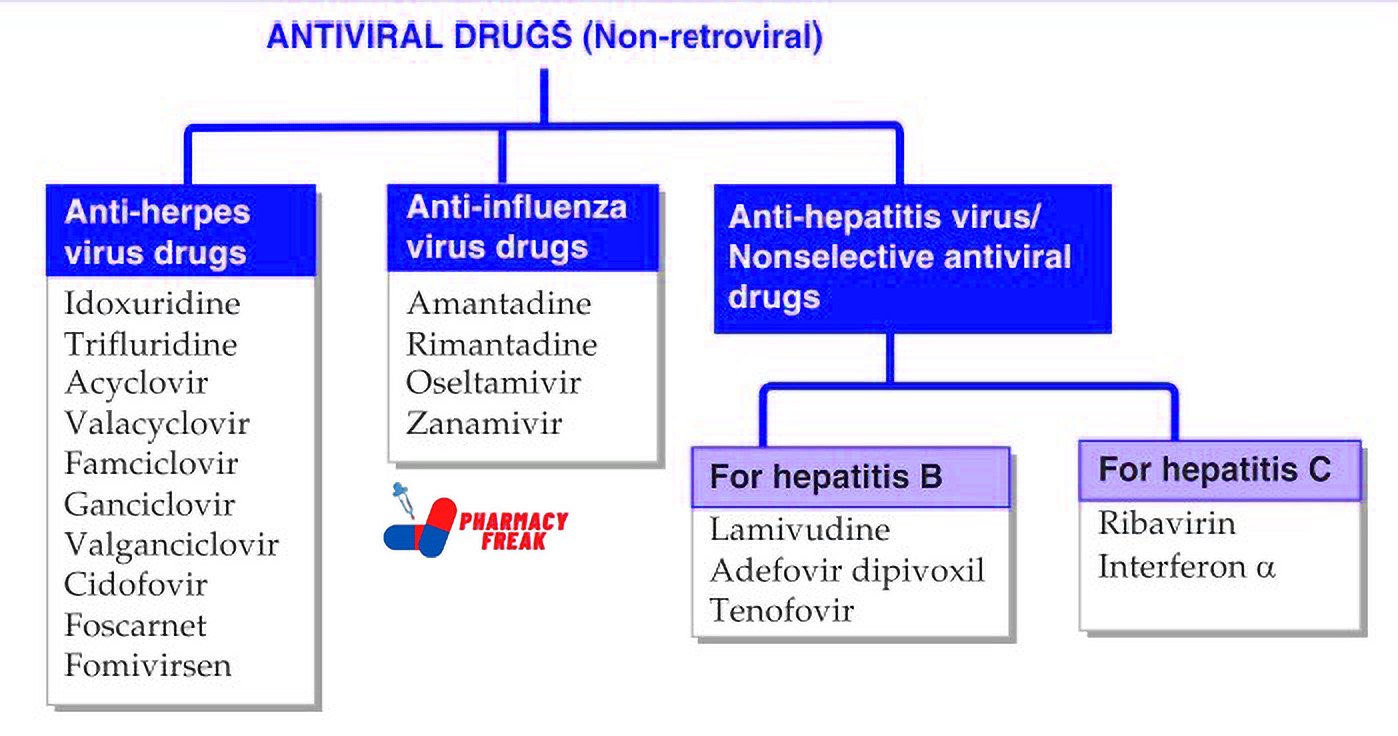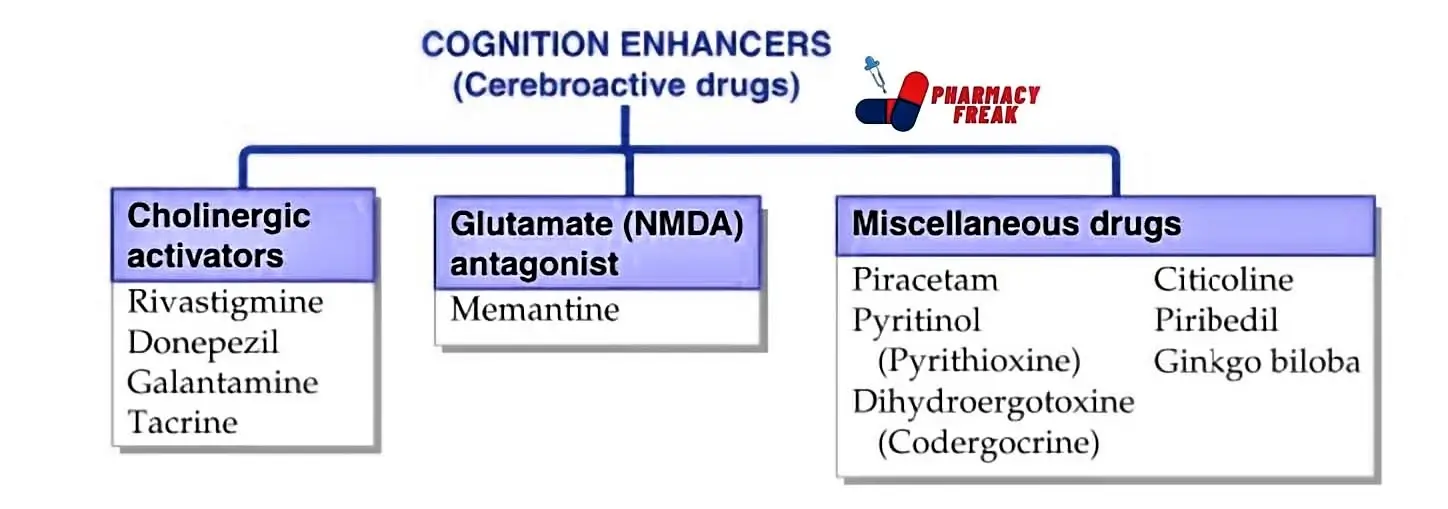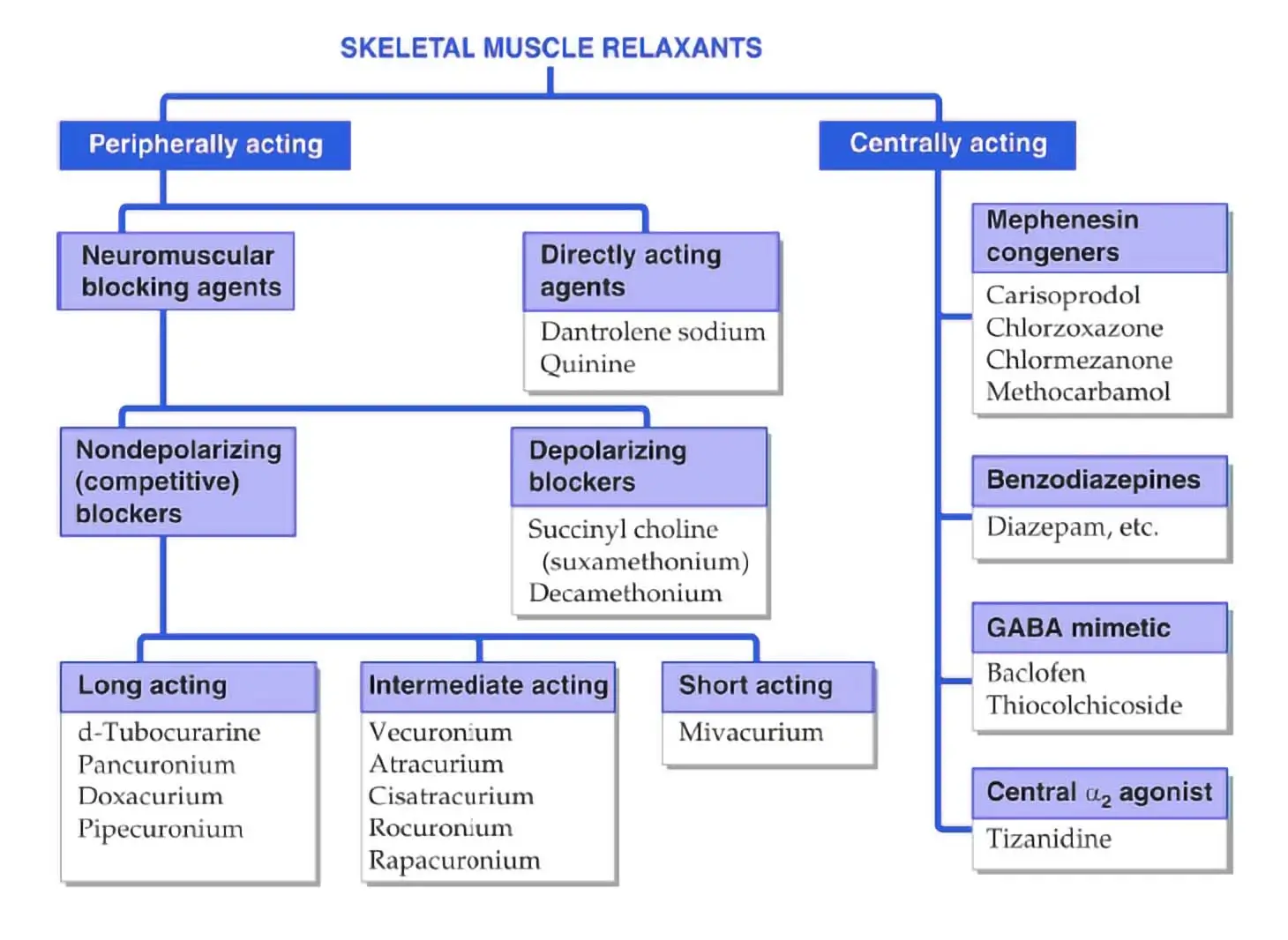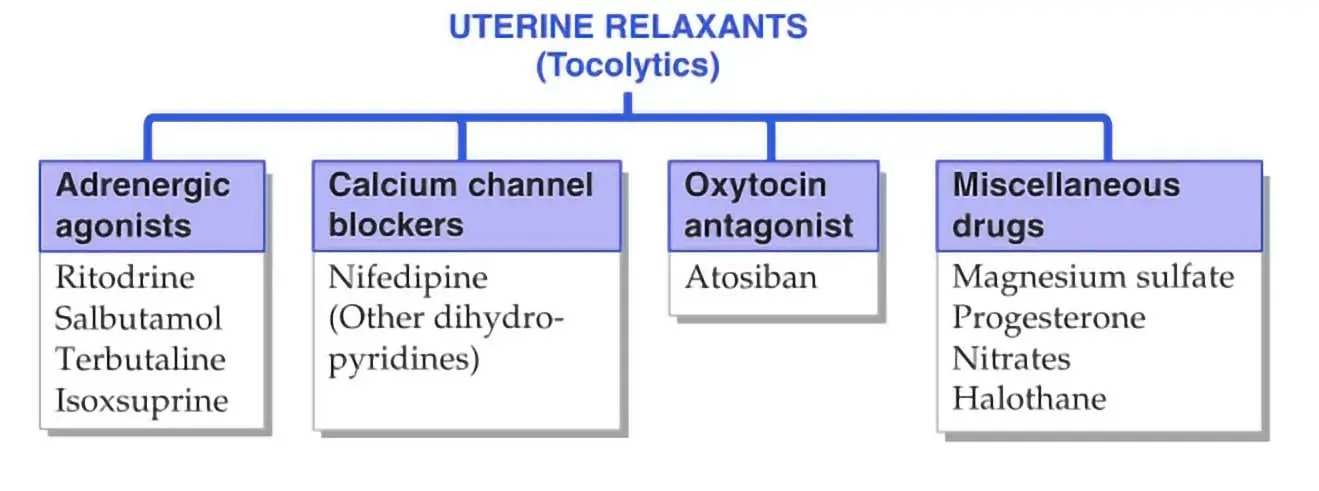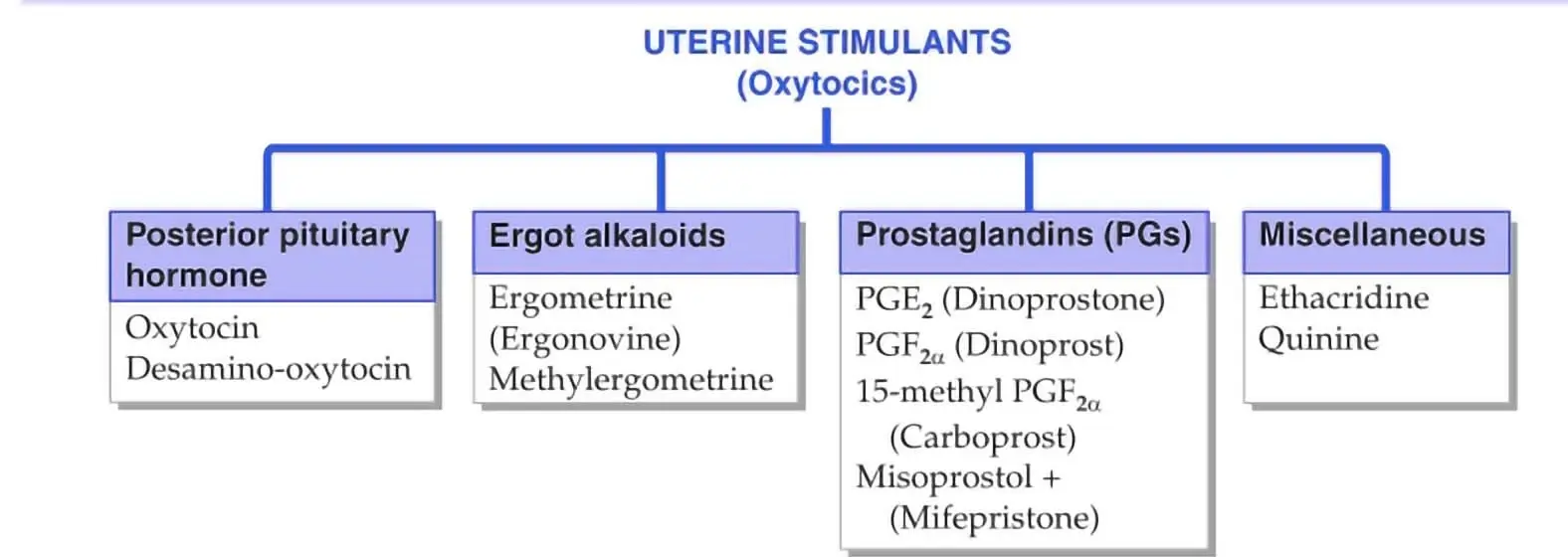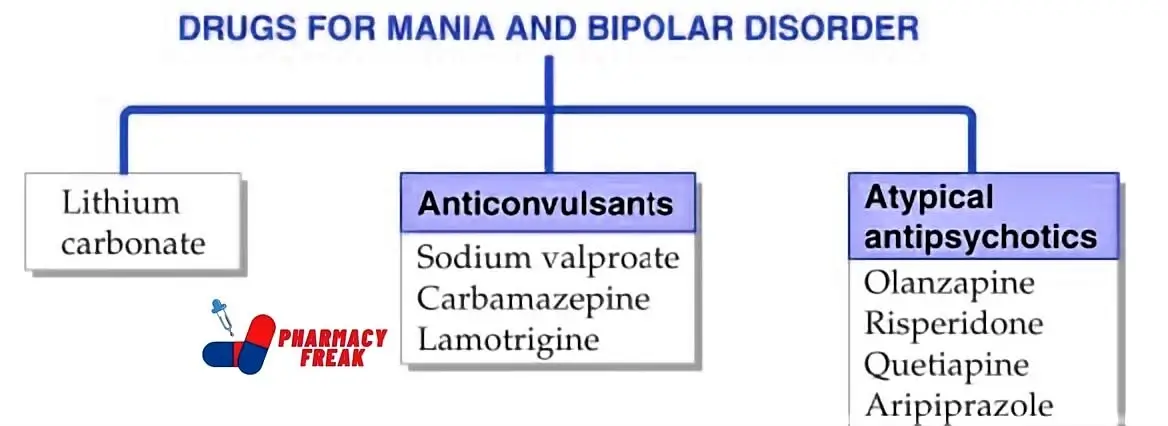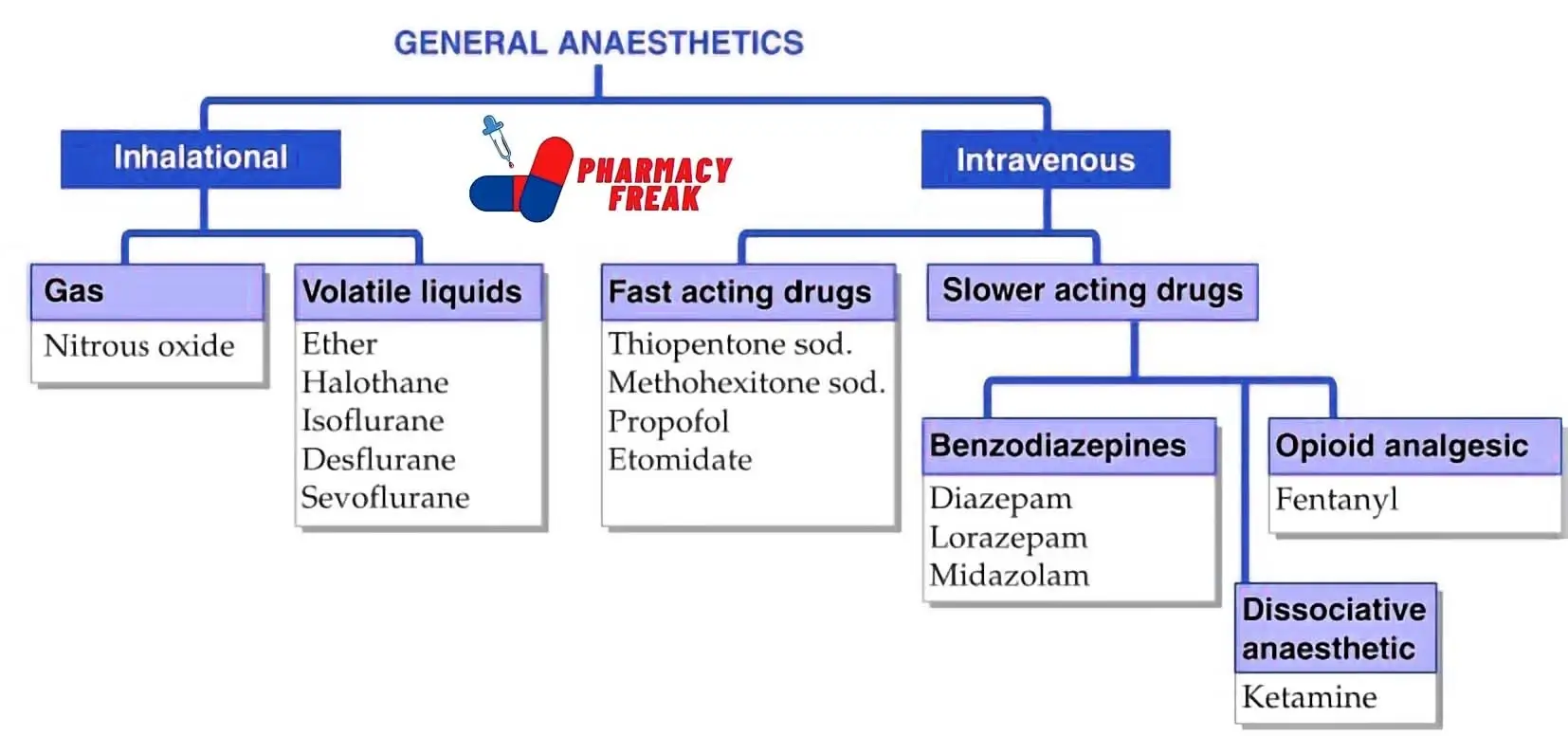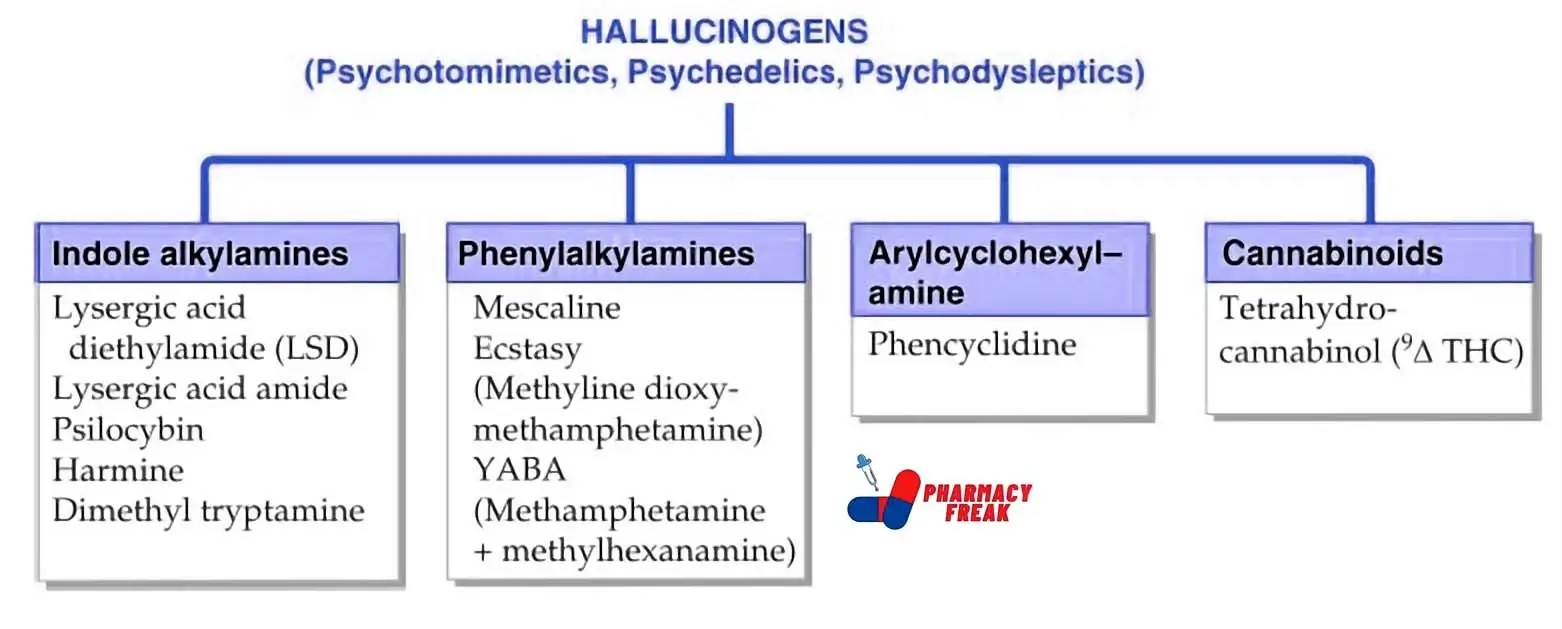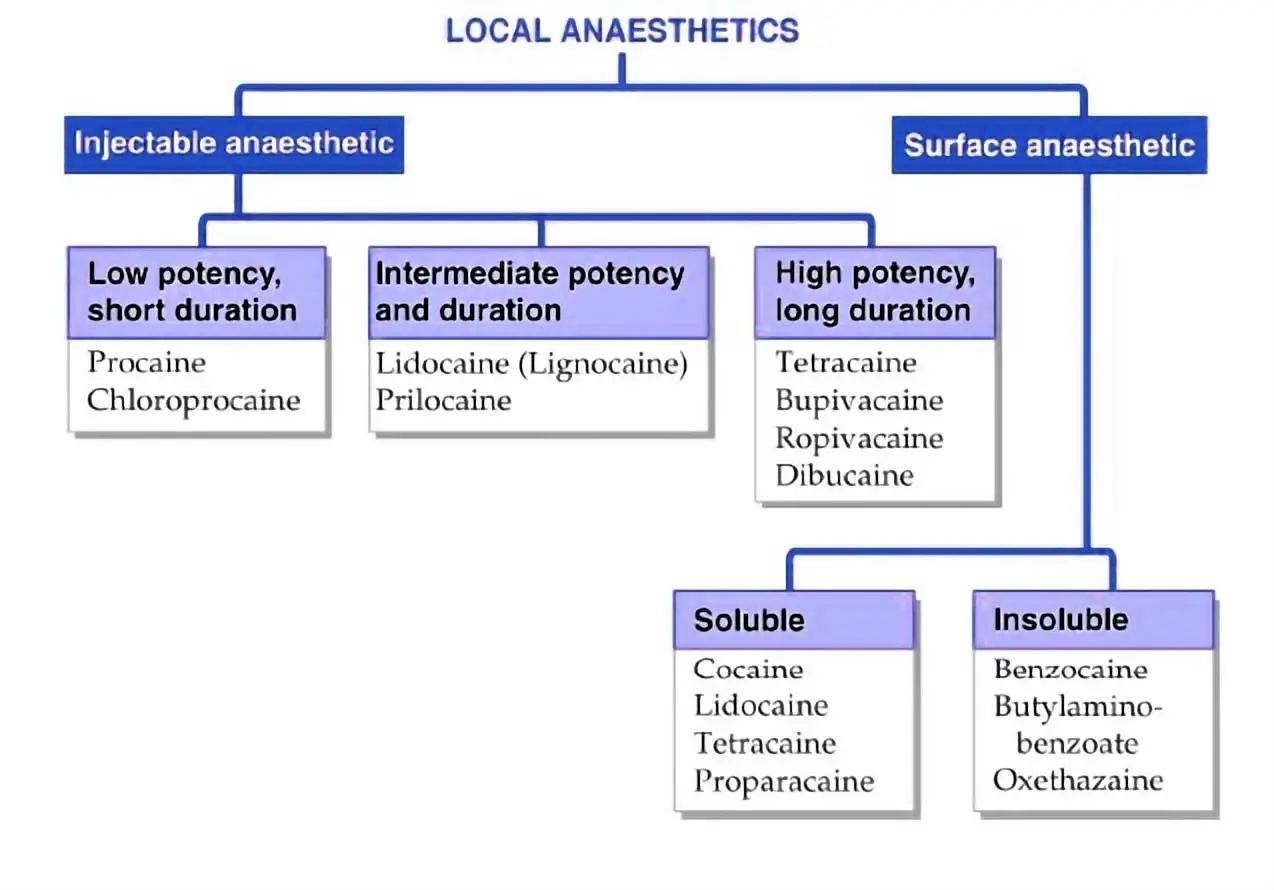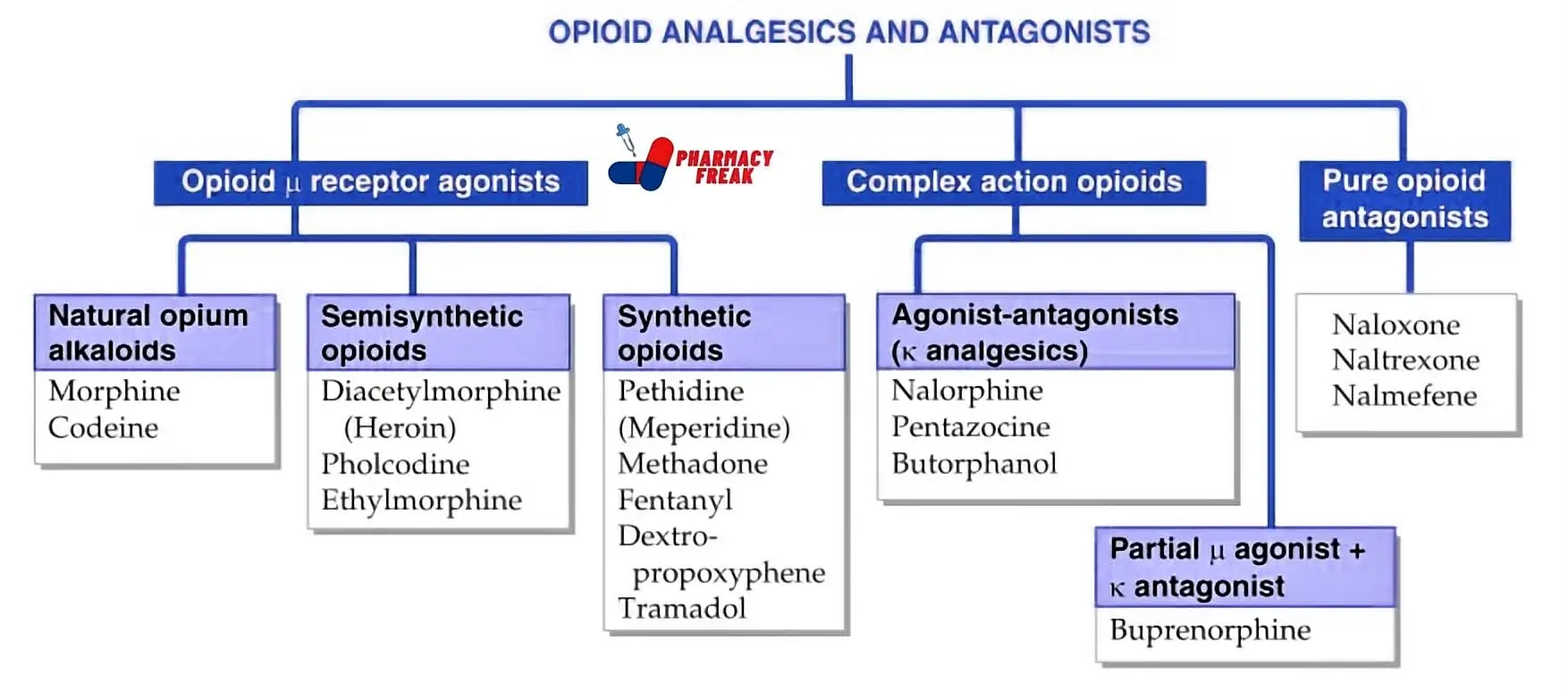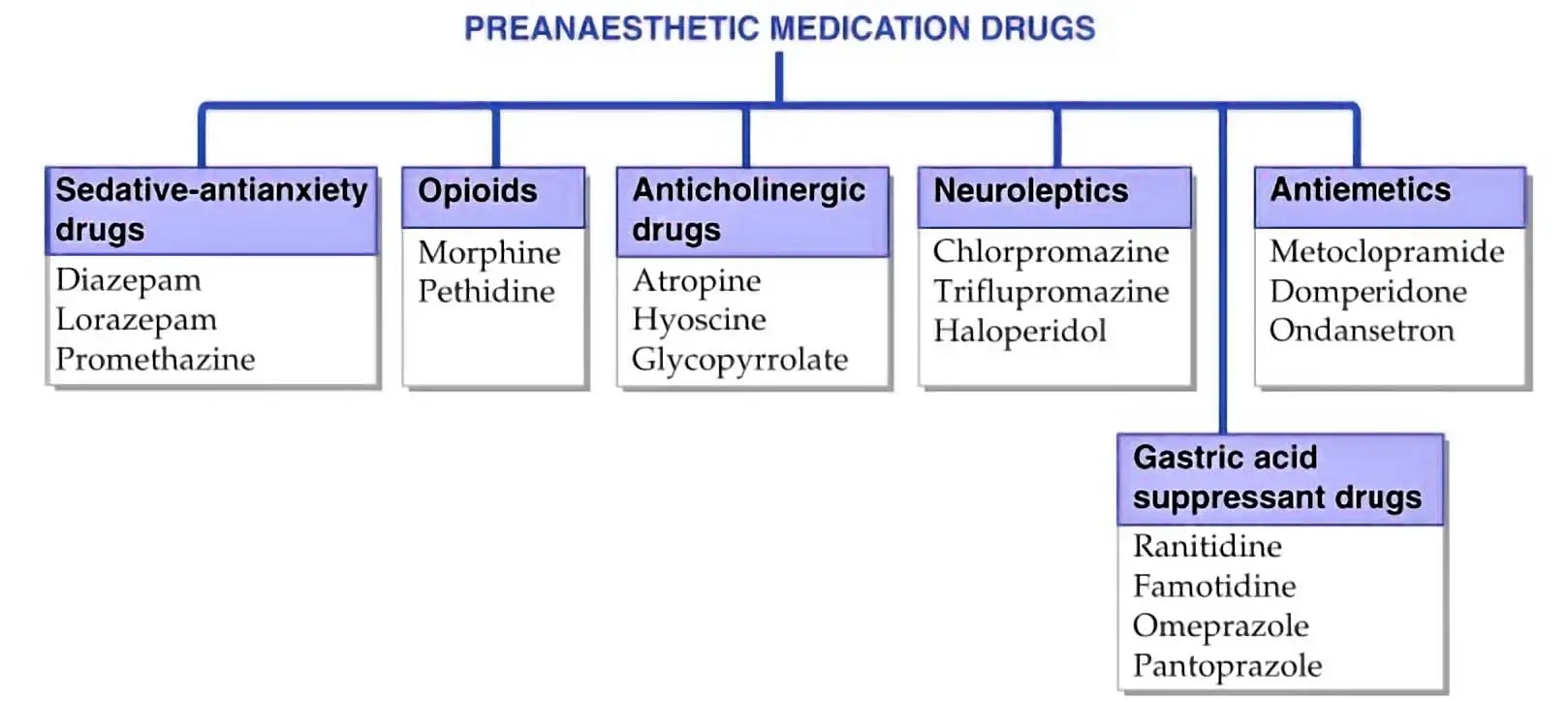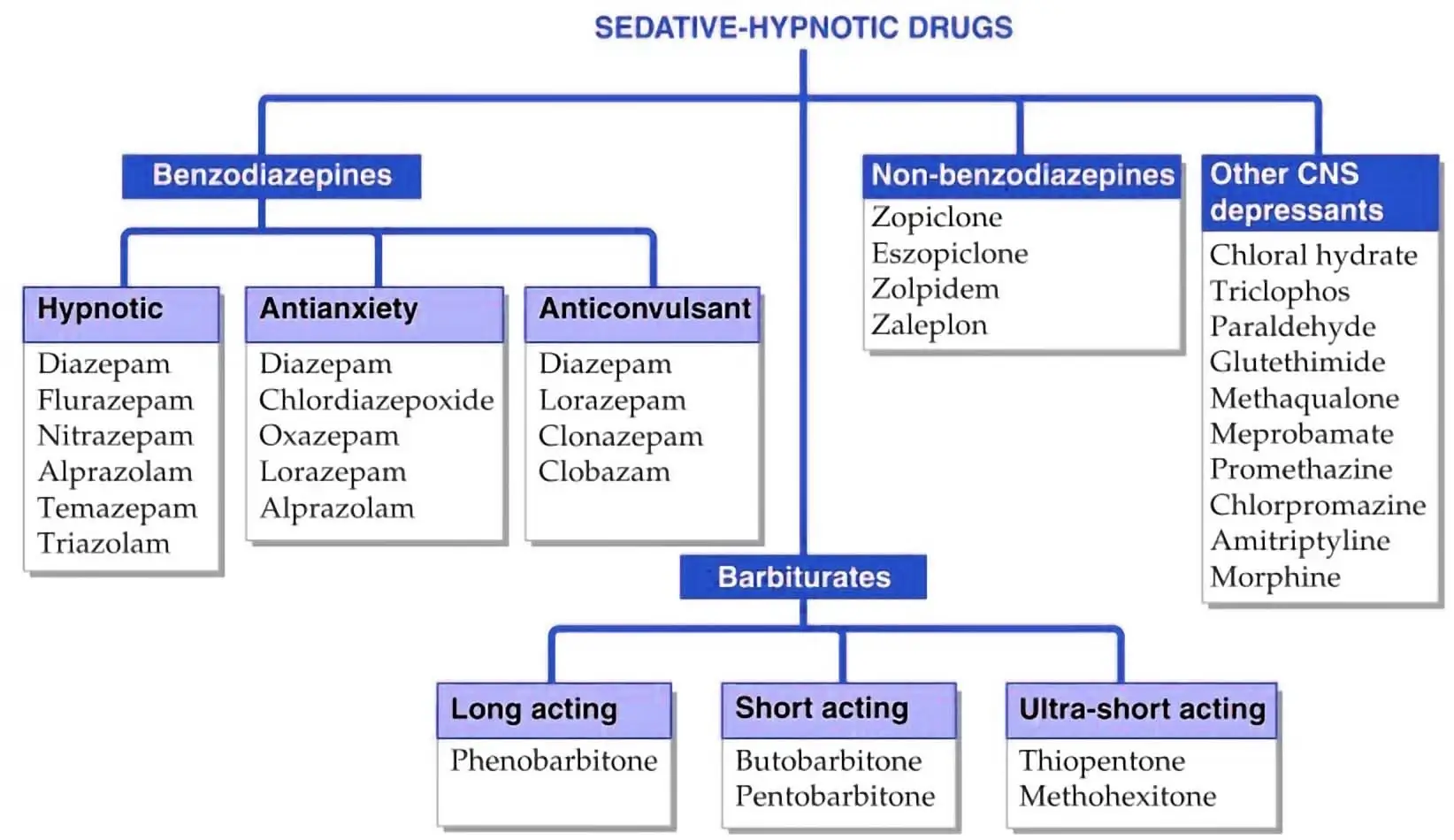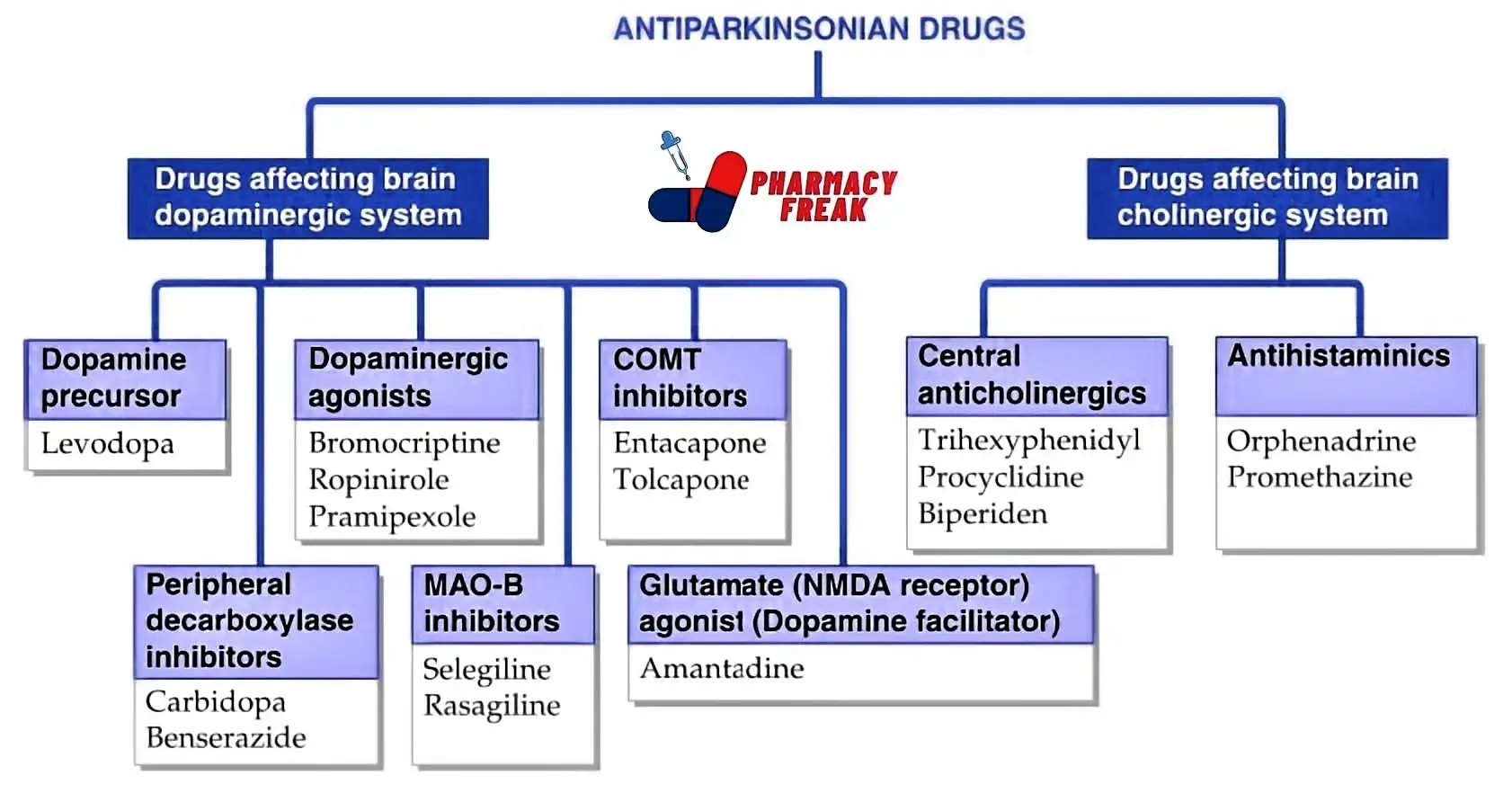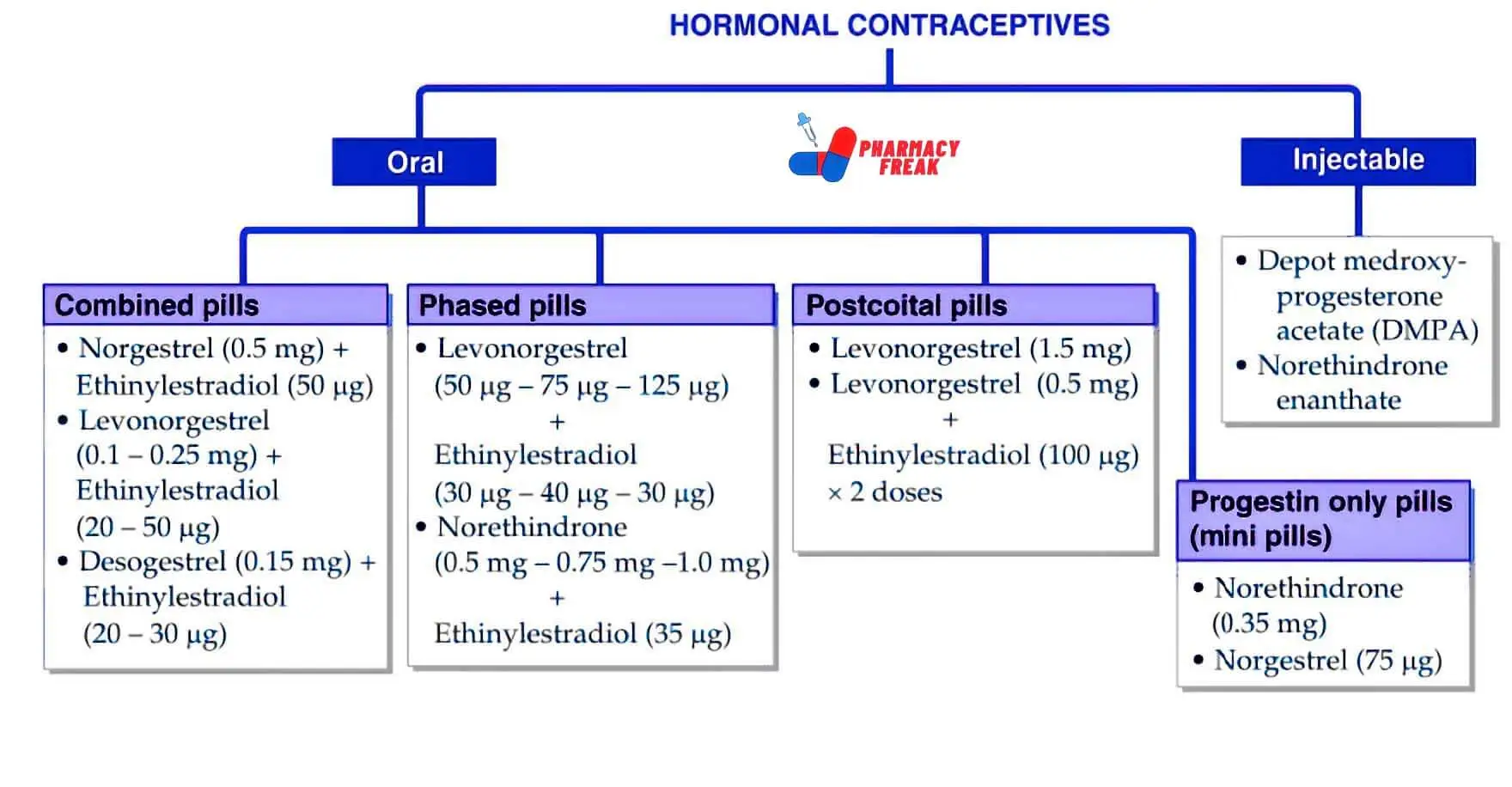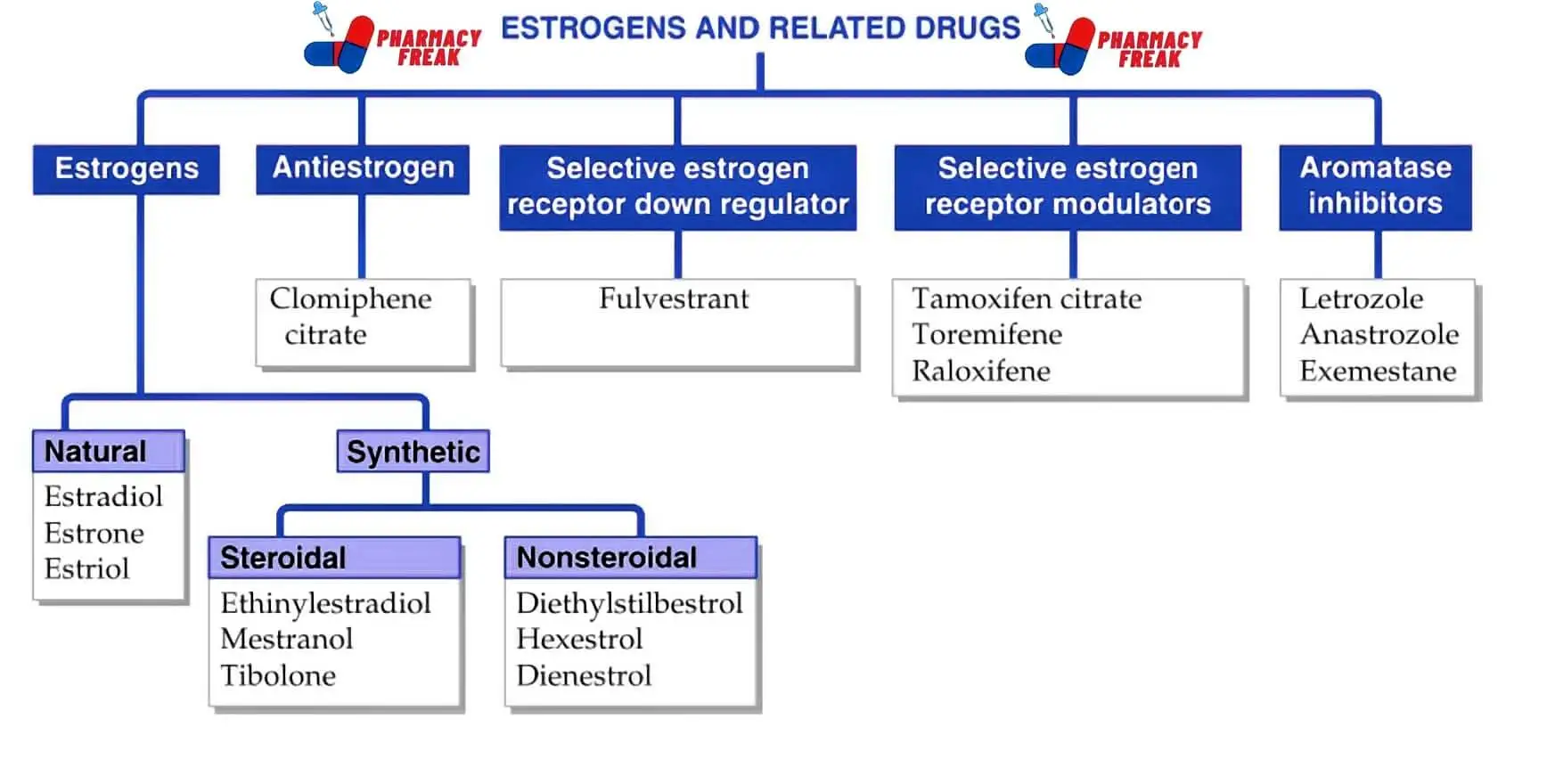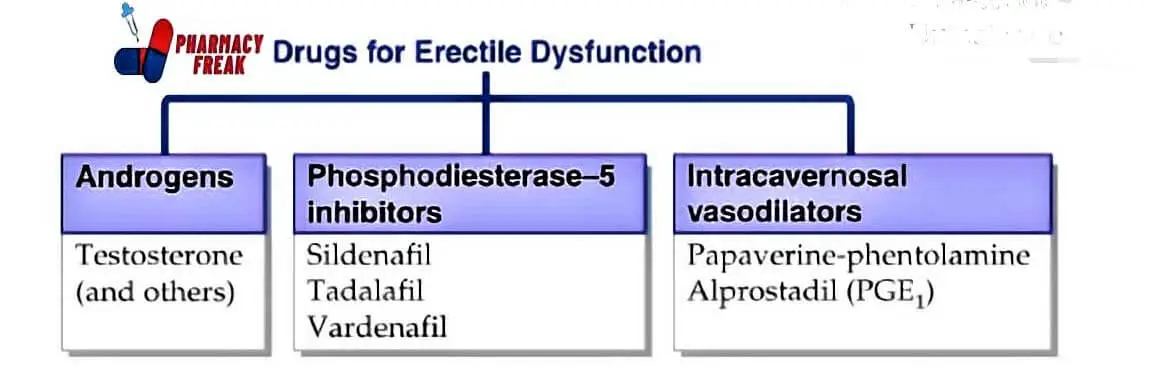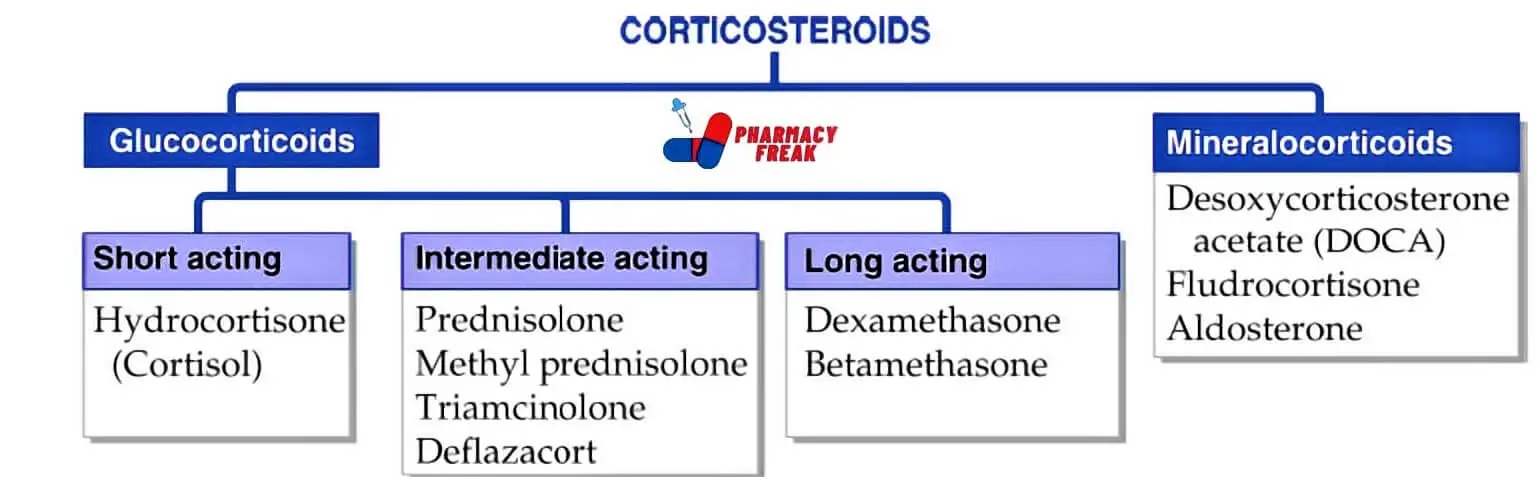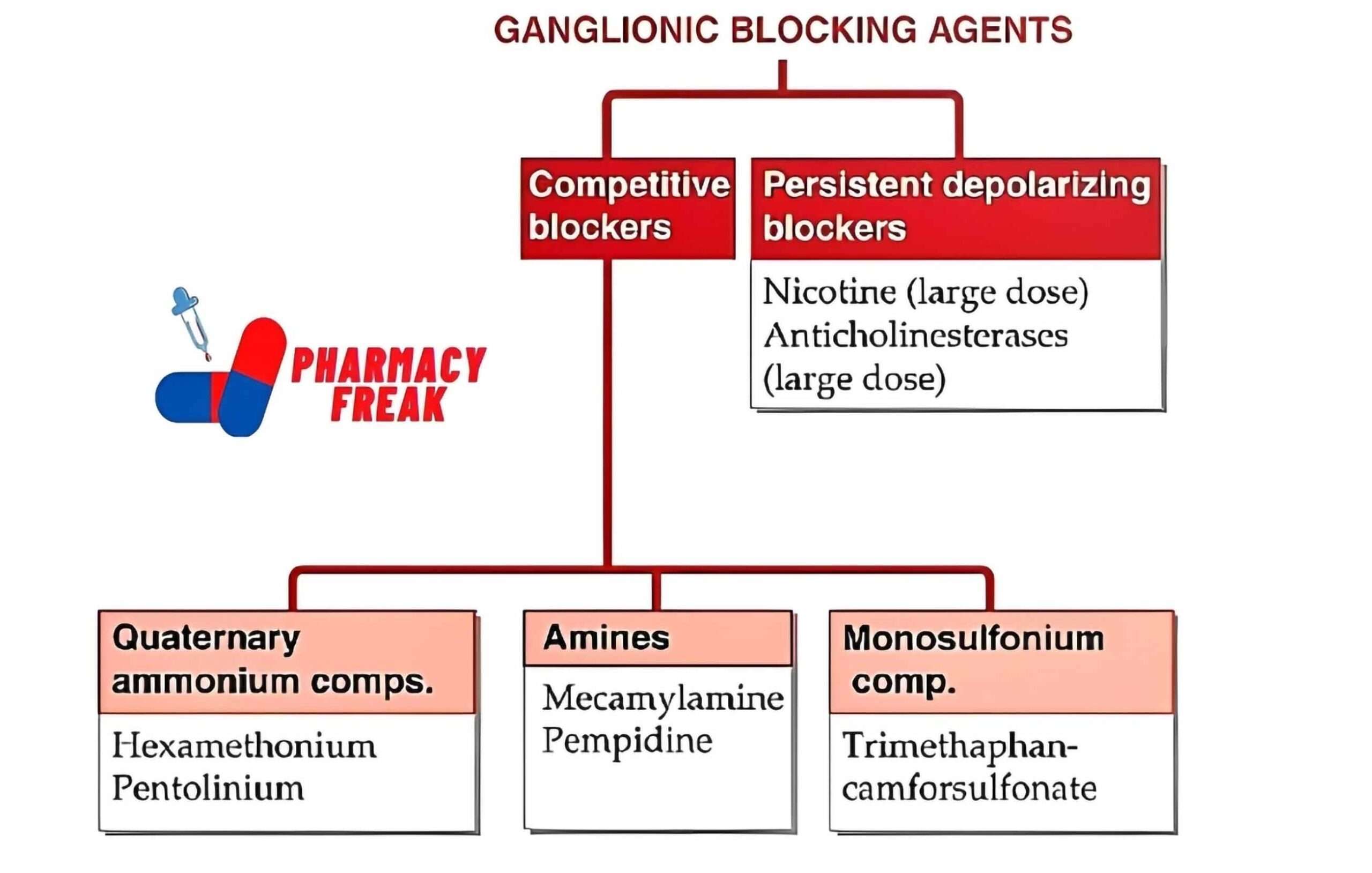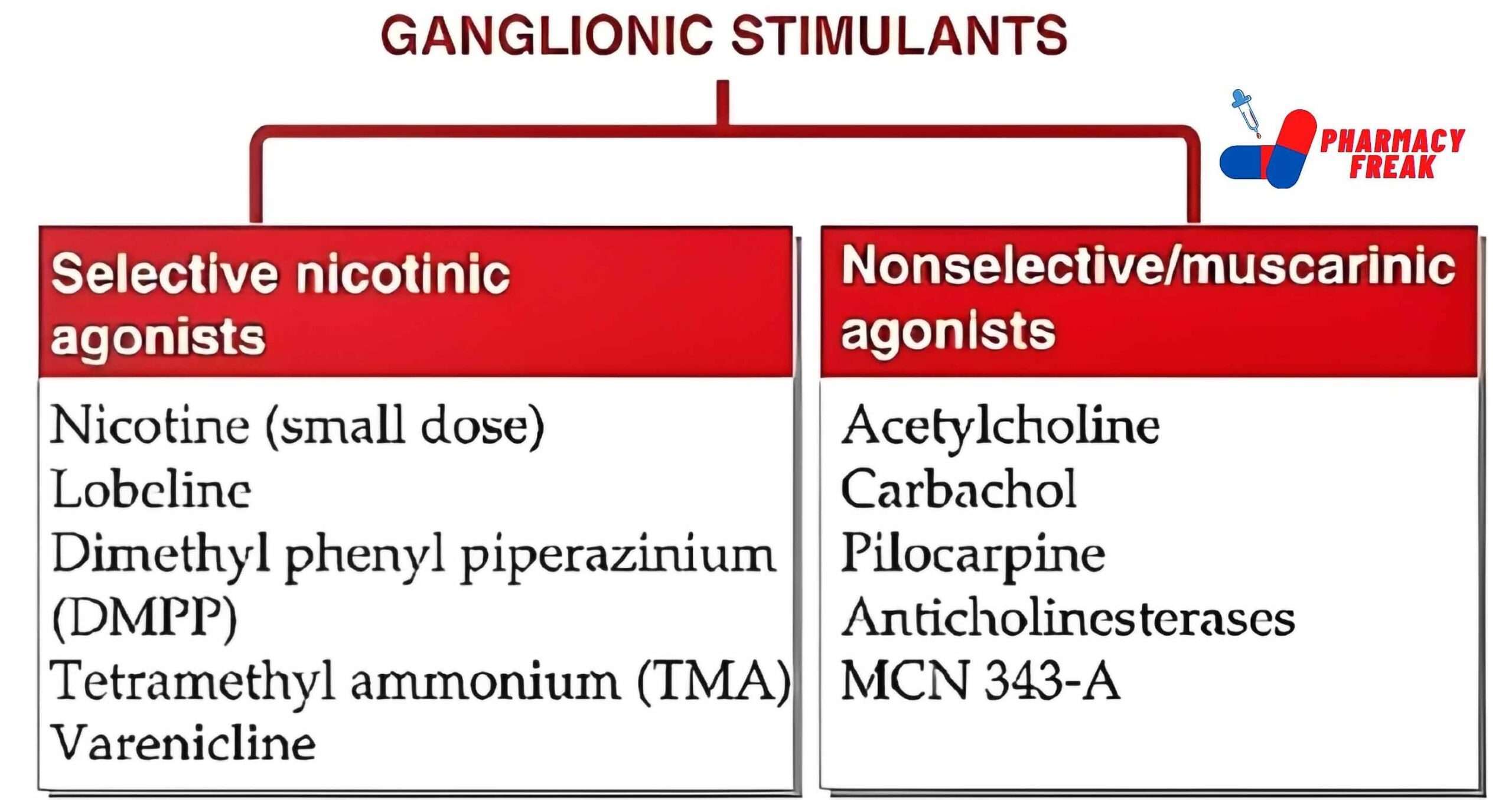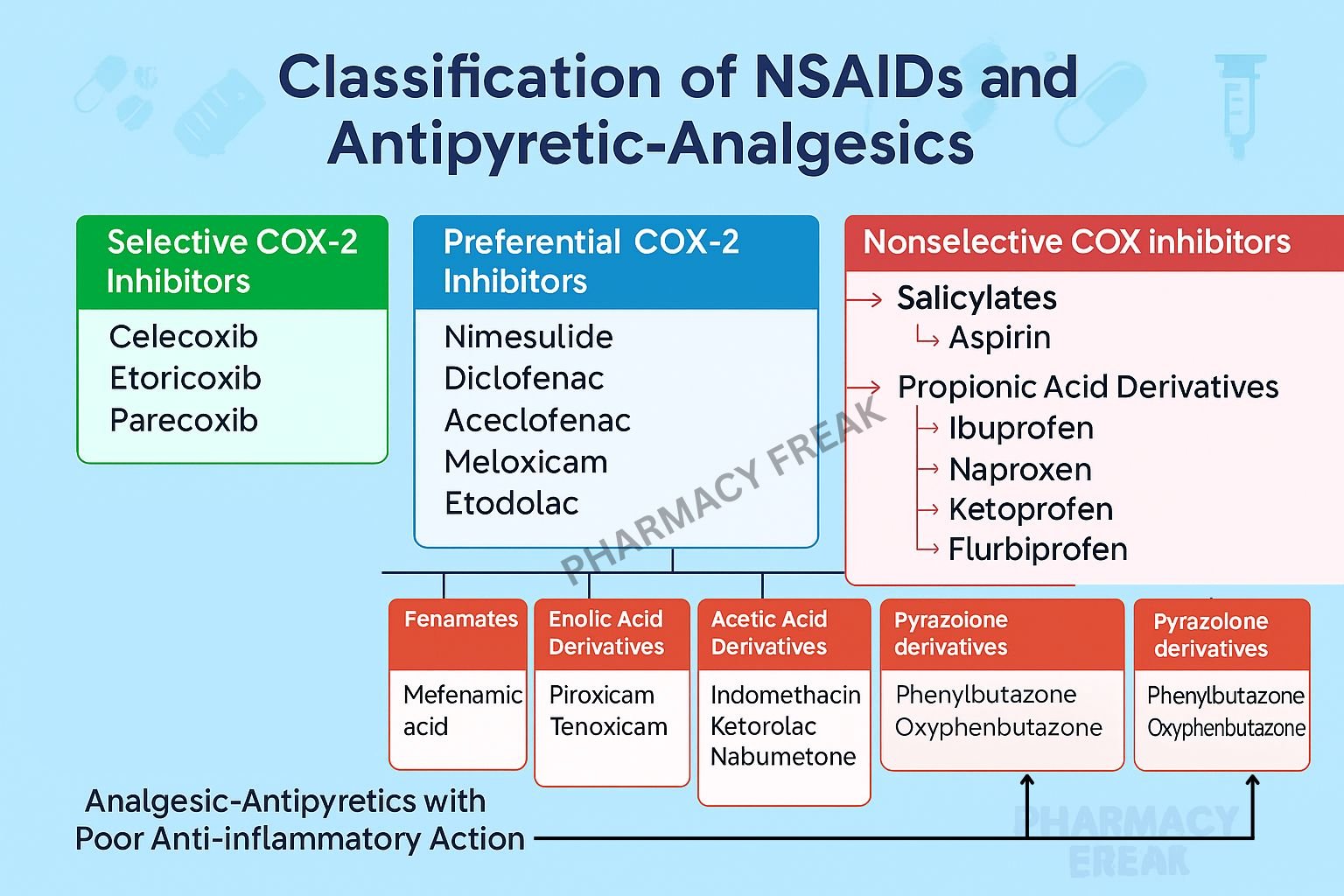
How to Understand the Drug Classification Chart
This chart may look technical at first, but once you understand the parts, it becomes easy to follow. Let’s walk through what each section means and why it’s important.
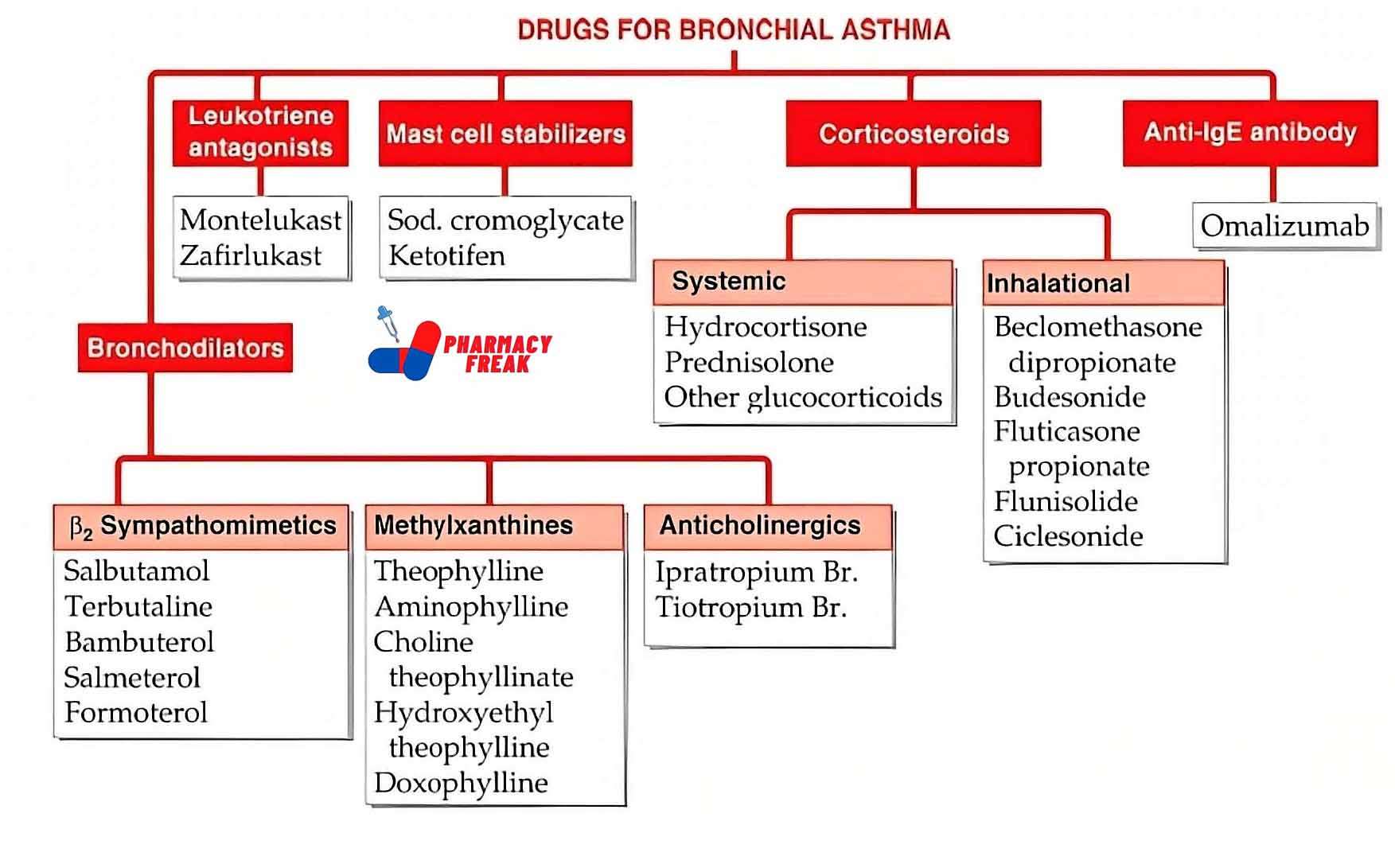
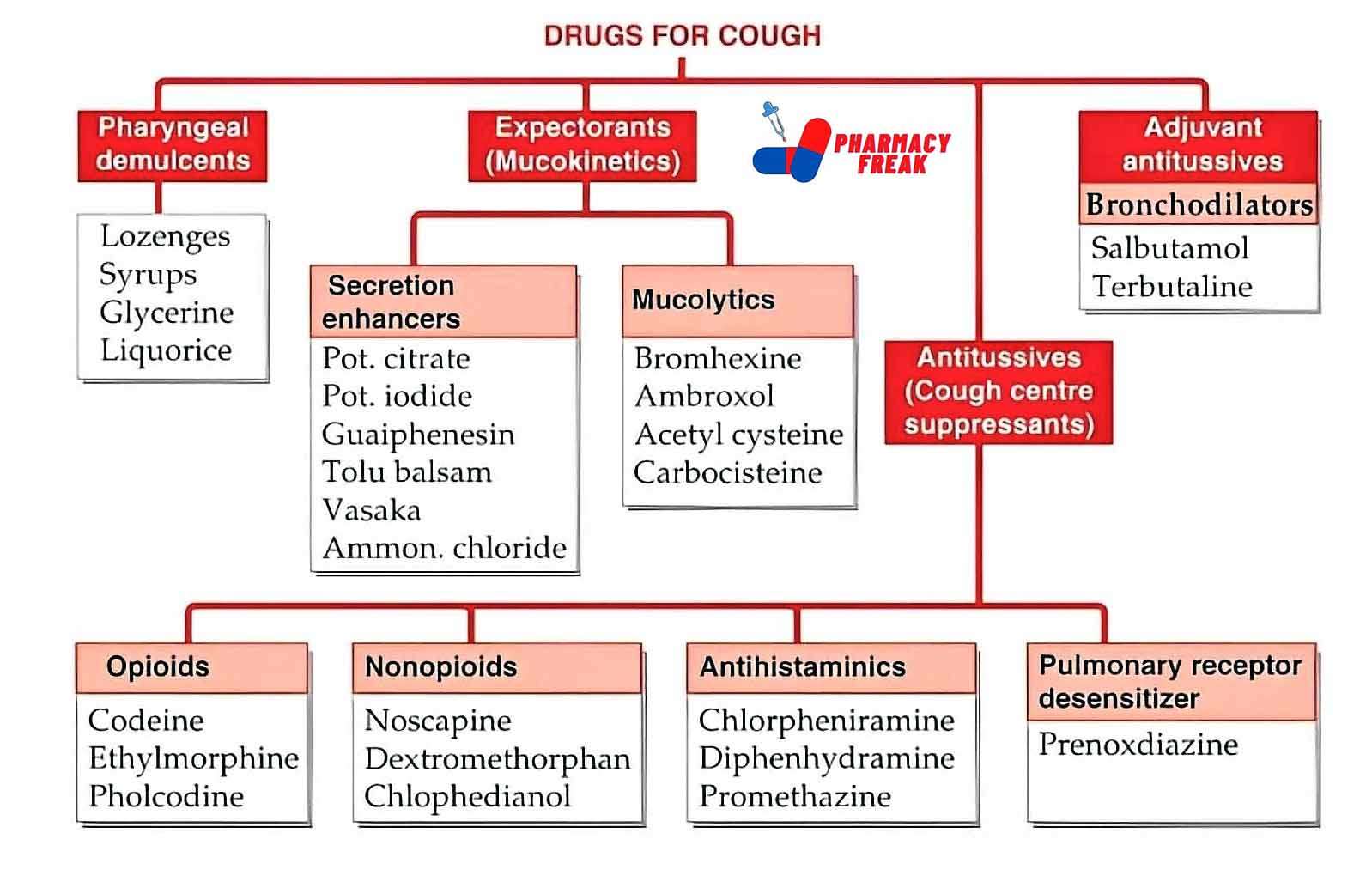
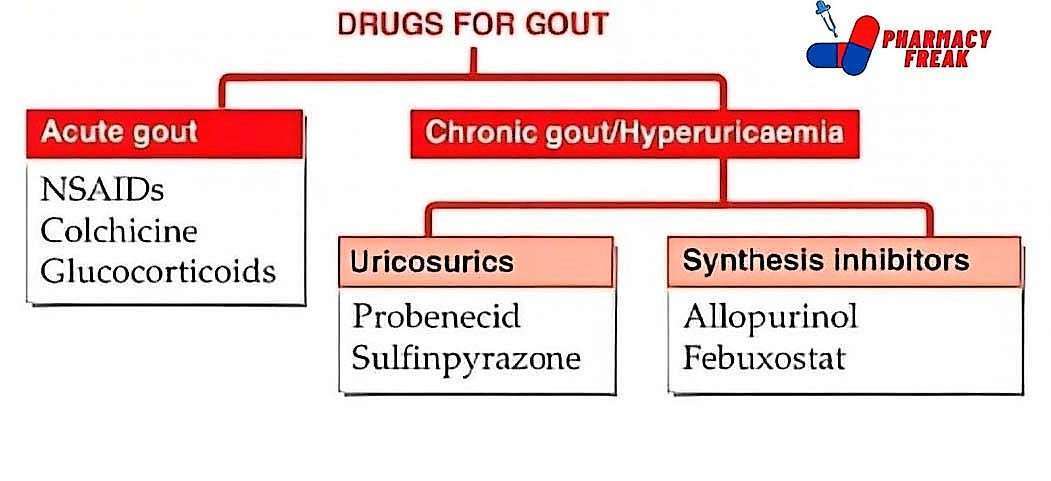
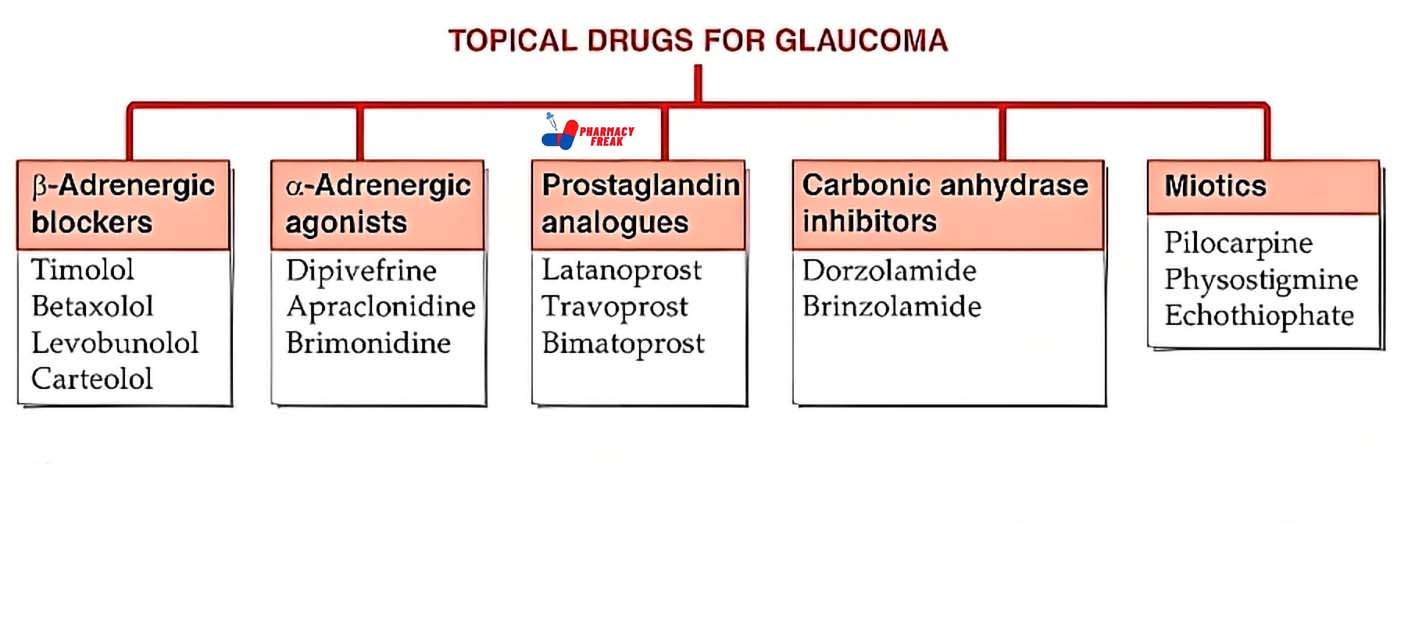
1. Therapeutic Classification: What the Drug Does in the Body
This part of the chart tells you the main purpose of a drug—what condition it treats or what effect it has.
For example:
Analgesics are used to relieve pain. These include drugs like paracetamol or ibuprofen.
Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, like penicillin or azithromycin.
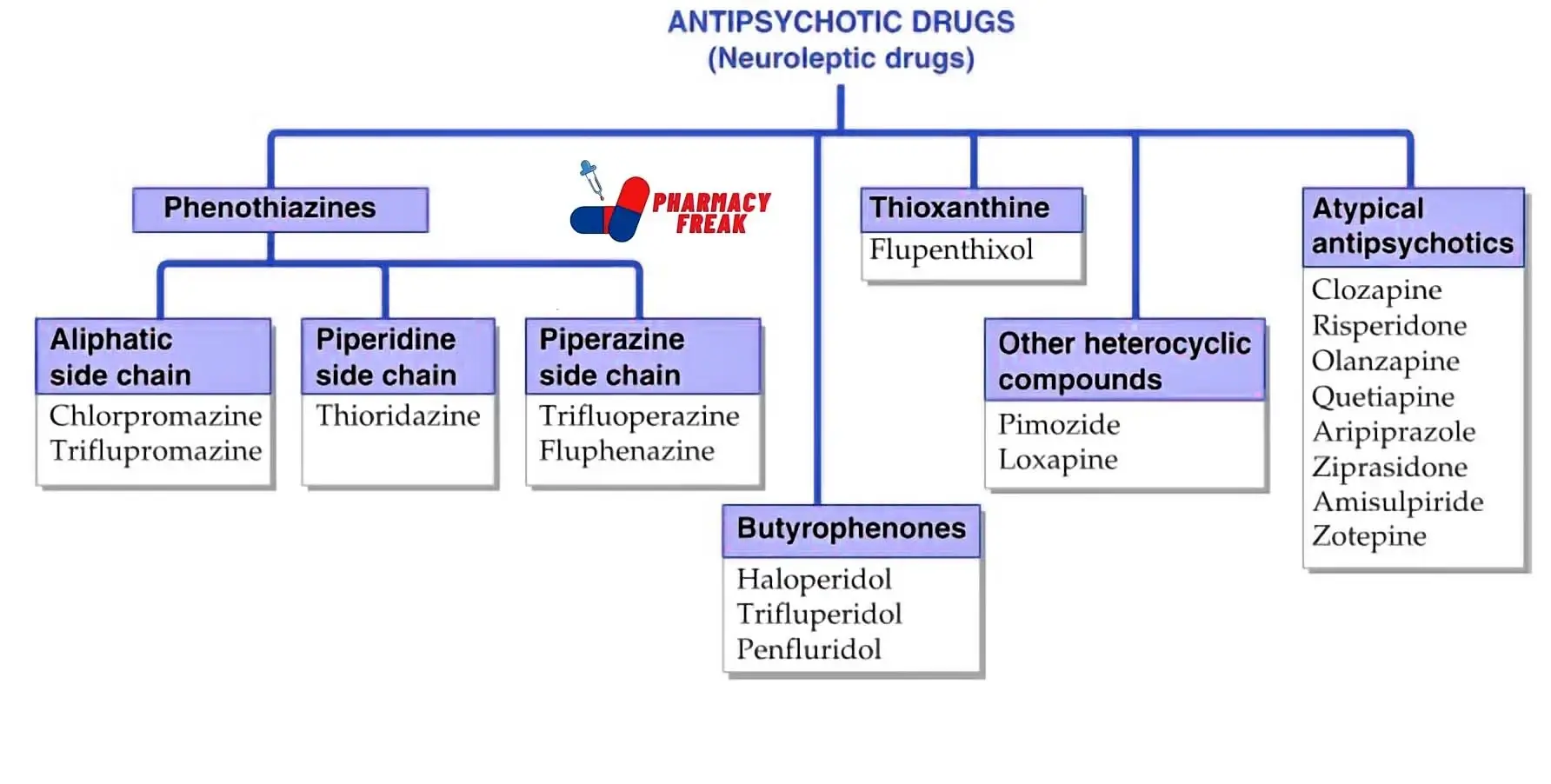
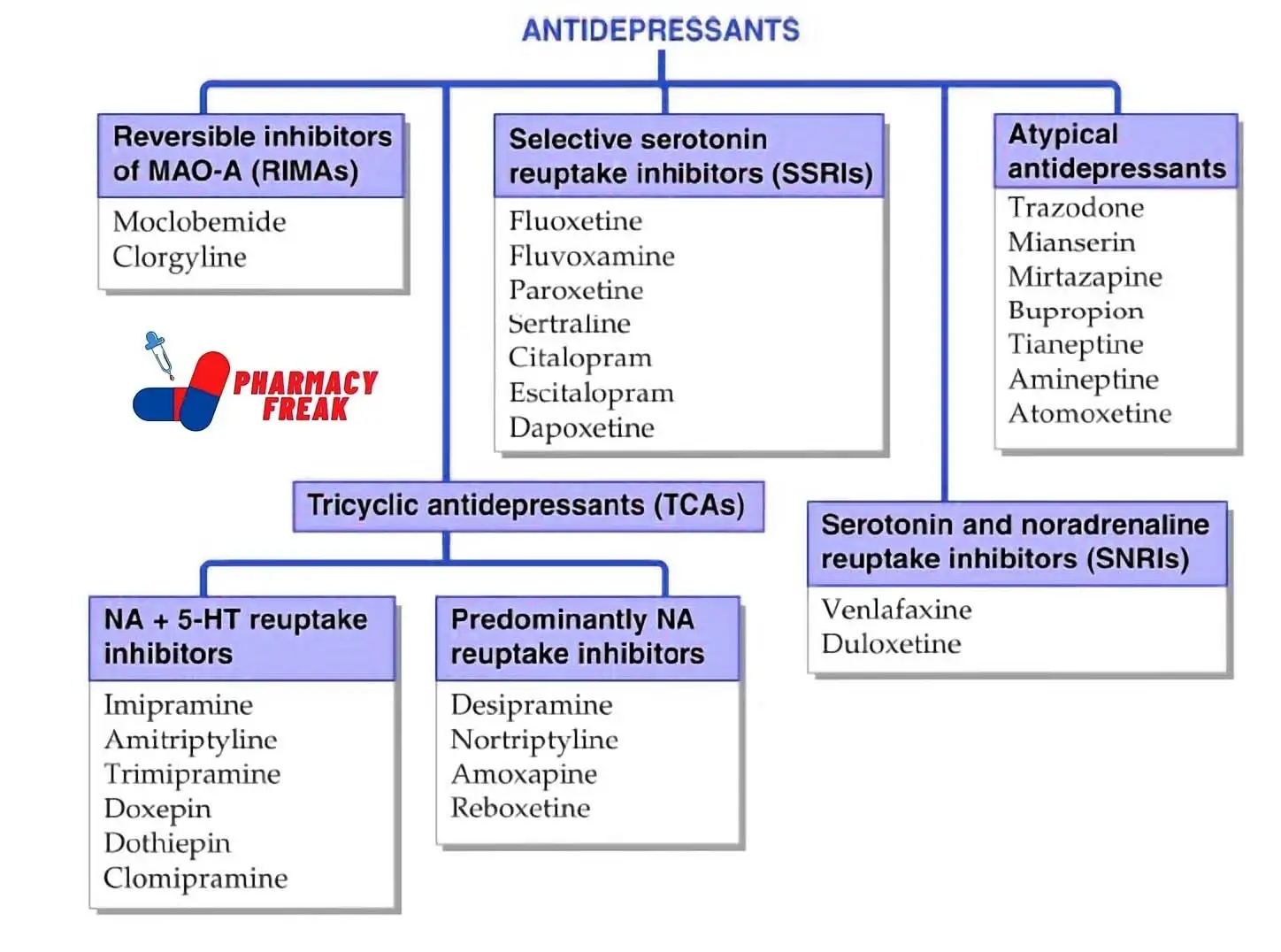
Antidepressants help manage depression and anxiety disorders.
Antacids reduce stomach acid and help with indigestion or heartburn.
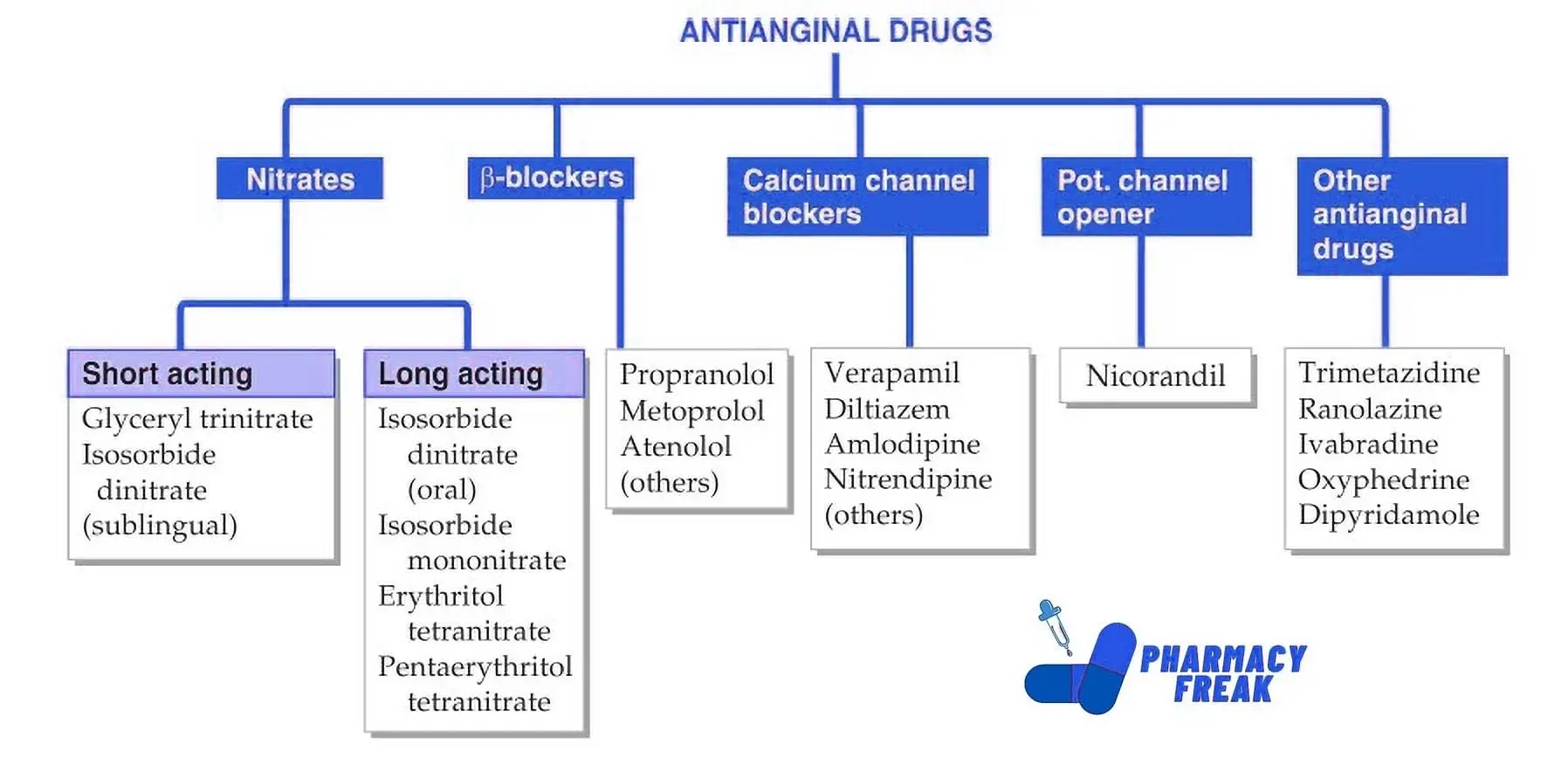
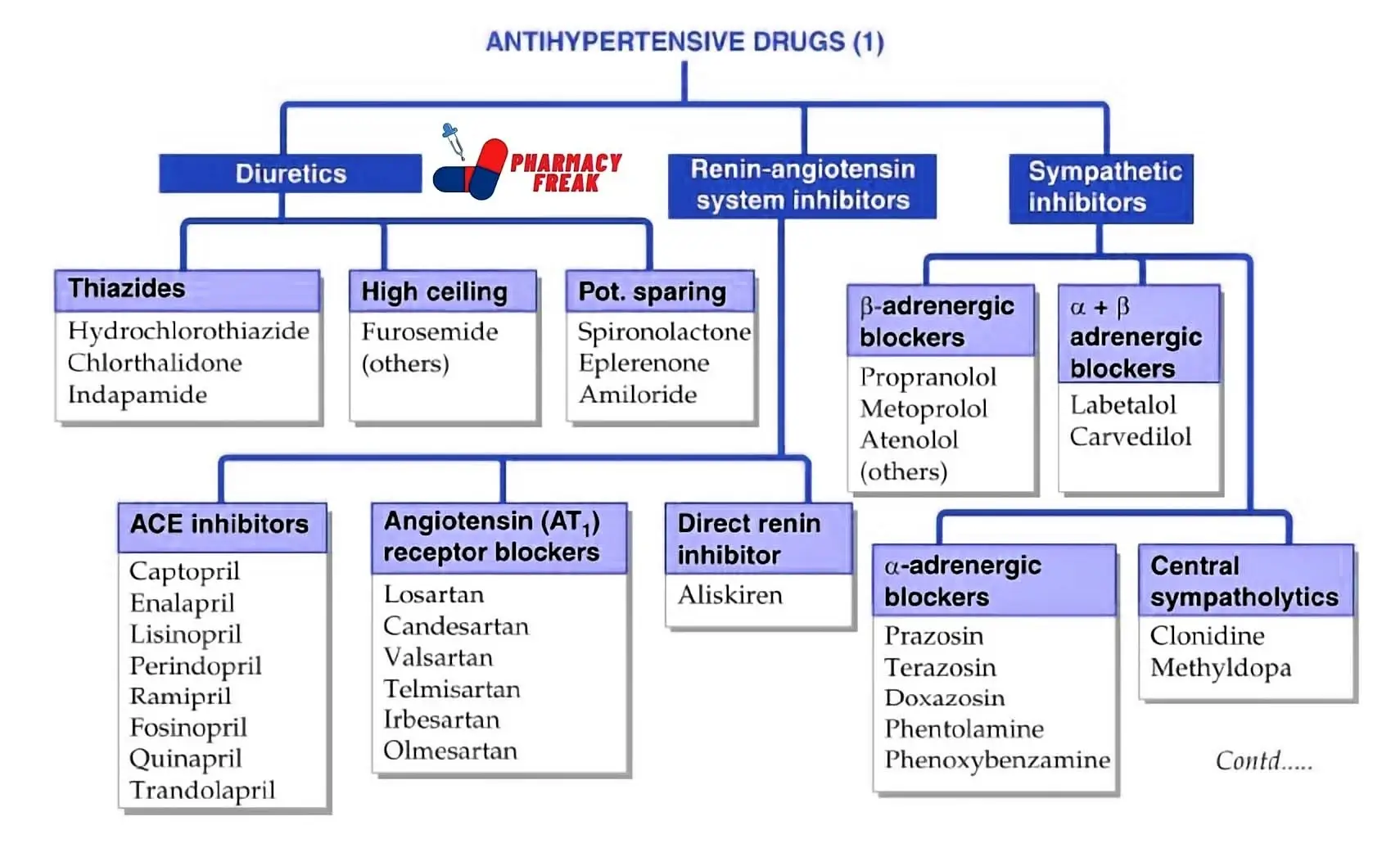
Antihypertensives lower high blood pressure.
This kind of grouping helps both patients and healthcare workers quickly understand a drug’s main function. If you’re ever prescribed a new medication, looking up its class can tell you what it’s supposed to do.
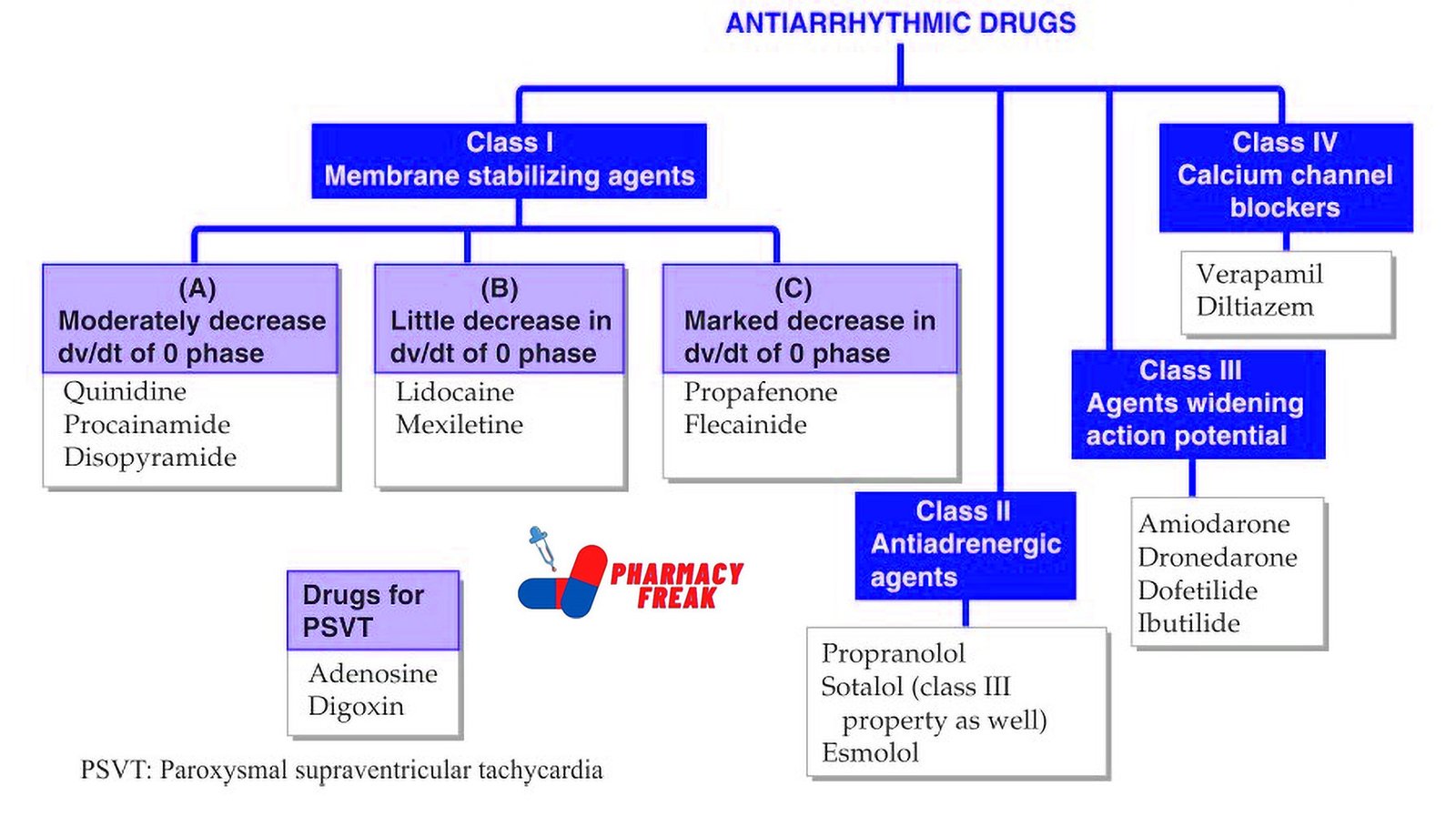
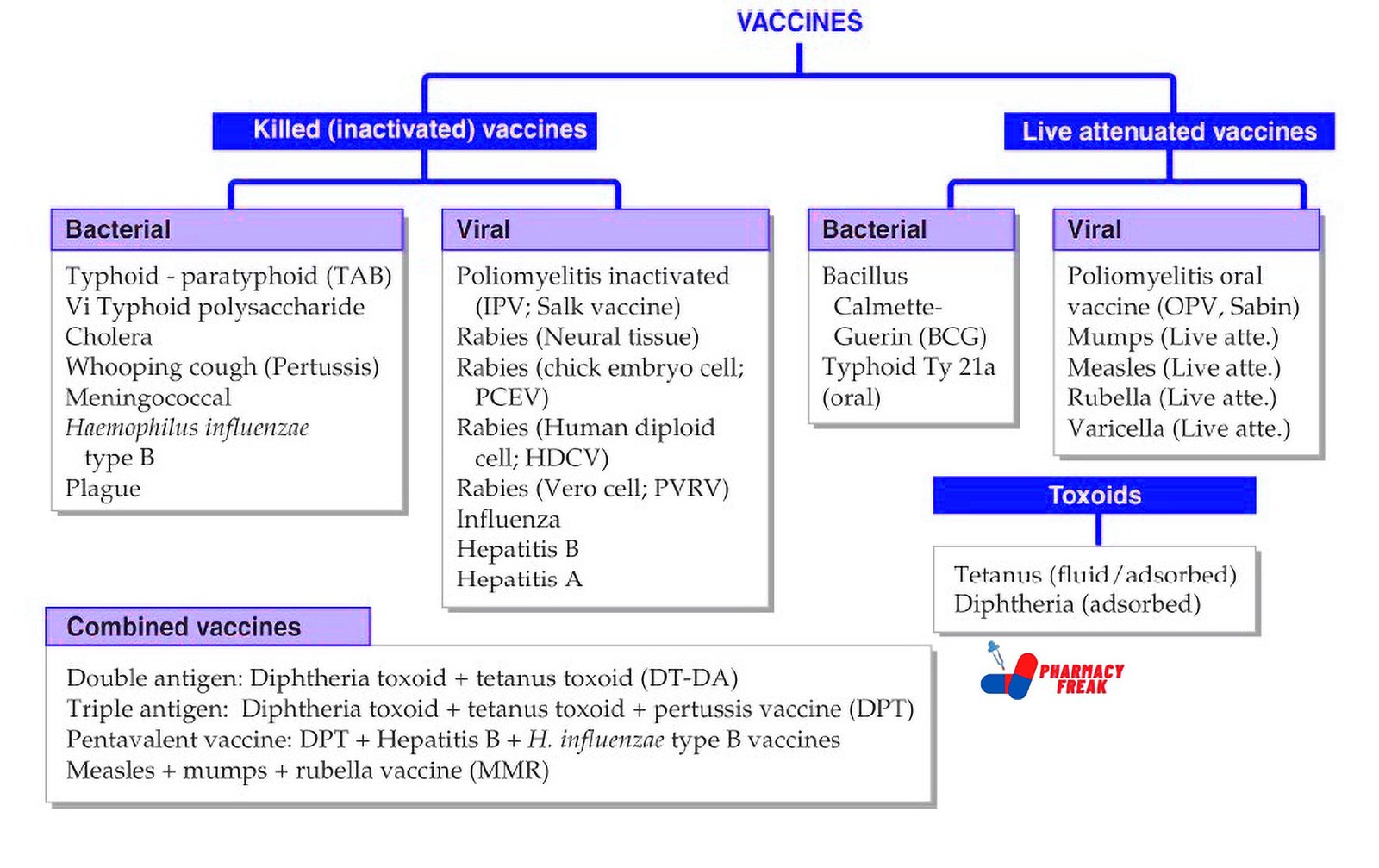
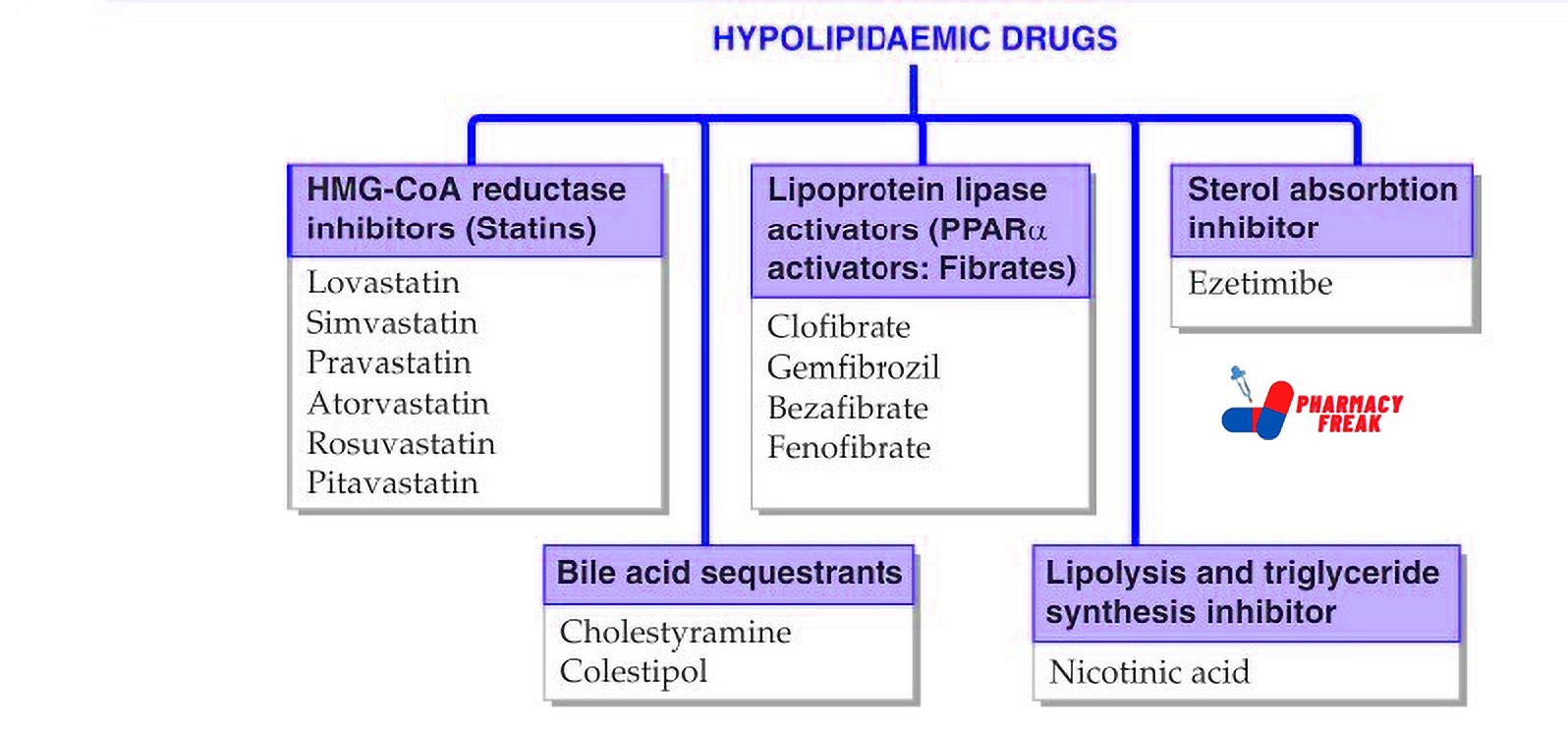
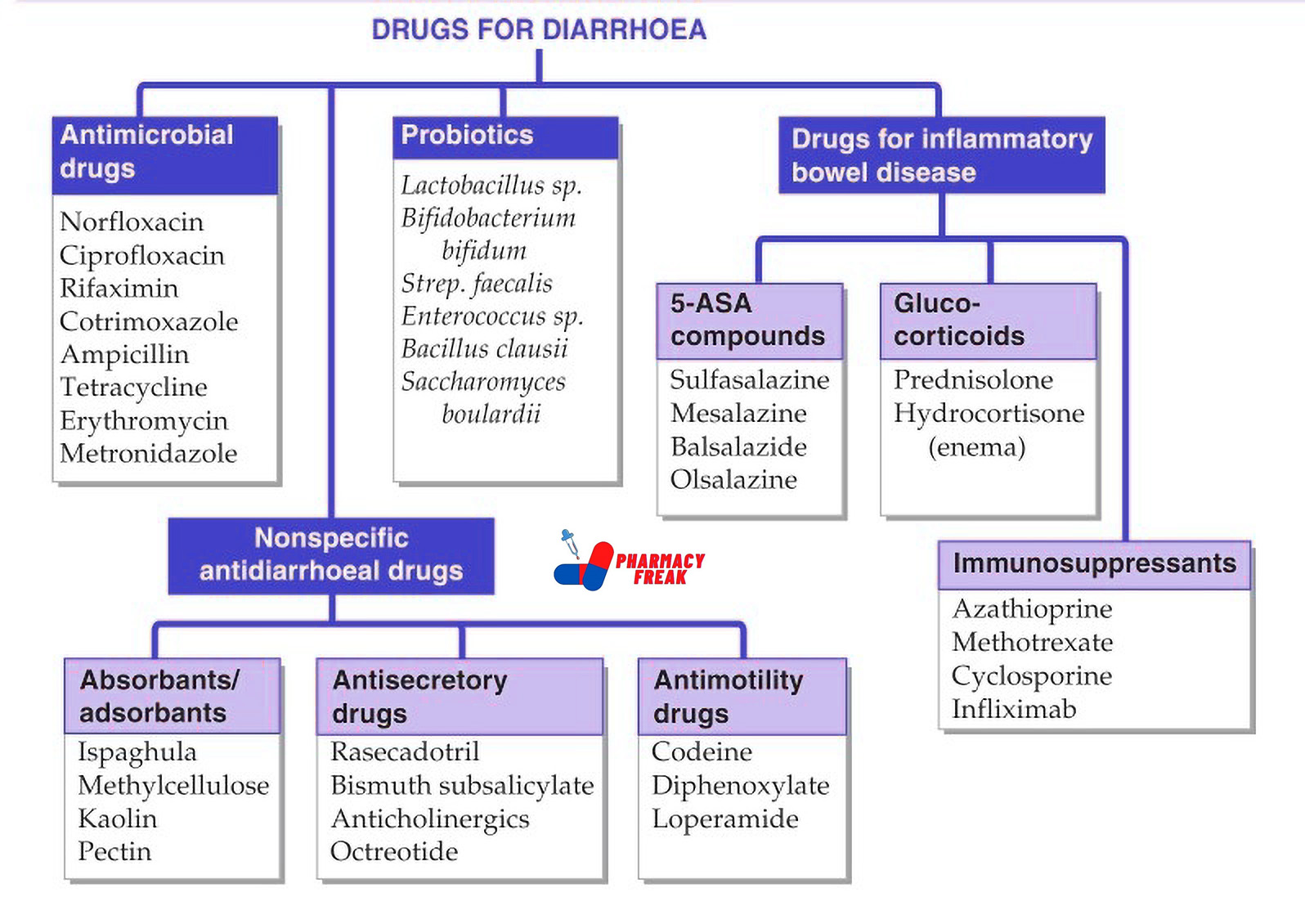
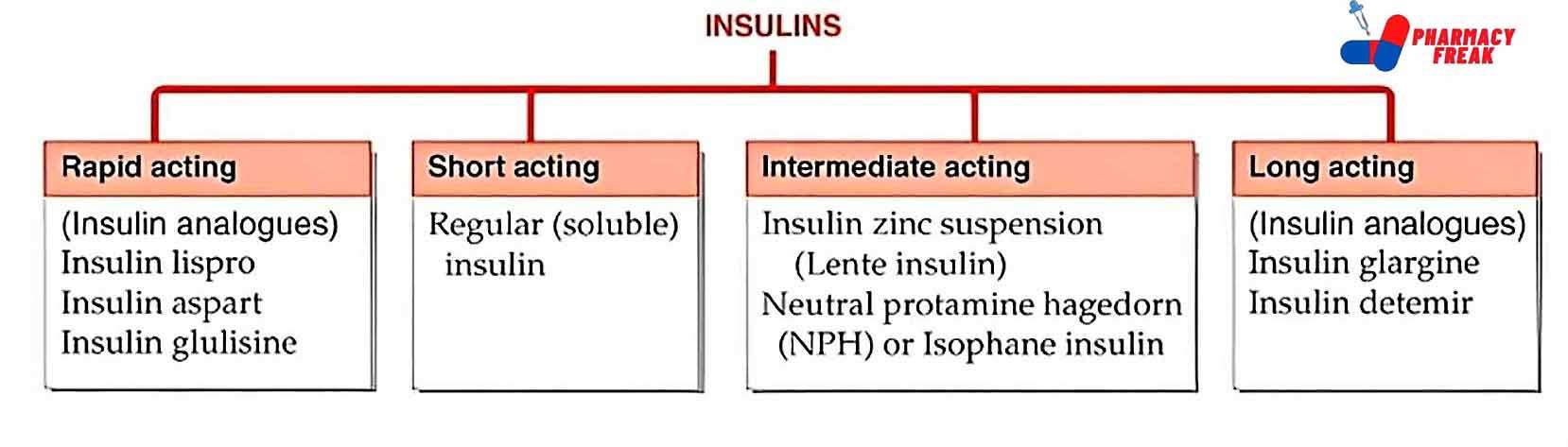
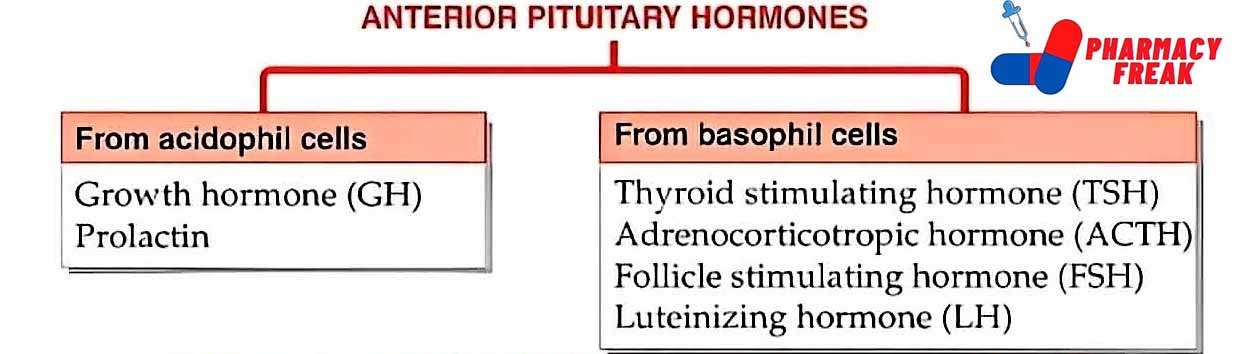
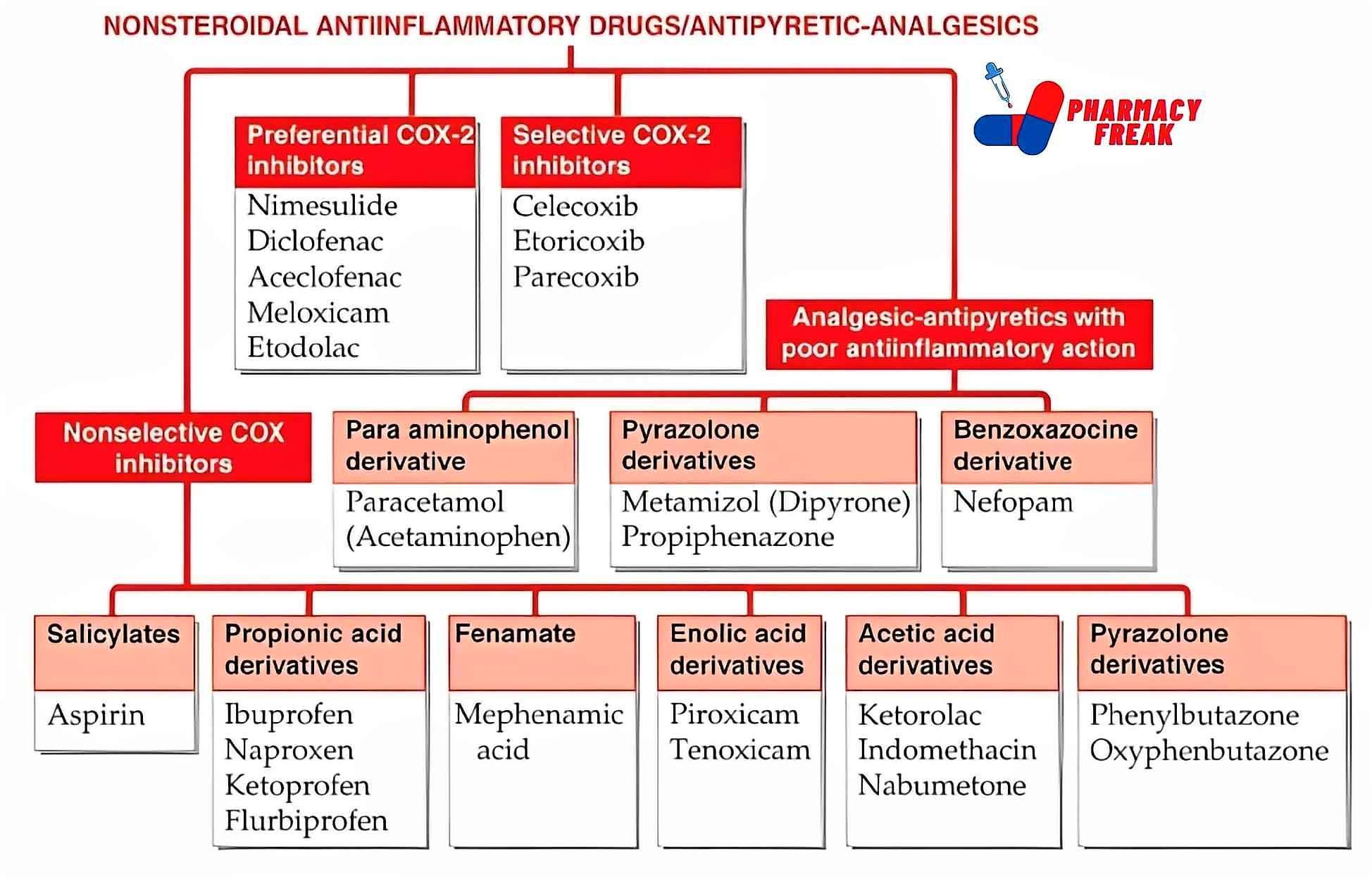
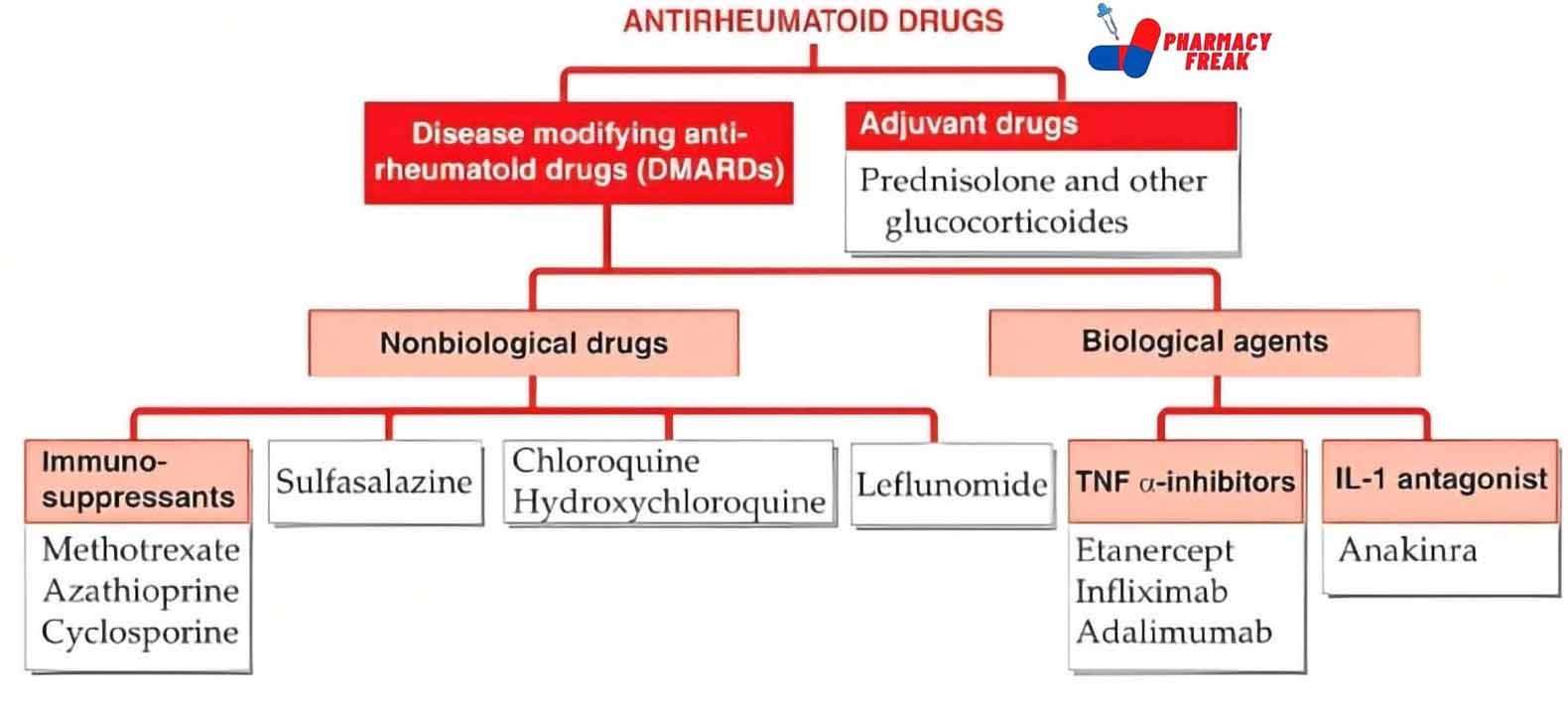
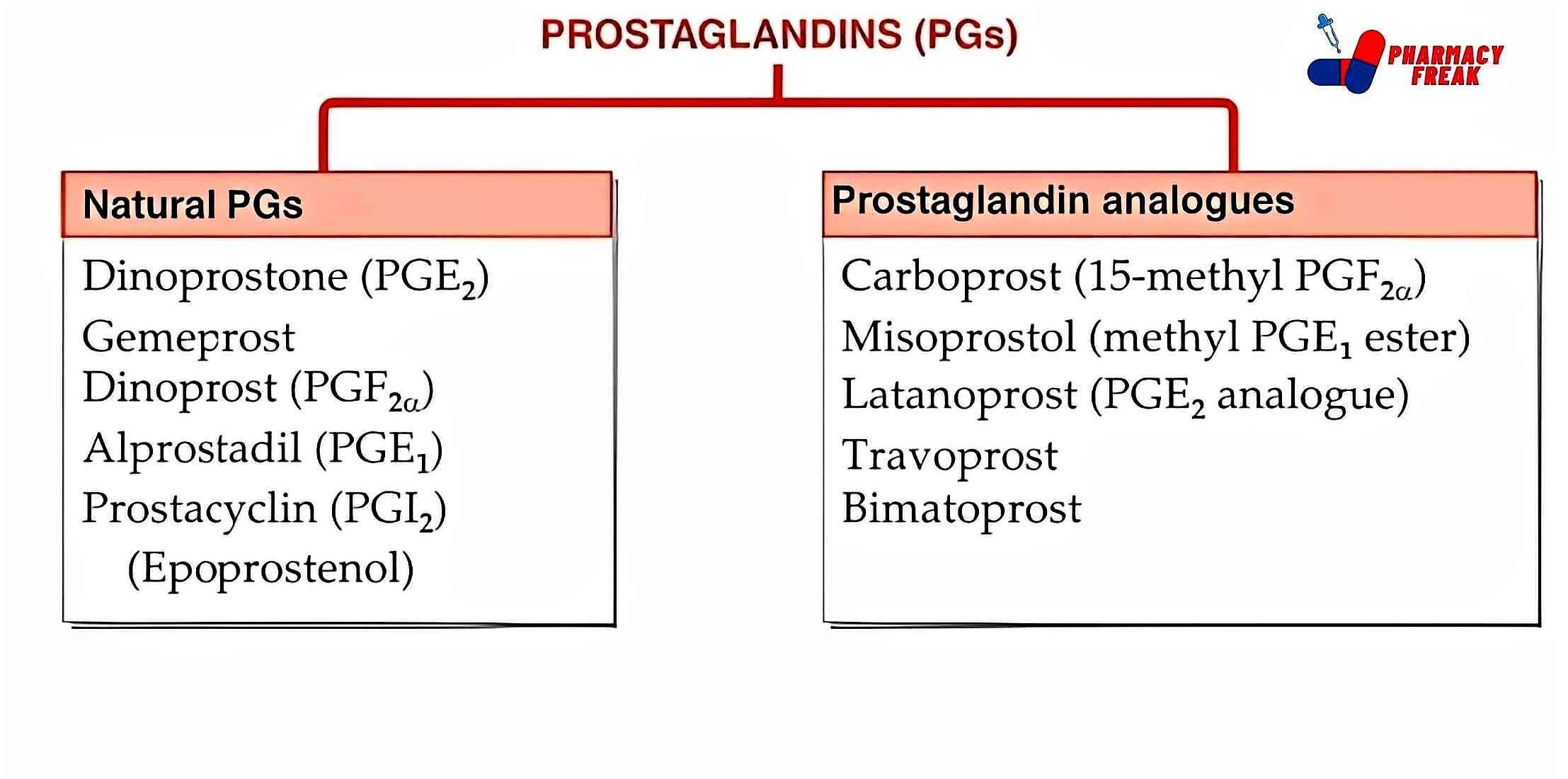
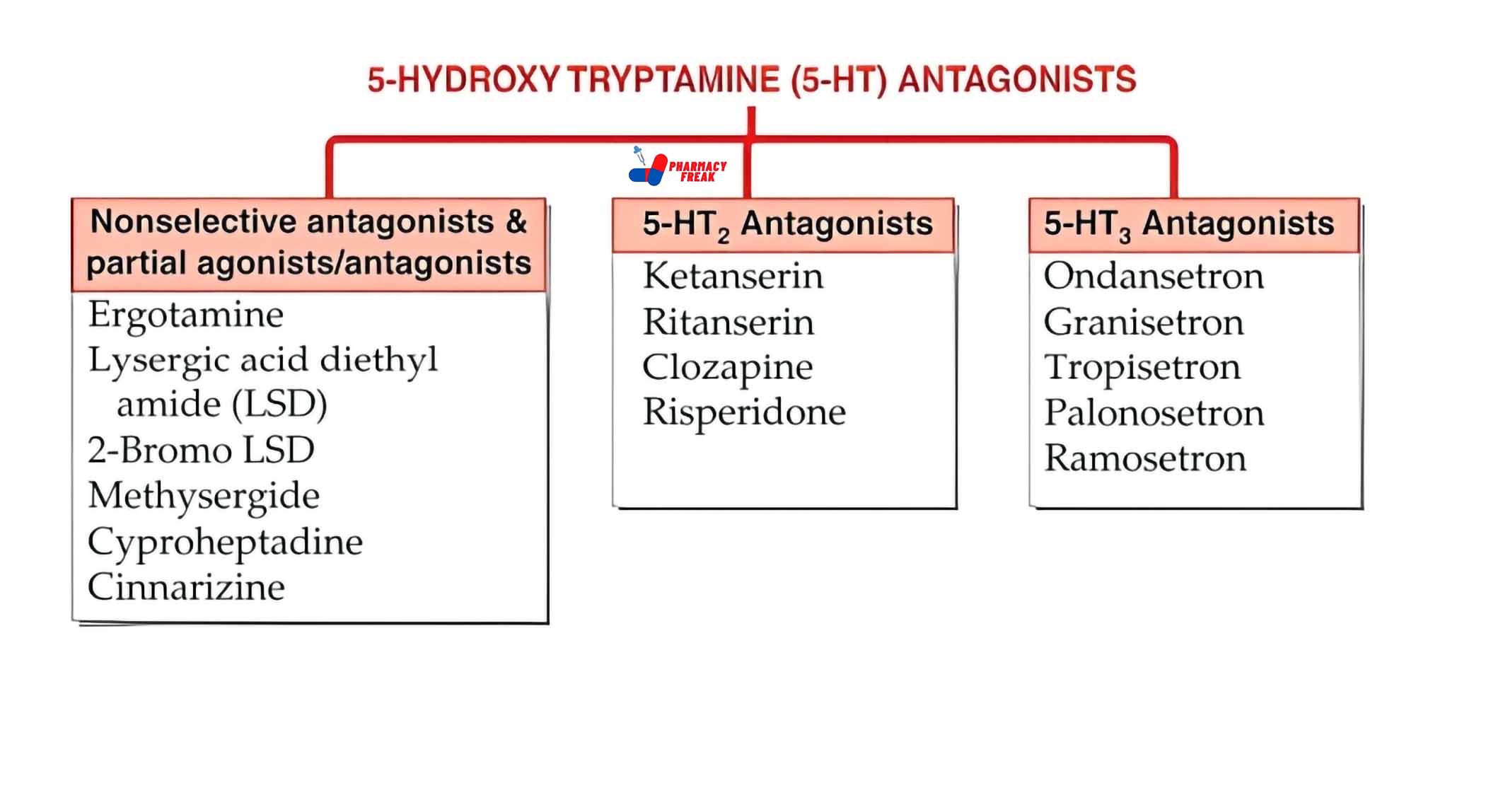
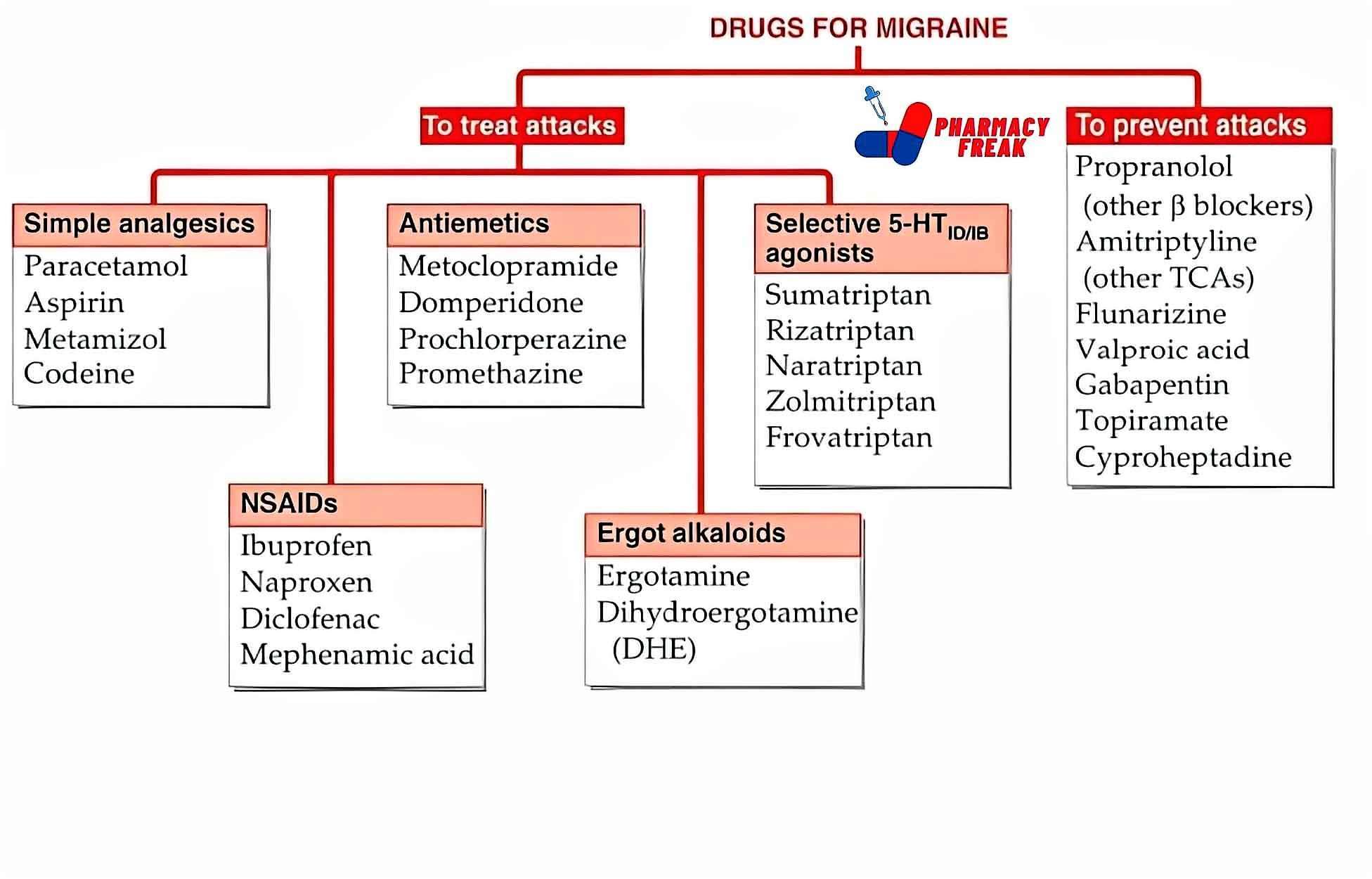
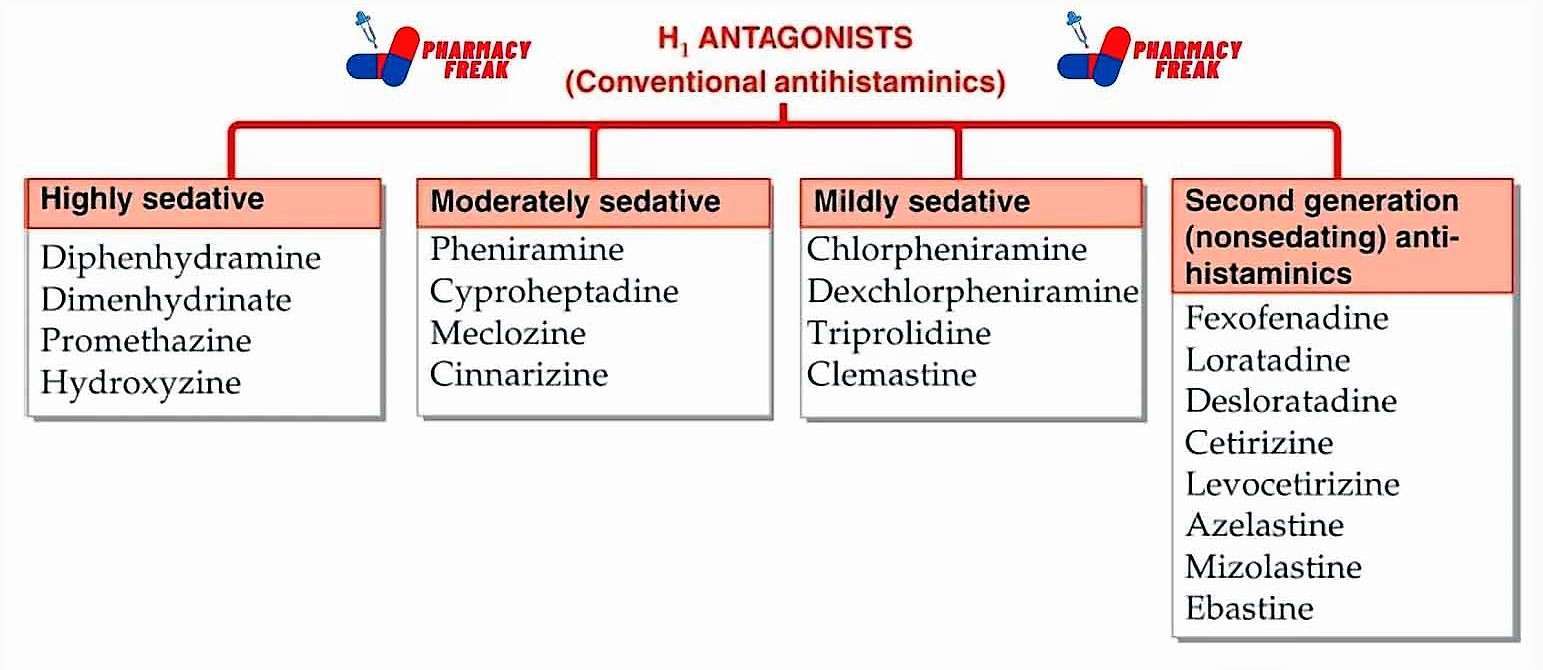
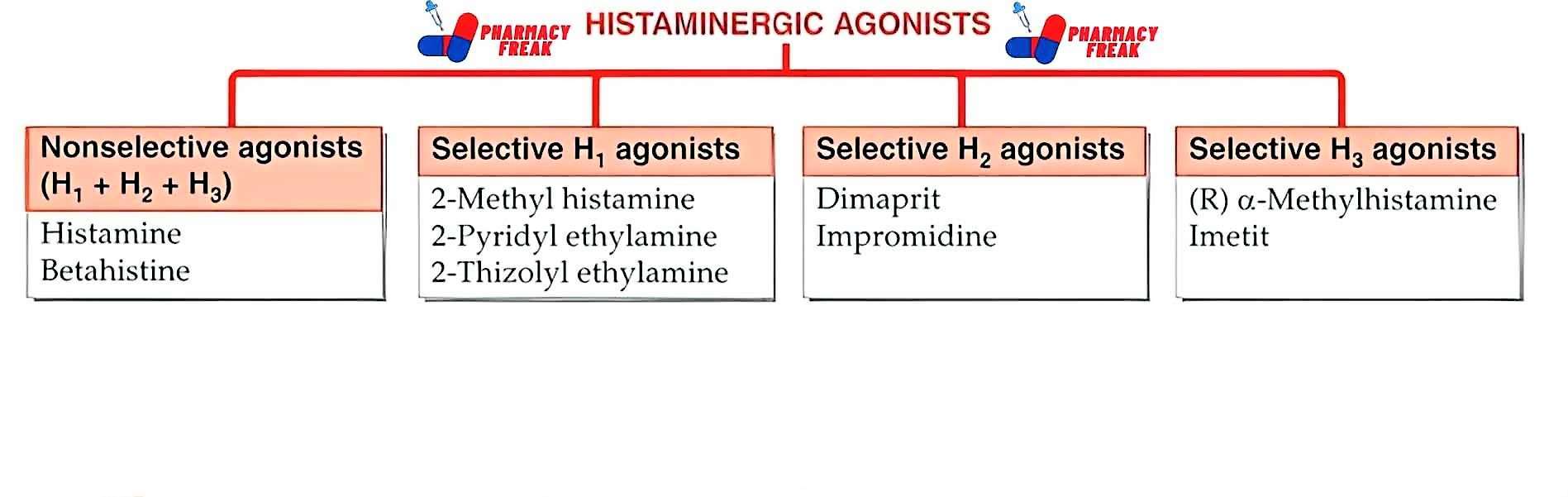
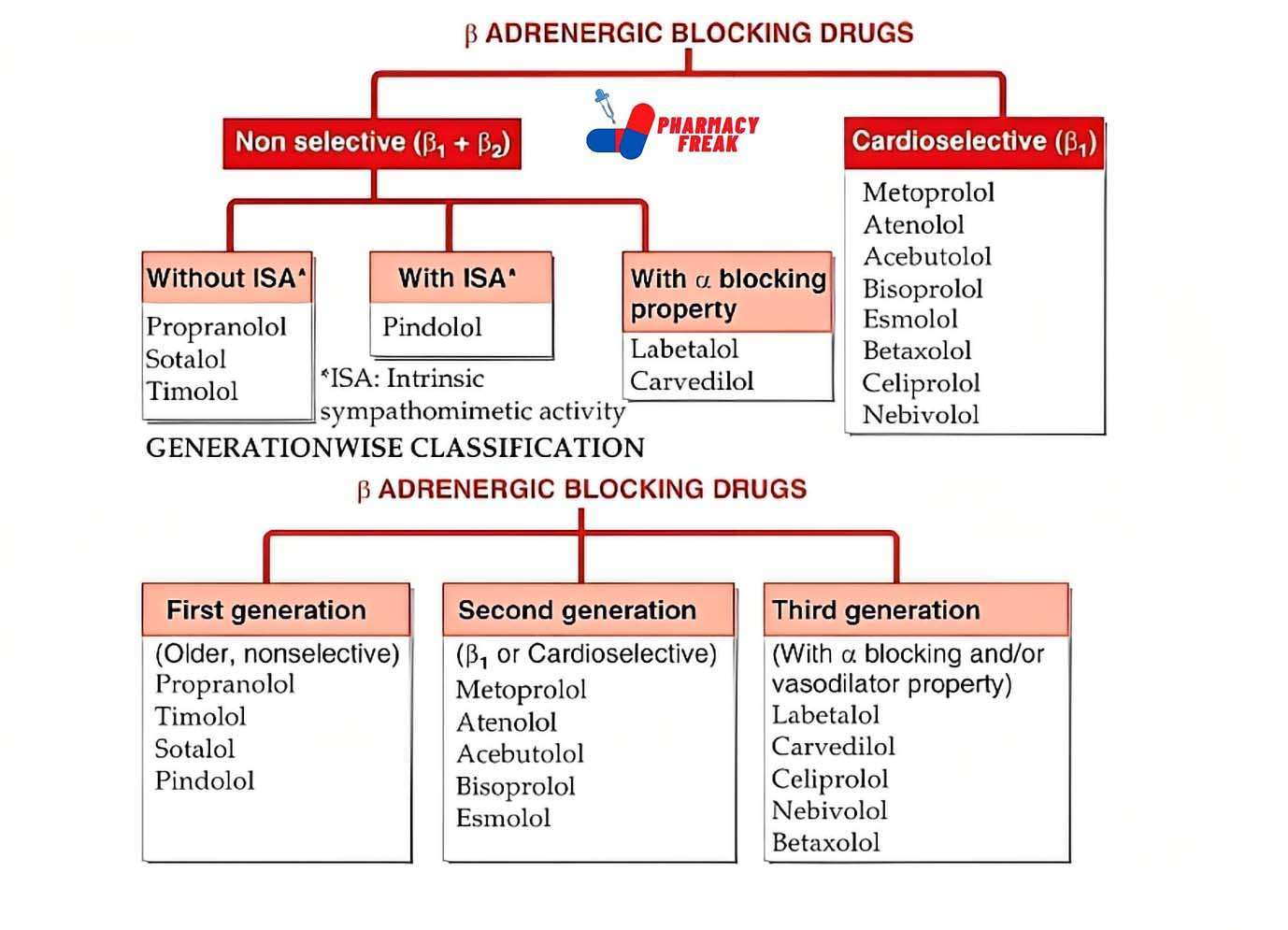
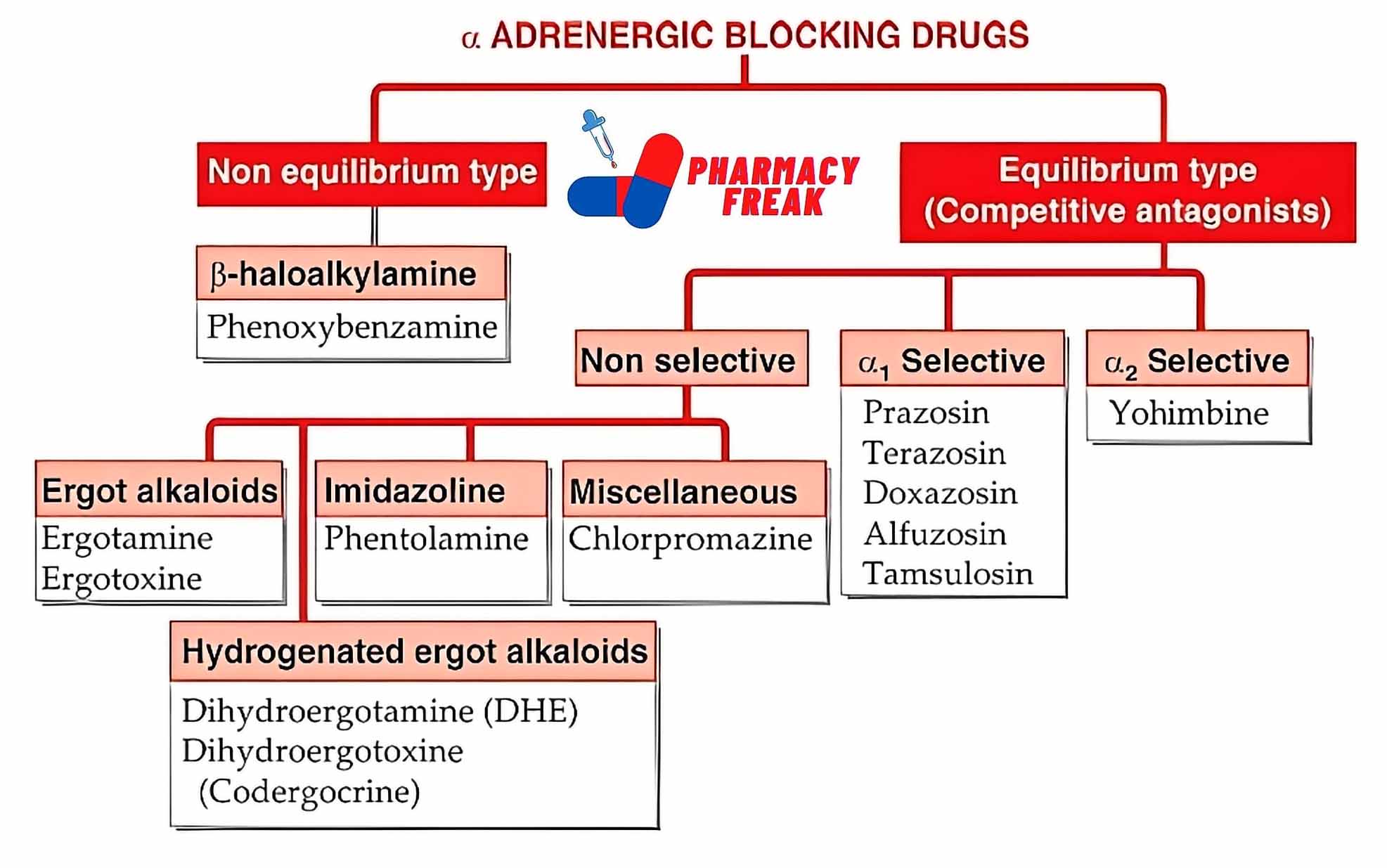
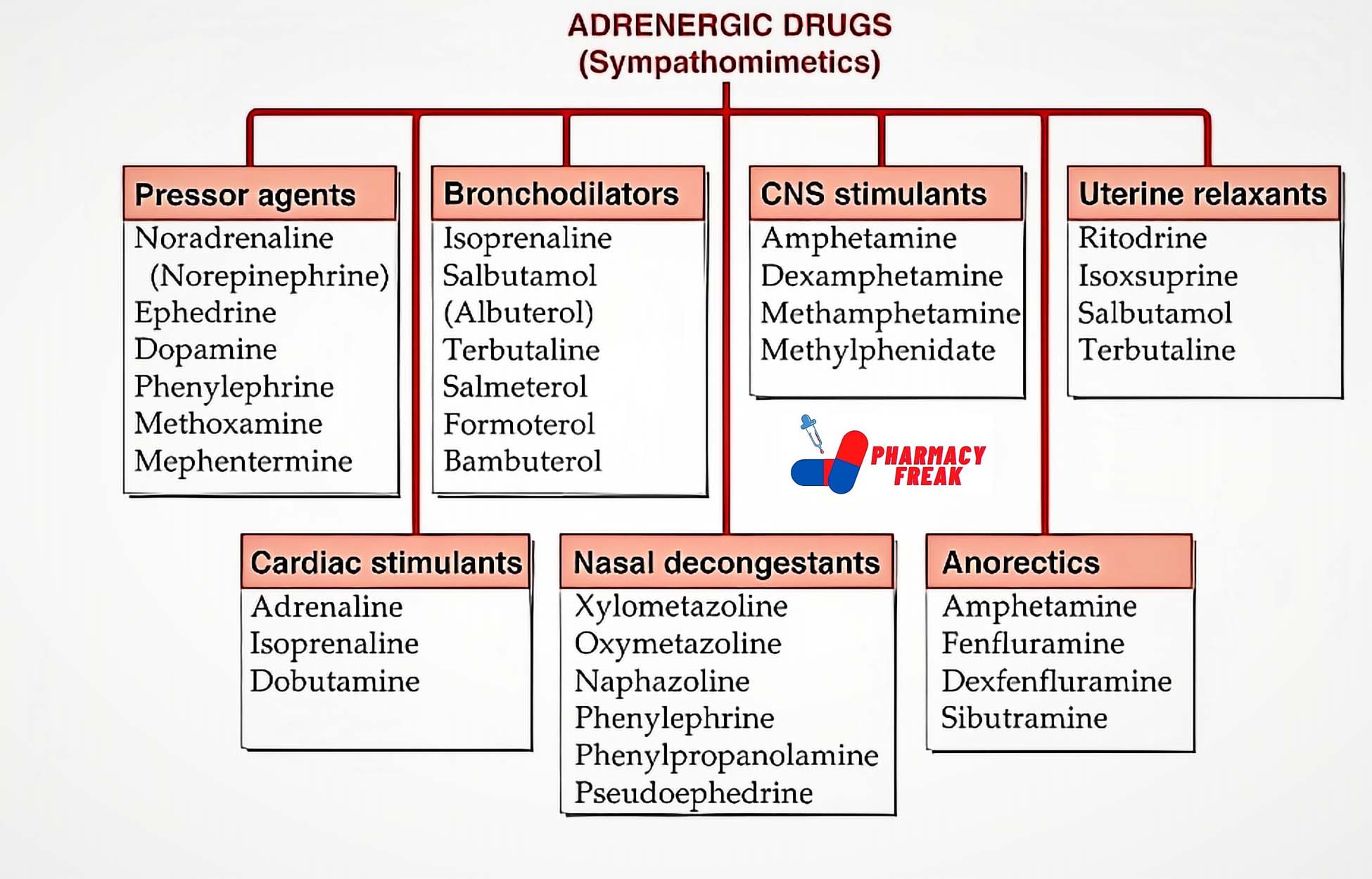
2. Pharmacological or Chemical Classification: How the Drug Works
While therapeutic classification tells us what a drug does, this section explains how it works inside the body. Drugs in the same pharmacological class usually work in similar ways—even if they treat different problems.
For example:
Beta blockers slow down the heart rate by blocking certain signals.
ACE inhibitors relax blood vessels to lower blood pressure.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) reduce acid in the stomach by blocking the pumps that produce it.
This type of classification is useful for understanding side effects, drug interactions, and alternatives. If two drugs work the same way, they may have similar effects—and risks.
3. Name Stems: Spotting Drug Types by Their Endings
Many drug names follow a pattern. These endings—or stems—can help you figure out what class a drug belongs to, even if the name is new to you.
Here are some common ones:
| Stem (Ending) | Drug Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ‑pril | ACE Inhibitors | Lisinopril |
| ‑statin | Cholesterol-lowering drugs | Atorvastatin |
| ‑olol | Beta Blockers | Propranolol |
| ‑vir | Antivirals | Acyclovir |
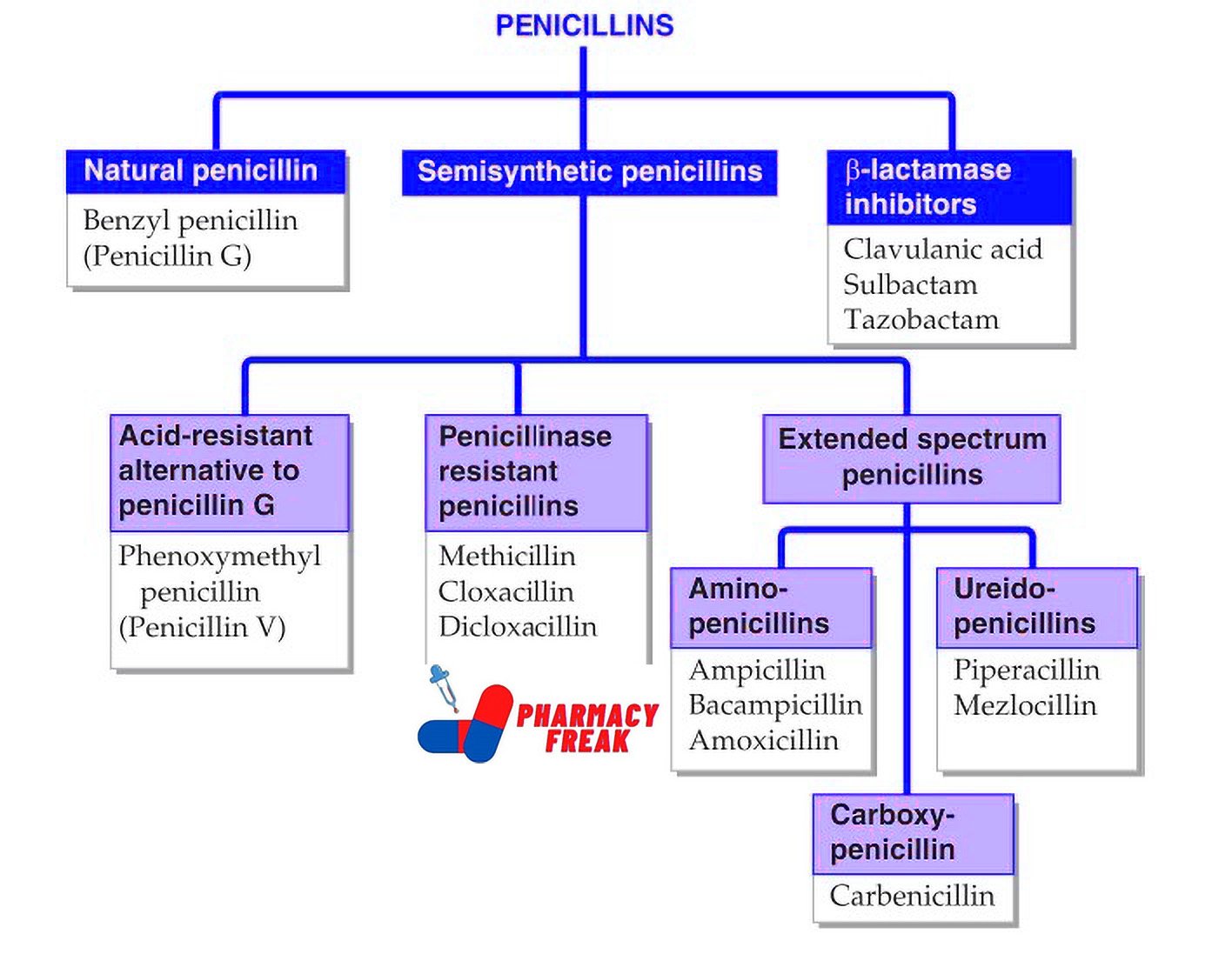
| ‑cillin | Penicillin antibiotics | Amoxicillin |
| ‑zepam / ‑zolam | Benzodiazepines (anti-anxiety) | Diazepam, Alprazolam |
This makes learning drug names easier and helps avoid confusion between similar-looking names.
4. Legal Classification: Controlled Substances and Drug Schedules
Some drugs are safe when used correctly—but dangerous when misused. That’s why they’re grouped by how strictly they’re controlled by law.
This part of the chart shows Schedules I through V, from most dangerous to least risky:
Schedule I: Illegal drugs with no medical use (e.g., heroin, LSD).
Schedule II: High risk of addiction, but used medically (e.g., morphine, oxycodone).
Schedule III: Moderate risk, includes steroids and certain pain medications.
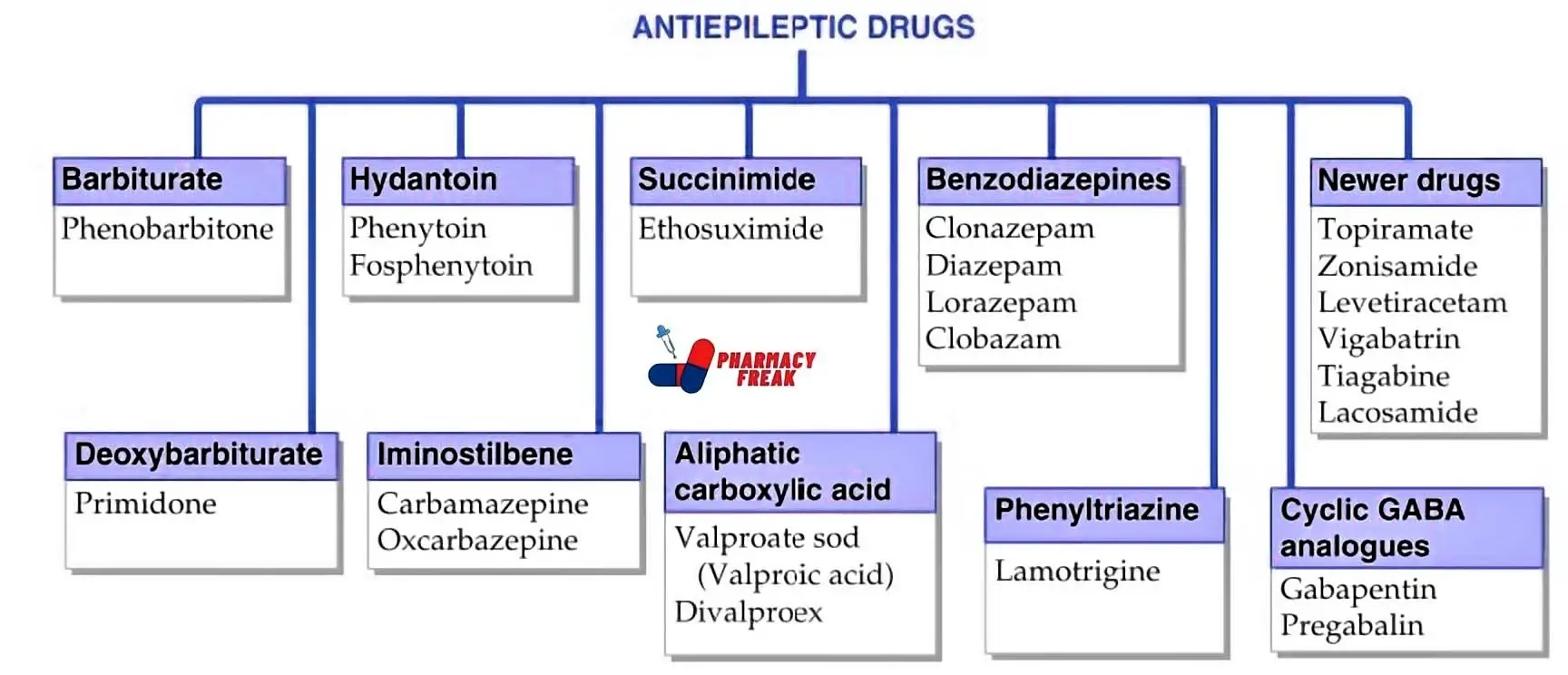
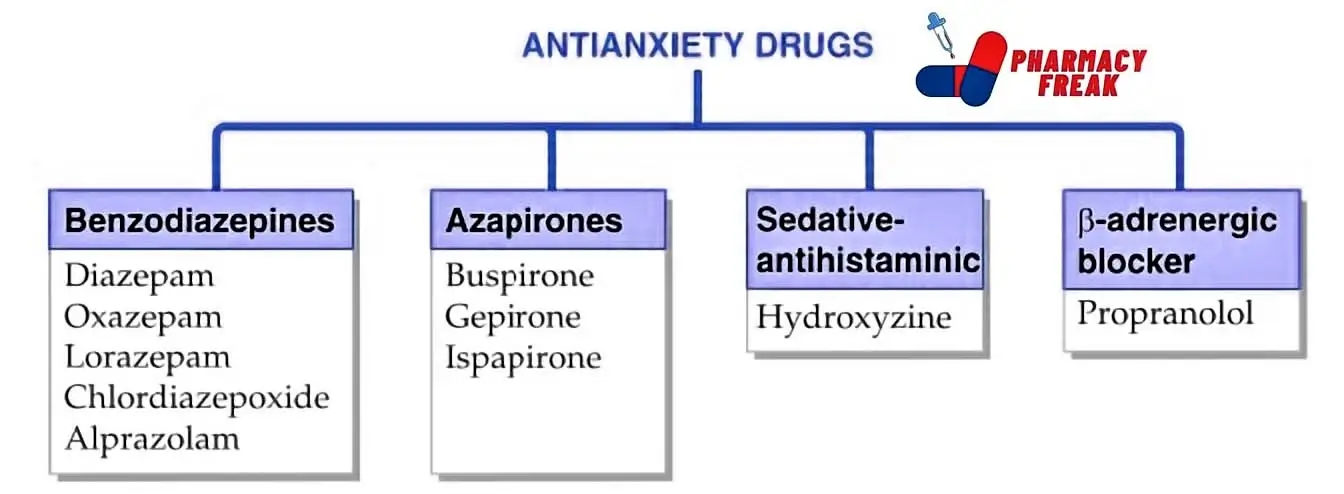
Schedule IV: Low risk, includes anti-anxiety drugs like diazepam.
Schedule V: Lowest risk, includes cough syrups with small amounts of codeine.
These schedules are important for understanding how addictive a drug can be, what the legal restrictions are, and why some prescriptions are more tightly controlled.
5. Optional: ATC Classification (World Health Organization System)
If your chart includes the ATC code (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical system), here’s how to explain it:
This system groups drugs based on:
Where they act in the body (e.g., cardiovascular system)
How they work
What they treat
Their chemical structure
For example, a drug code might look like:
C09AA03
Here’s how to read it:
C = Cardiovascular system
09 = Drugs affecting blood pressure
AA = ACE inhibitors
03 = Specific drug (e.g., enalapril)
This system is used worldwide and gives a very detailed look at how a drug fits into larger categories.
Final Thoughts: Why Drug Classification Matters
Understanding how drugs are classified helps everyone—patients, students, nurses, and doctors. It makes it easier to:
Learn and remember drug names
Know what a medication is used for
Be aware of possible side effects or interactions
Use drugs more safely and effectively