Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins (PGs) are lipid compounds derived from arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is a fatty acid found in cell membranes. They have roles in different physiological processes, including inflammation, pain, blood clotting, and reproduction.
Cells in almost all tissues produce PGs, which are rapidly metabolised and deactivated. They have a short half-life and act locally at the site of synthesis, making them difficult to study.
PGE, PGF, and PGI are three different types of PGs. Each type serves a specific purpose in the body. PGE2, for example, is involved in inflammation and pain, whereas PGF2a is involved in smooth muscle contraction in the uterus and bronchi.
Because of their involvement in a wide range of physiological processes, PGs have been the focus of pharmaceutical research. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit the synthesis of PGs. They are commonly used to treat pain, inflammation, and fever. Misoprostol drug mimics the action of PGs. Misoprostol is also used to prevent and treat stomach ulcers.
USES
Prostaglandins (PGs) have several important uses in the body. Here are some of the most significant uses:
- Inflammation and pain relief: Certain PGs, such as PGE2, play a role in the inflammatory response, contributing to pain and swelling. Aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit the synthesis of PGs so they are used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Blood clotting: PGs like thromboxane A2 aid in blood clotting, which is required to prevent excessive bleeding after injury. Aspirin and other drugs inhibit the synthesis of thromboxane A2. They are used to prevent blood clots that can cause heart attacks and strokes.
- Reproductive functions: PGs are necessary for reproductive functions such as ovulation, fertilisation, implantation, and labour. Misoprostol and other drugs that mimic the action of PGs are used to induce labour or to help expel the contents of the uterus after a miscarriage.
- Gastrointestinal protection: PGs help protect the stomach and intestine linings from stomach acid damage. Misoprostol and other drugs that mimic the action of PGs are used to prevent and treat stomach ulcers caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Glaucoma treatment: Some PGs, such as latanoprost, are used to treat glaucoma by lowering intraocular pressure. This reduces the risk of optic nerve damage and loss of vision.
CLASSIFICATION
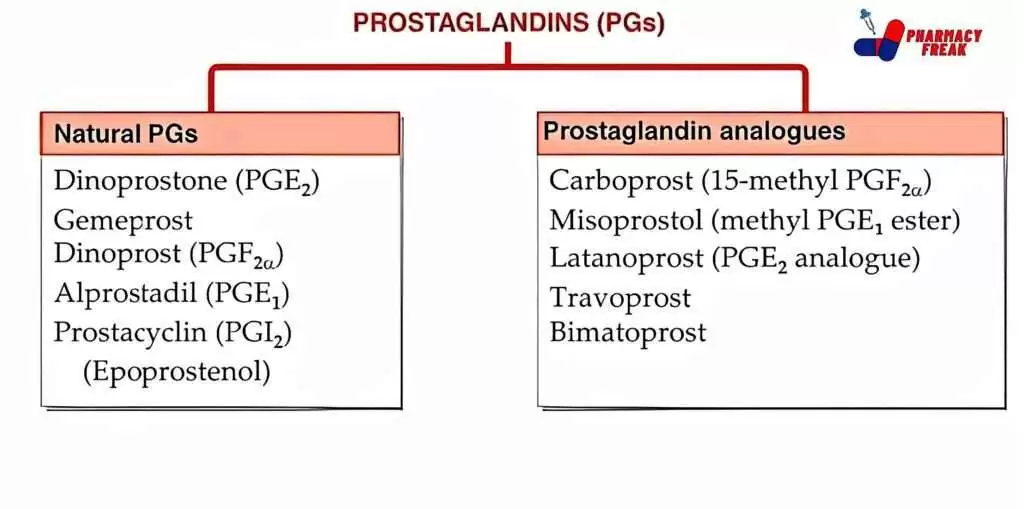
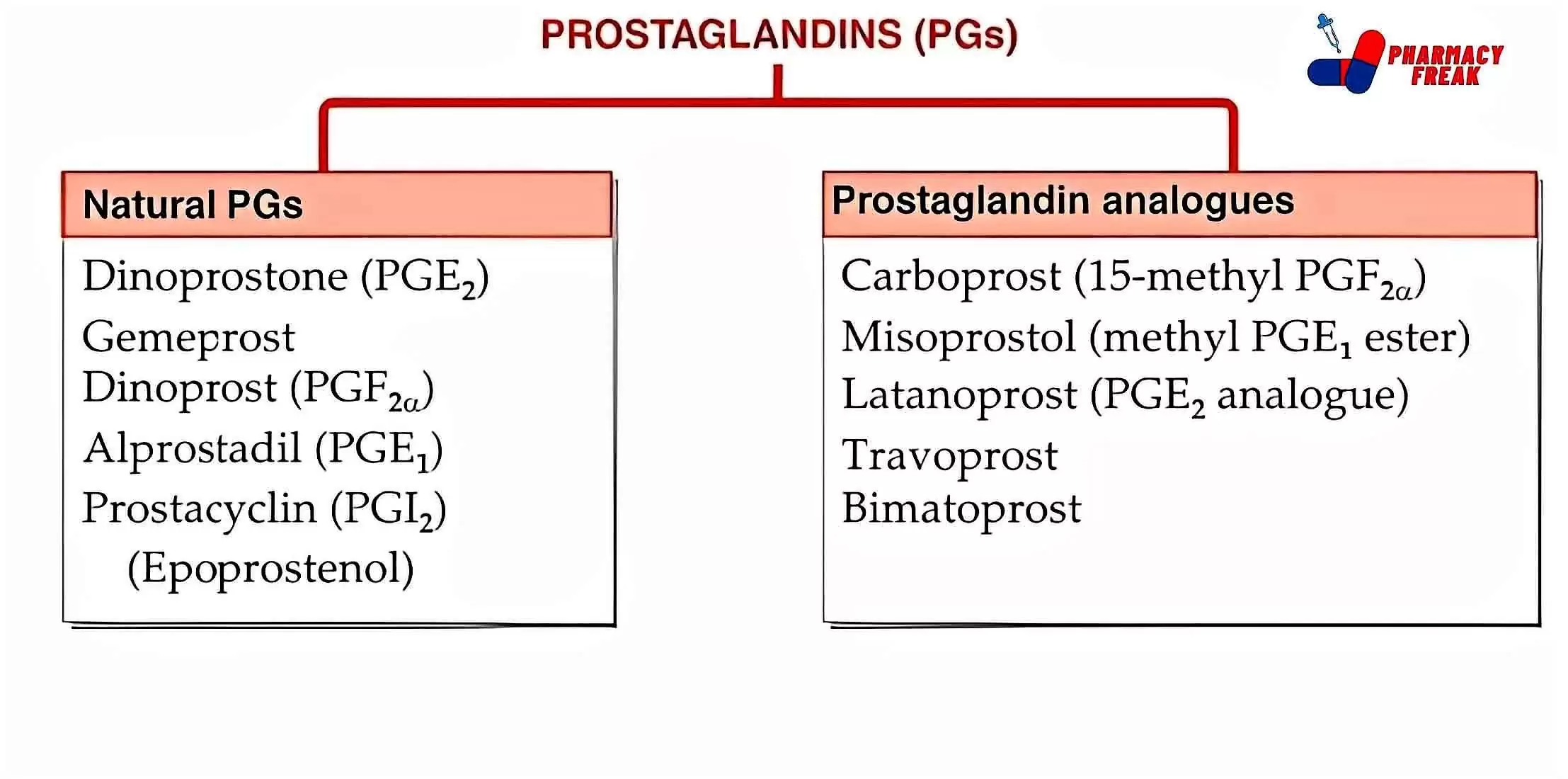
Prostaglandins (PGs)
- Natural PGs – Dinoprostone (PGE₂), Gemeprost, Dinoprost (PGF20), Alprostadil (PGE₁), Prostacyclin (PGI2),(Epoprostenol)
- Prostaglandin analogues – Carboprost (15-methyl PGF2a), Misoprostol (methyl PGE, ester), Latanoprost (PGE2 analogue), Travoprost, Bimatoprost
Related links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- ScienceDirect- Prostaglandins

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com