Opioid analgesics and antagonists play a pivotal role in managing pain and reversing the effects of opioids when necessary. These medications are commonly used in healthcare settings, particularly for pain relief and in cases of opioid overdose.
Table of Contents
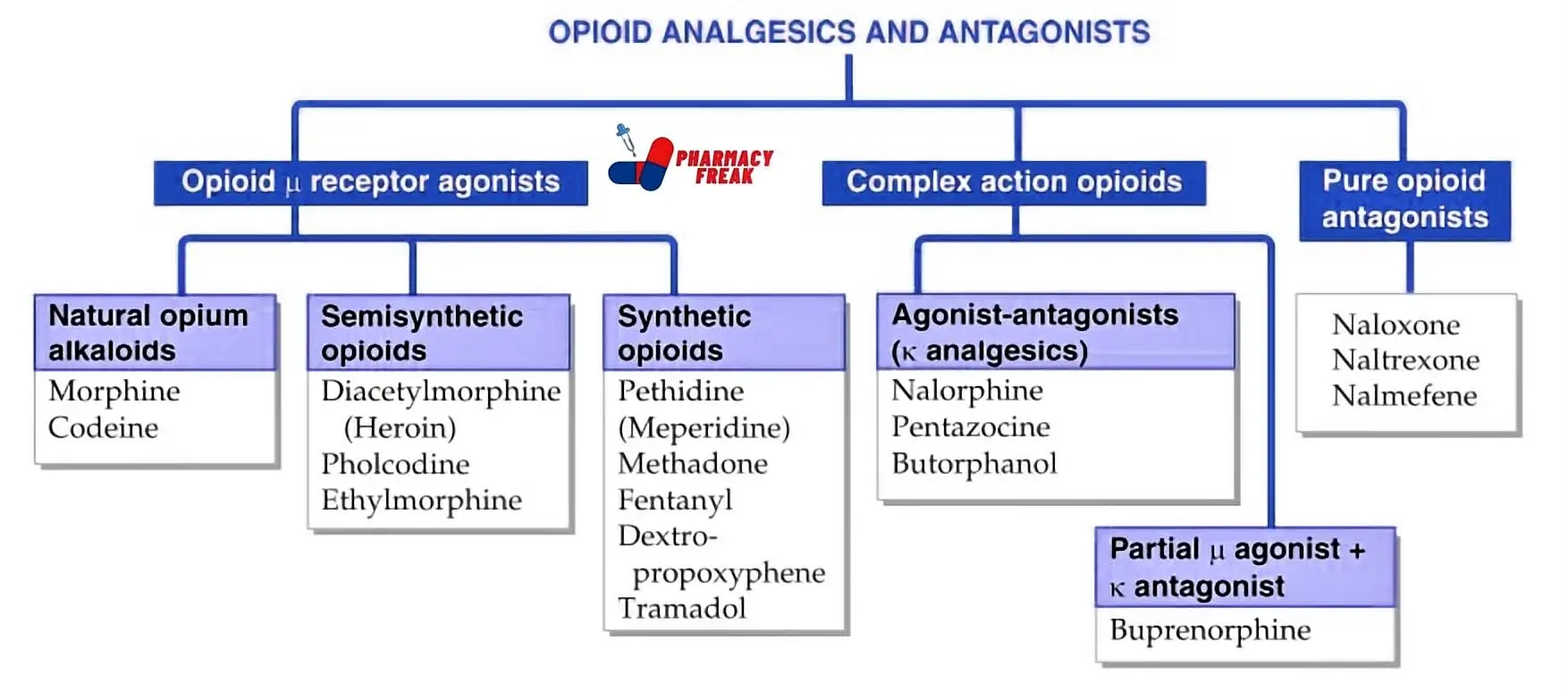
Opioid Analgesics
Opioid analgesics are medications primarily used to relieve pain. They work by binding to specific receptors in the brain, spinal cord, and gastrointestinal tract, reducing the perception of pain.
Natural Opioids
These opioids are derived from the opium poppy plant, Papaver somniferum.
- Morphine: Often considered the gold standard for pain relief, morphine is commonly used in hospitals for moderate to severe pain.
- Codeine: Codeine is frequently used for mild to moderate pain and is also found in some cough syrups.
Semi-Synthetic Opioids
These opioids are synthesized from natural opioids.
- Hydrocodone: Hydrocodone is commonly used in combination with other medications to manage pain.
- Oxycodone: Oxycodone is used for both acute and chronic pain management.
Synthetic Opioids
These opioids are entirely man-made and not derived from natural sources.
- Fentanyl: Fentanyl is highly potent and used for severe pain, often in the form of patches or lozenges.
- Tramadol: Tramadol is used for various types of pain and has a lower risk of addiction compared to other opioids.
Mixed Agonist-Antagonist Opioids
These opioids have a unique property of both stimulating and blocking opioid receptors.
- Buprenorphine: Buprenorphine is used to treat opioid addiction and manage pain.
Opioid Antagonists
Opioid antagonists are medications that block the effects of opioids. They are primarily used to reverse opioid overdoses.
- Naloxone (Narcan)- Naloxone is a fast-acting opioid antagonist used as an emergency treatment for opioid overdoses. It can quickly reverse the life-threatening effects of opioid overdose.
- Naltrexone- Naltrexone is used in the long-term management of opioid addiction and alcohol dependence. It blocks the euphoric effects of opioids.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Basic opioid pharmacology
Related Links