Histaminergic agonists
Histaminergic agonists are a type of drug that stimulates the body’s histamine receptors. Histamine is a chemical that the body produces naturally and is involved in a variety of physiological processes such as immune response, inflammation, and sleep-wake cycle regulation.
Histamine receptors come in a variety of forms, including H1, H2, H3, and H4 receptors. Histaminergic agonists can activate one or more of these receptors, and their effects are dependent on which receptor is activated.
Uses
- Treating allergies:- Allergies such as hay fever, hives, and allergic conjunctivitis are commonly treated with H1 receptor agonists. They work by blocking histamine’s action on H1 receptors, which helps to alleviate symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Reducing stomach acid:– H2 receptor agonists are used to treat conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcers by reducing stomach acid production.
- Regulating sleep:- Histamine regulates the sleep-wake cycle, and drugs targeting H1 receptors can have sedative effects. These medications are occasionally used as sleep aids or to treat insomnia.
- Treating neurological disorders:– H3 receptor agonists are being studied for their potential use in the treatment of neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s, schizophrenia, and ADHD.
- Treating inflammatory and autoimmune diseases:– H4 receptor agonists are being researched for their potential role in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as asthma, allergies, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Investigating the role of histamine:- Histamine and histaminergic agonists are also used in research to study histamine’s role in various physiological processes and disease states.
CLASSIFICATION
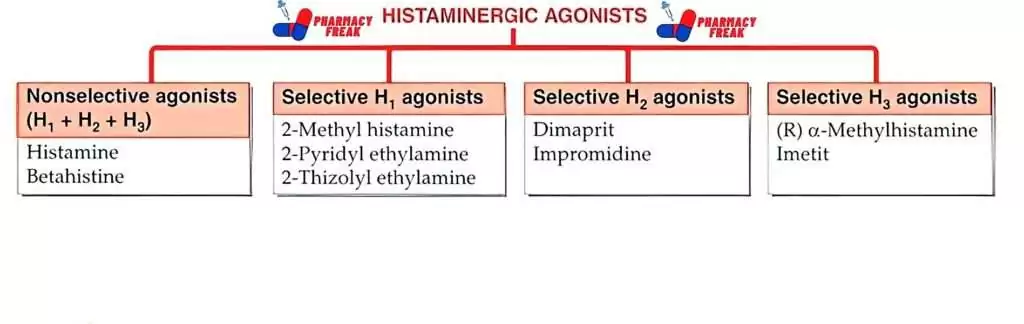
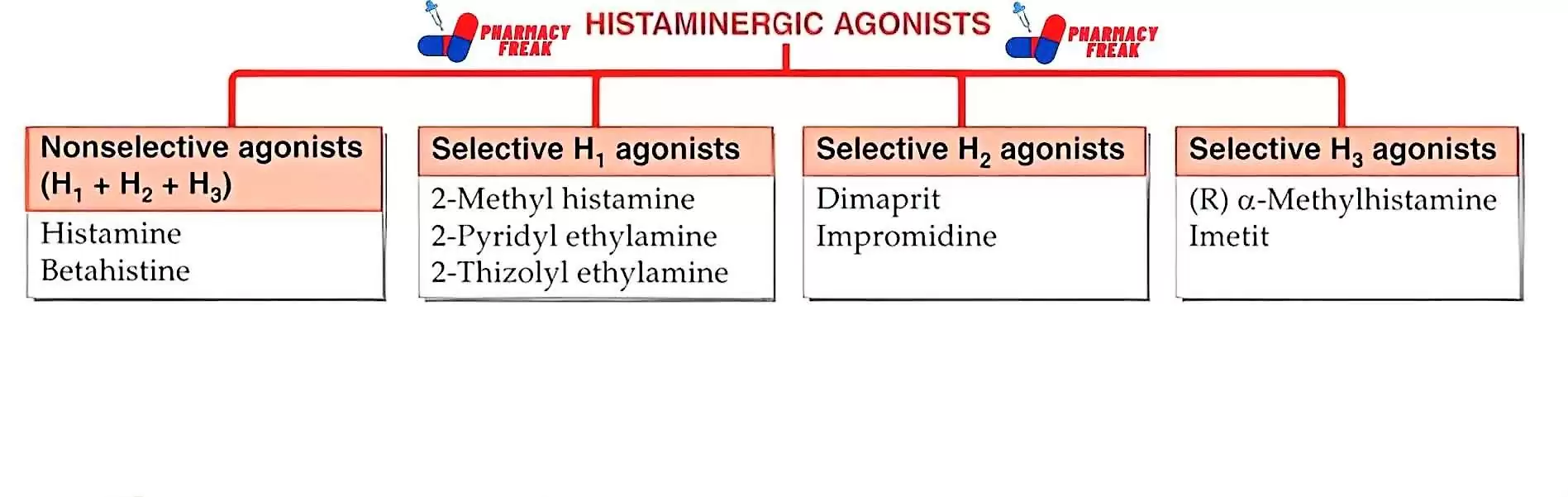
HISTAMINERGIC AGONISTS
- Nonselective agonists (H₁ + H₂ + H3)– Histamine, Betahistine
- Selective H₁ agonists– 2-Methyl histamine, 2-Pyridyl ethylamine, 2-Thizolyl ethylamine
- Selective H₂ agonists– Dimaprit, Impromidine
- Selective H3 agonists– (R) a-Methylhistamine Imetit
Related Links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Histamine receptors, agonists, and antagonists in health and disease

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com