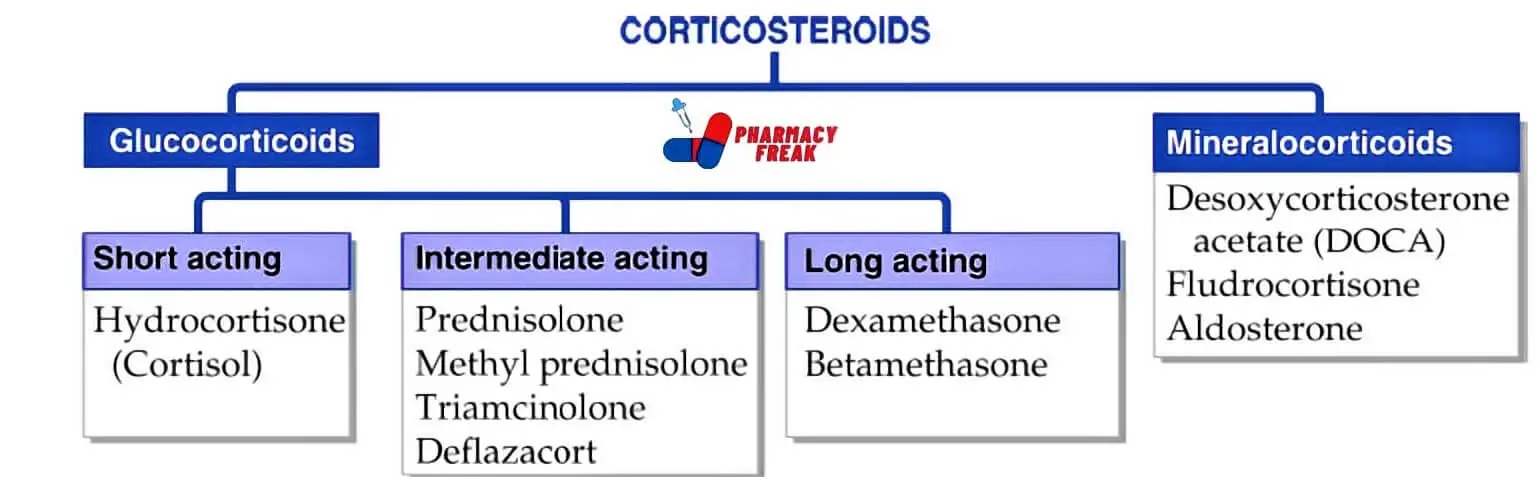
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex. They have a wide range of physiological effects and are often used in medicine to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Corticosteroids can be classified into several categories based on their structure and function. Here is a classification of corticosteroids
Table of Contents
Here is a classification of corticosteroids
- Glucocorticoids
- Short acting- Hydrocortisone (Cortisol)
- Intermediate acting- Prednisolone, Methyl prednisolone, Triamcinolone, Deflazacort
- Long acting- Dexamethasone, Betamethasone
- Mineralocorticoids- Desoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA), Fludrocortisone, Aldosterone
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that primarily affect glucose metabolism and have potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties.
- Natural Glucocorticoids: These are hormones produced naturally by the adrenal glands.
- Cortisol (Hydrocortisone): Cortisol is the primary natural glucocorticoid in the human body. It regulates various physiological processes, including metabolism and immune response.
- Synthetic Glucocorticoids: These are manufactured corticosteroids that mimic the actions of cortisol and are used for medical purposes.
- Prednisone: Prednisone is a commonly prescribed synthetic glucocorticoid used to treat inflammation and autoimmune conditions.
- Dexamethasone: Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid with potent anti-inflammatory effects. It is used for various medical conditions, including reducing inflammation in cancer patients.
- Methylprednisolone: This synthetic glucocorticoid is often used to treat allergic reactions, inflammation, and autoimmune disorders.
Mineralocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids primarily regulate electrolyte and water balance in the body. The most well-known mineralocorticoid is aldosterone.
- Aldosterone: Aldosterone promotes the reabsorption of sodium and the excretion of potassium in the kidneys, helping to maintain blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
Topical Corticosteroids
These are corticosteroids formulated for topical application on the skin or mucous membranes.
- Creams, Ointments, and Lotions: Topical corticosteroids are available in various forms for treating skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis.
Examples include hydrocortisone cream and betamethasone ointment.
Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICS)
Inhaled corticosteroids are used to treat respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
They reduce airway inflammation and improve breathing.
Examples include fluticasone, budesonide, and beclomethasone.
Systemic Corticosteroids
Systemic corticosteroids are taken orally or through injection and have a widespread effect on the body.
They are used for conditions like severe allergies, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory disorders.
Examples include prednisone, methylprednisolone, and dexamethasone.
Nasal Corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroids are used to treat allergic rhinitis and nasal congestion.
They reduce inflammation in the nasal passages.
Examples include fluticasone nasal spray and mometasone nasal spray.
Joint Injections
Corticosteroid injections can be administered directly into joints to reduce inflammation and relieve pain in conditions like arthritis.
It’s important to note that corticosteroids should only be used under medical supervision, as they can have side effects and should not be discontinued abruptly.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Corticosteroids
Related Links