Skeletal muscle relaxants are a group of medications used to alleviate muscle spasms and muscle pain. They are typically prescribed for conditions like back pain, muscle injuries, or certain neurological disorders. These medications work by affecting the communication between nerves and muscles, ultimately helping to relax and relieve tense muscles.
Table of Contents
Classification of Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
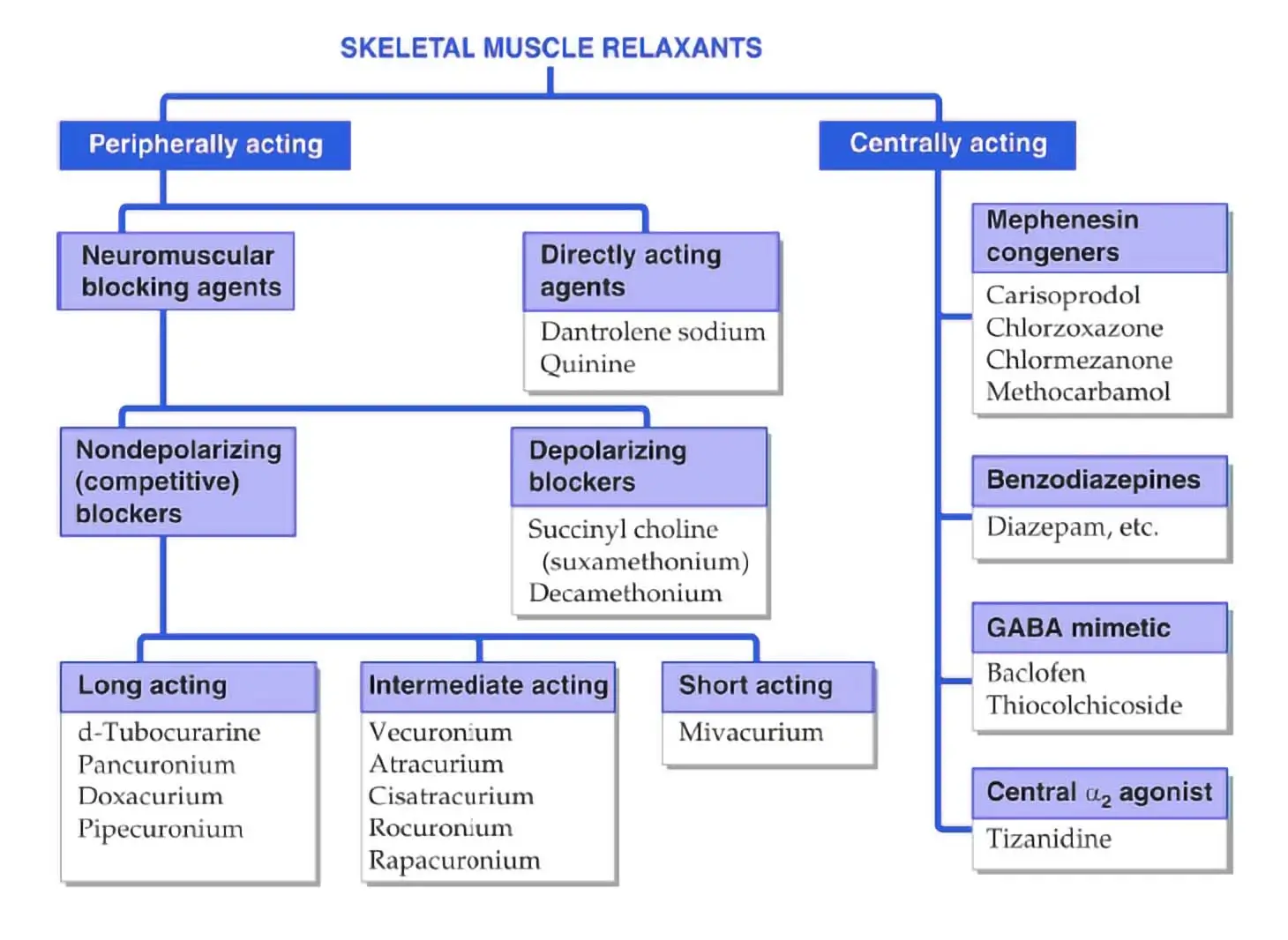
SKELETAL MUSCLE RELAXANTS
- Peripherally acting
- Neuromuscular blocking agents
- Nondepolarizing (competitive) blockers
- Long acting – D-Tubocurarine, Pancuronium, Doxacurium, Pipecuronium
- Intermediate acting- Vecuronium, Atracurium, Cisatracurium, Rocuronium, Rapacuronium
- Short Acting– Mivacurium
- Depolarizing blockers- Succinyl choline (suxamethonium), Decamethonium
- Nondepolarizing (competitive) blockers
- Directly acting agents– Dantrolene, sodium, Quinine
- Neuromuscular blocking agents
- Centrally acting
- Mephenesin congeners- Carisoprodol, Chlorzoxazone, Chlormezanone, Methocarbamol
- Benzodiazepines– Diazepam, etc.
- GABA mimetic- Baclofen, Thiocolchicoside
- Central a2 agonist- Tizanidine
Skeletal muscle relaxants are classified into two main categories: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics. Let’s take a closer look at each of these categories:
- Neuromuscular Blockers:
- These are often used in surgical settings and intensive care units. They are administered to induce muscle paralysis during surgery or to assist with mechanical ventilation.
- Examples of neuromuscular blockers include drugs like succinylcholine and vecuronium.
- These medications are typically administered intravenously and are closely monitored by medical professionals.
- Spasmolytics (Spasmogenic Muscle Relaxants):
- Spasmolytics are used to alleviate muscle spasms and pain related to conditions like musculoskeletal injuries, fibromyalgia, and certain neurological disorders.
- These are further classified into two groups:
- Antispasmodic Medications: These work by reducing muscle spasms without causing sedation. They are often prescribed for acute conditions.
- Antispastic Medications: These are used for chronic conditions and often have a sedative effect to help manage long-term muscle spasticity.
Common Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
Now, let’s explore some common skeletal muscle relaxants:
- Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril):
- A widely used antispasmodic medication for relieving muscle spasms.
- It may cause drowsiness and should be used with caution when operating heavy machinery or driving.
- Baclofen (Lioresal):
- An antispastic medication commonly prescribed for conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS).
- It works by acting on the spinal cord to reduce muscle spasticity.
- Diazepam (Valium):
- Often used as an antispasmodic medication.
- It has sedative properties and should be used with caution.
- Tizanidine (Zanaflex):
- Primarily used for muscle spasticity caused by conditions like MS or spinal cord injuries.
- It may cause drowsiness and should be used carefully.
- Methocarbamol (Robaxin):
- Commonly used for short-term relief of muscle spasm.
- It may cause dizziness and drowsiness.
Using Skeletal Muscle Relaxants
It’s important to use muscle relaxants under the guidance of a healthcare professional. These medications should be taken as prescribed and should not be shared with others. If you experience severe side effects or allergic reactions, contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Skeletal muscle relaxants
Related Links