Progestins are essential compounds that play a vital role in various physiological processes within the human body. In this guide, we will break down the classification of progestins, providing you with a straightforward understanding of these compounds.
What Are Progestins?
Progestins, short for “progesterone derivatives,” are synthetic compounds designed to mimic the effects of the natural hormone progesterone. They are commonly used in hormonal therapies, contraceptives, and other medical applications.
Classification of Progestins
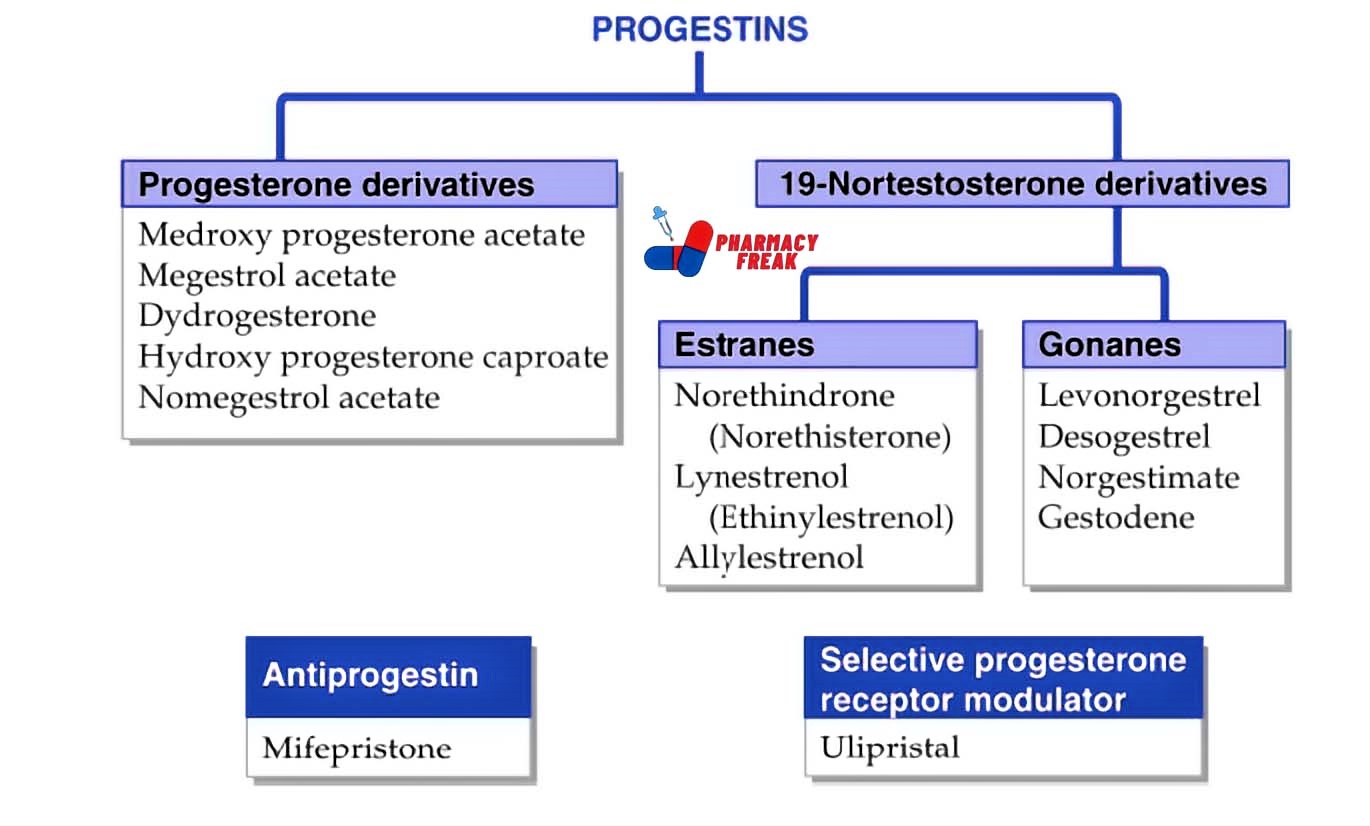
- PROGESTINS
- Progesterone derivatives- Medroxy progesterone acetate, Megestrol acetate, Dydrogesterone, Hydroxy progesterone caproate, Nomegestrol acetate
- 19-Nortestosterone derivatives
- Estranes- Norethindrone (Norethisterone), Lynestrenol (Ethinylestrenol), Allylestrenol
- Gonanes- Levonorgestrel, Desogestrel, Norgestimate, Gestodene
Progestins are also classified into different generations based on their structural and functional properties. Understanding these classifications can help us comprehend their uses and effects more clearly.
First Generation
The first-generation progestins, such as hydroxyprogesterone and medroxyprogesterone acetate, were among the earliest developed. They are primarily used in hormonal therapies and have antiestrogenic properties.
Second Generation
Second-generation progestins, including norethindrone and norgestrel, exhibit improved bioavailability and potency compared to their predecessors. They are commonly found in oral contraceptives.
Third Generation
Progestins like desogestrel and norgestimate belong to the third generation. They are developed to have even fewer androgenic effects while maintaining their contraceptive efficacy.
Fourth Generation
Drospirenone is an example of a fourth-generation progestin. It has anti-mineralocorticoid properties and is often used in combination with estrogen in birth control pills.
Key Points about Progestins
- Progestins are synthetic compounds resembling progesterone.
- They are categorized into four generations based on their structural and functional characteristics.
- First-generation progestins have antiestrogenic properties.
- Second-generation progestins are commonly used in oral contraceptives.
- Third-generation progestins aim to minimize androgenic effects while maintaining contraceptive effectiveness.
- Fourth-generation progestins, like drospirenone, have anti-mineralocorticoid properties.
Why is Understanding Progestin Classification Important?
For students studying medicine, pharmacy, or related fields, grasping the classification of progestins is fundamental. It aids in comprehending how different generations of progestins are applied in various medical contexts, including hormonal therapies and contraceptives.
In conclusion, progestins are a diverse group of synthetic compounds that mimic progesterone’s effects. Their classification into four generations helps medical professionals tailor treatments and therapies to specific patient needs. As you continue your studies, this knowledge will prove invaluable in understanding hormonal medications and their applications.
Remember, progestins play a pivotal role in medical advancements, and your understanding of their classification is a crucial step in your educational journey.
By adhering to these guidelines, we’ve provided you with an informative guide to the classification of progestins. In simple terms and concise sentences, we’ve illuminated a complex topic that is essential for students pursuing medical studies. As you continue learning, this understanding will serve as a solid foundation for your future endeavors.
Related Links
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Classification and pharmacology of progestins