Pharmacodynamics is the topic of 4th sem, B.Pharmacy. Here, we have provided the MCQs (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS) for the preparation of B.Pharmacy and GPAT.
Pharmacodynamics
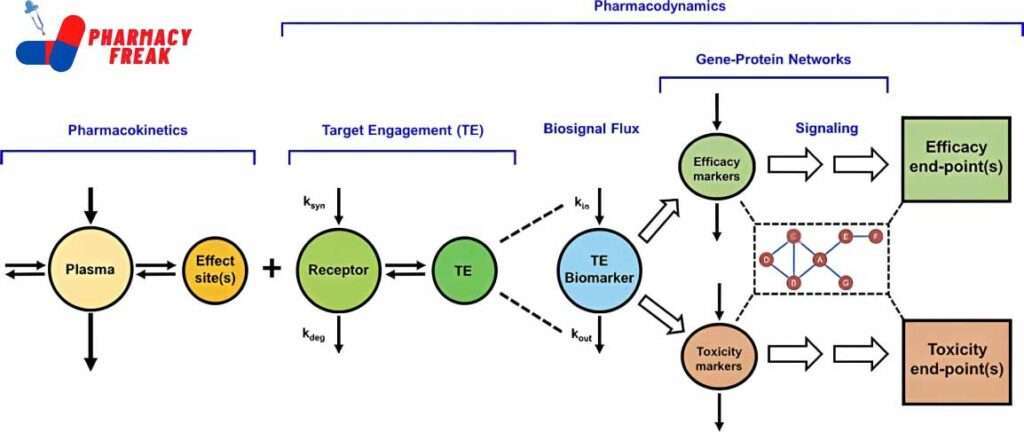
It is defined as the study of the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and their mode of action, including the correlation of their action and effect with their chemical structure. It is the study of what a drug does to the body. The effect of drugs on the living organism.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS PHARMACODYNAMICS
1. Pharmacodynamics involves the study of the following EXCEPT…
- A. Biological and therapeutic effects of drugs
- B. Absorption and distribution of drugs
- C. Mechanisms of drug action
- D. Drug interactions
ANSWER- B. Absorption and distribution of drugs
2. Pharmacodynamics involves the study of the following?
- A. Mechanisms of drug action
- B. Biotransformation of drugs in the organism
- C. Distribution of drugs in the organism
- D. Excretion of drug from the organism
ANSWER- A. Mechanisms of drug action
3. Pharmacodynamics involves the following?
- A. Information about the main mechanisms of drug absorption
- B. Information about unwanted effects
- C. Information about biological barriers
- D. Information about the excretion of a drug from the organism
ANSWER- B. Information about unwanted effects
4. What does “affinity” mean?
- A. A measure of how tightly a drug binds to plasma proteins
- B. A measure of how tightly a drug binds to a receptor
- C. A measure of inhibiting potency of a drug
- D. A measure of the bioavailability of a drug
ANSWER- B. A measure of how tightly a drug binds to a receptor
5. Target proteins to which a drug molecule binds are…
- A. Only receptors
- B. Only ion channels
- C. Only carriers
- D. All of the above
ANSWER- D. All of the above
6. An agonist is a substance that…
- A. Interacts with the receptor without producing any effect
- B. Interacts with the receptor and initiates changes in cell function, producing various effects
- C. Increases the concentration of another substance to produce the effect
- D.Interacts with plasma proteins and doesn’t produce any effect
ANSWER- B. Interacts with the receptor and initiates changes in cell function, producing various effects
7. If an agonist can produce maximal effects and has high efficacy it’s called…
- A. Partial agonist
- B. Antagonist
- C. Agonist-antagonist
- D. Full agonist
ANSWER- D. Full agonist
8. An antagonist is a substance that……..
- A. Binds to the receptors and initiates changes in cell function, producing a maximal effect.
- B. Binds to the receptors and initiates changes in cell function, producing a submaximal effect
- C. Interacts with plasma proteins and doesn’t produce any effect.
- D. Binds to the receptors without directly altering their functions.
ANSWER- D. Binds to the receptors without directly altering their functions.
9. Tick the second messenger of the G-protein-coupled (metabotropic) receptor…
- A. Adenylyl cyclase
- B. Sodium ions
- C. CAMP
- D. Phospholipase C
ANSWER- C. CAMP
10. Tick the substance which changes the activity of an effector element but doesn’t belong second messenger:
- A. CAMP
- B. cGMP
- C. G-Protein
- D. Calcium ions
ANSWER- C. G-Protein
11. Tick the substances whose mechanisms are based on interaction with ion channels?
- A. Sodium channel blockers
- B. Calcium channel blockers
- C. Potassium channels activators
- D. All of the above
ANSWER- D. All of the above
12. Pick out the correct definition of a toxic dose?
- A. The amount of substance to produce the minimal biological effect
- B. The amount of substance to produce effects hazardous for an organism
- C. The amount of substance to produce the necessary effect in most patients
- D. The amount of substance to fast creation of high concentration of medicine in an organisms
ANSWER- B. The amount of substance to produce effects hazardous for an organism
13. What term is used to describe a more gradual decrease in responsiveness to a deg, taking days or weeks to develop?
- A Refractoriness
- B. Cumulative effect
- C. Tolerance
- D. Tachyphylaxis
ANSWER- C. Tolerance
14 Receptors are usually
- A. Lipids
- B. Protein
- C.DNA
- D. None
ANSWER- B. Protein
15. True statement concerning competitive inhibition.
- A) Competitive in addition is based on reversible drug/antagonist binding at receptor sites.
- B) With competitive inhibition, the dose-effects curve shifted to the left
- C) With competitive inhibition, maximal drug effect cannot be obtained, even at high agonist concentrations
- D. All the above
ANSWER- A) Competitive in addition is based on reversible drug/antagonist binding at receptor sites.
16. Major role of receptor
- A. Determine the rate of elimination
- B. determine drug action selectivity
- C. Provide a means of blocking drug action as well as mediating drug action
- D. Both A and D
ANSWER- D. Both A and D
For more MCQs click on the below link.

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com

Good MCQs