H1 antagonists
H1 antagonists, also known as antihistamines, are a type of medication that prevents histamine from acting on H1 receptors. Histamine is a chemical that mast cells release in response to an allergic reaction, causing itching, swelling, and inflammation. H1 antagonists can alleviate or prevent these symptoms by blocking H1 receptors.
Allergies such as hay fever, hives, and allergic conjunctivitis are commonly treated with H1 antagonists. They can also be used to treat motion sickness, insomnia, and certain types of anxiety. However, because different H1 antagonists have varying degrees of sedation, some may be better suited to treating sleep disorders than others.
Diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine are some common H1 antagonists. Depending on the dose and formulation, they are available over-the-counter or by prescription. As with any medication, it’s critical to stick to the recommended dosage and consult with a doctor if you have any questions or concerns about using H1 antagonists.
USES
H1 antagonists have a variety of uses, including:
- Treating allergies:– H1 antagonists are commonly used to treat hay fever symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose. They can also aid in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, hives, and other allergic reactions.
- Relieving symptoms of motion sickness:- H1 antagonists can help with motion sickness symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, and vomiting.
- Treating insomnia:- Some H1 antagonists are sedative and can be used to treat sleep disorders.
- Managing anxiety:- H1 antagonists can help reduce anxiety symptoms, especially when used in conjunction with other medications.
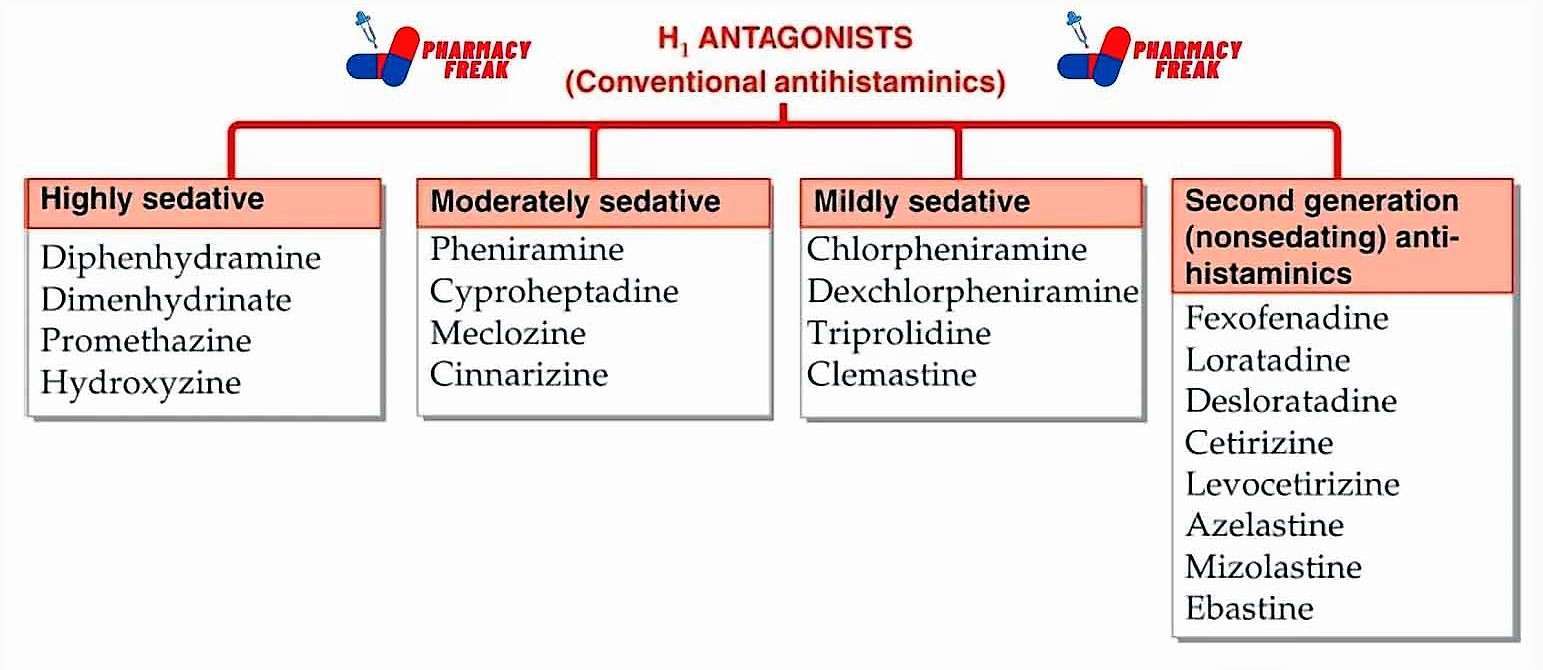
Classification
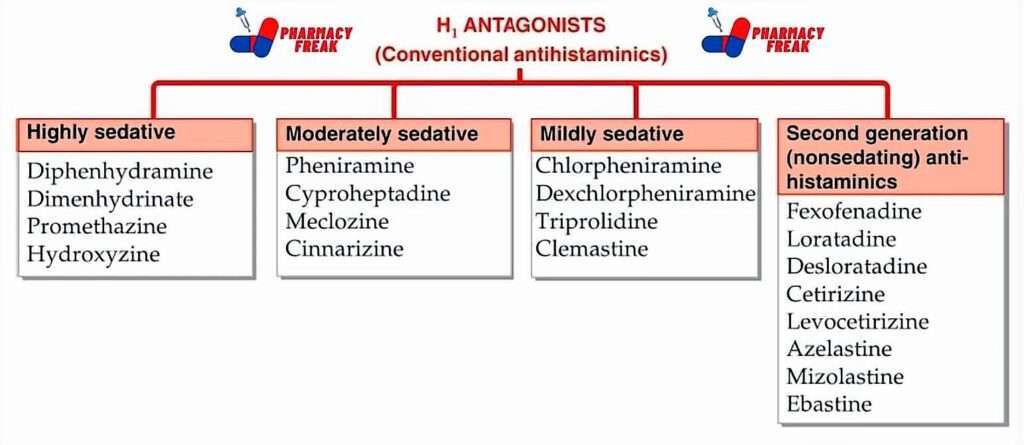
H1 antagonists (Conventional antihistaminics)
- Highly sedative:- Diphenhydramine, Dimenhydrinate, Promethazine, Hydroxyzine
- Moderately sedative:- Pheniramine, Cyproheptadine, Meclozine, Cinnarizine
- Mildly sedative:- Chlorpheniramine, Dexchlorpheniramine, Triprolidine, Clemastine
- Second generation (nonsedating) anti- histaminics– Fexofenadine, Loratadine, Desloratadine, Cetirizine, Levocetirizine, Azelastine, Mizolastine, Ebastine
Related Links
CLASSIFICATION OF HISTAMINERGIC AGONISTS
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- Science Direct- Histamine H1 Receptor Antagonist

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com