Thyroid inhibitors are medications that slow down the function of the thyroid gland.
They are typically used to treat conditions such as hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland is overactive. Common thyroid inhibitors include propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole (Tapazole). These medications work by blocking the production of thyroid hormones, which helps to reduce symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Side effects of thyroid inhibitors can include rash, nausea, and liver problems, so it’s important to talk to your doctor before taking them.
Classification
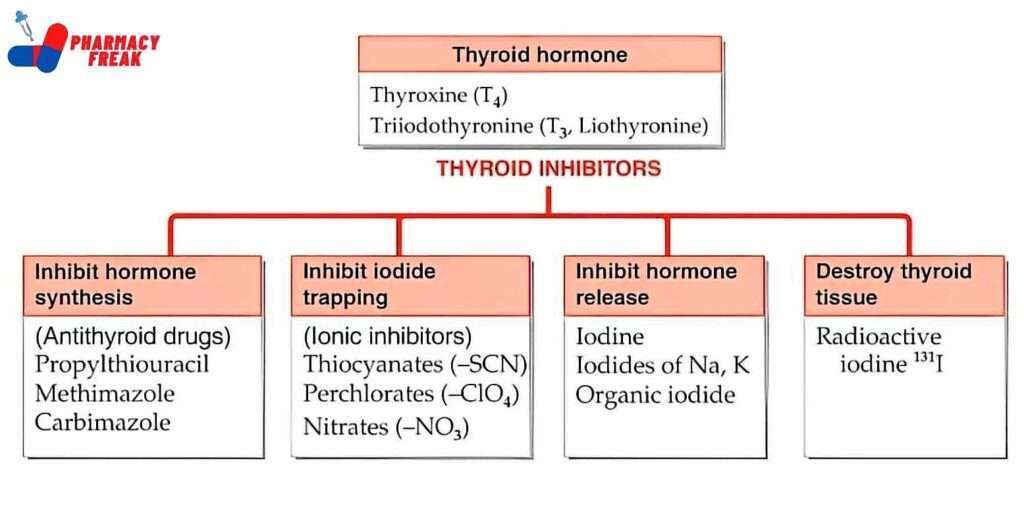
Thyroid Inhibitors
- Inhibit hormone synthesis– (Antithyroid drugs) Propylthiouracil, Methimazole, Carbimazole
- Inhibit iodide trapping-(lonic inhibitors) Thiocyanates (-SCN), Perchlorates (-CIO4), Nitrates (-NO3)
- Inhibit hormone release-Iodine, Iodides of Na, K Organic iodide
- Destroy thyroid tissue– Radioactive iodine 131 I
Reference
- Classification Of Thyroid Inhibitors- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Antithyroid Drugs

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com
