Ganglionic stimulants
Ganglionic stimulants are drugs that activate the autonomic ganglia. These are nerve cell clusters that regulate involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. They were historically used to treat conditions such as hypotension and urinary retention, but are now rarely used due to their high potential for adverse effects, such as hypertension, tachycardia, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
Classification
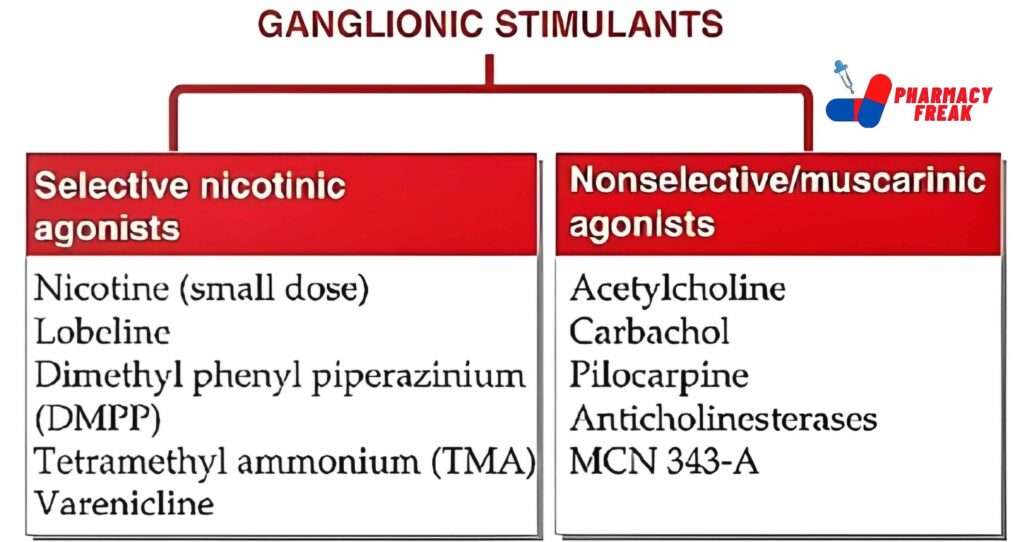
GANGLIONIC STIMULANTS
- Selective nicotinic agonists– Nicotine (small dose), Lobeline, Dimethyl phenyl piperazinium (DMPP), Tetramethyl ammonium (TMA)
- Nonselective/muscarinic agonists– Acetylcholine, Carbachol, Pilocarpine, Anticholinesterases, MCN 343-A, Varenicline
Related Links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Ganglionic stimulants (N K Bissada, L T Welch, A E Finkbeiner)

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com

This article was so nice to read