NSAIDs
It is also called ANTIPYRETIC-ANALGESICS or NSAIDs. NSAIDs are frequently used to treat pain, to reduce inflammation, and lower fever. They function by preventing the body from producing prostaglandins. Prostaglandinsare substances that contribute to inflammation and discomfort.
Aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen are a few examples of NSAIDs. These drugs are very commonly used. Many medications can be bought without a prescription.
NSAIDs can have negative effects, while being generally safe and efficient when used as recommended. Some individuals may feel queasy, nauseous, or vomit. The risk of stomach bleeding, kidney damage, and cardiac issues can all rise with prolonged NSAID use.
Follow the recommended dosage and consult your doctor if you have any questions or pre-existing medical conditions that you think may be affected by NSAIDs.
USES
The main purposes of NSAIDs are to treat pain, lessen inflammation, and lower fever. They are used to treat a number of conditions.
- migraines and headaches
- Arthritis (includes osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis)
- Period cramps
- joint and muscle ache
- tooth ache
- pain following surgery
- fever and other cold or flu-related symptoms
Depending on the particular medication and disease being treated, NSAIDs are given in a variety of strengths and dosages. It can be easily with or without a prescription. Follow the dosage recommendations and consult your doctor if any complications arises
CLASSIFICATION
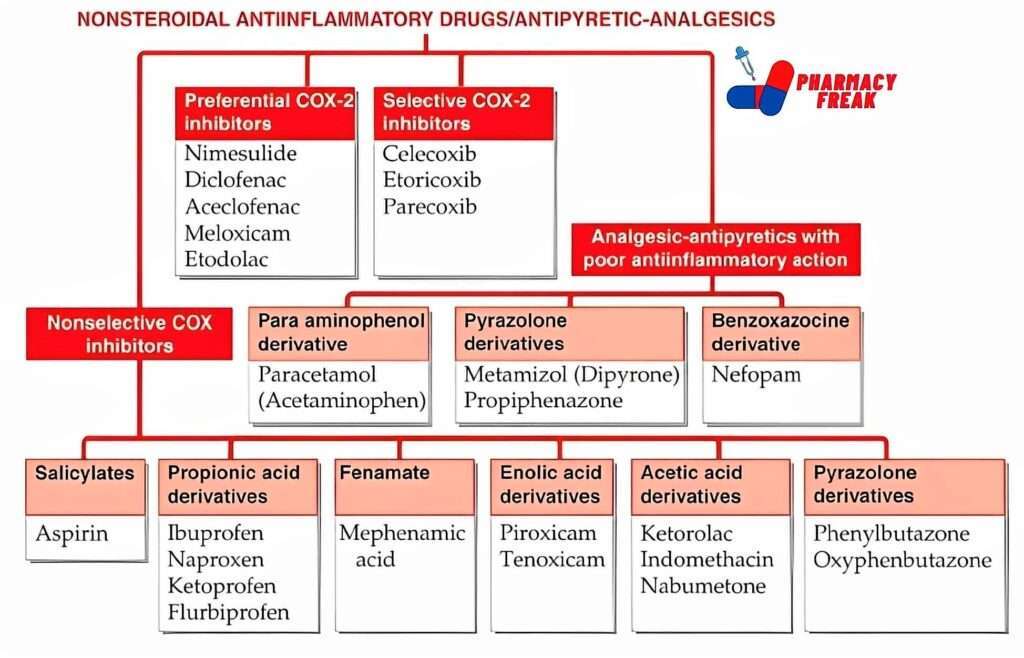
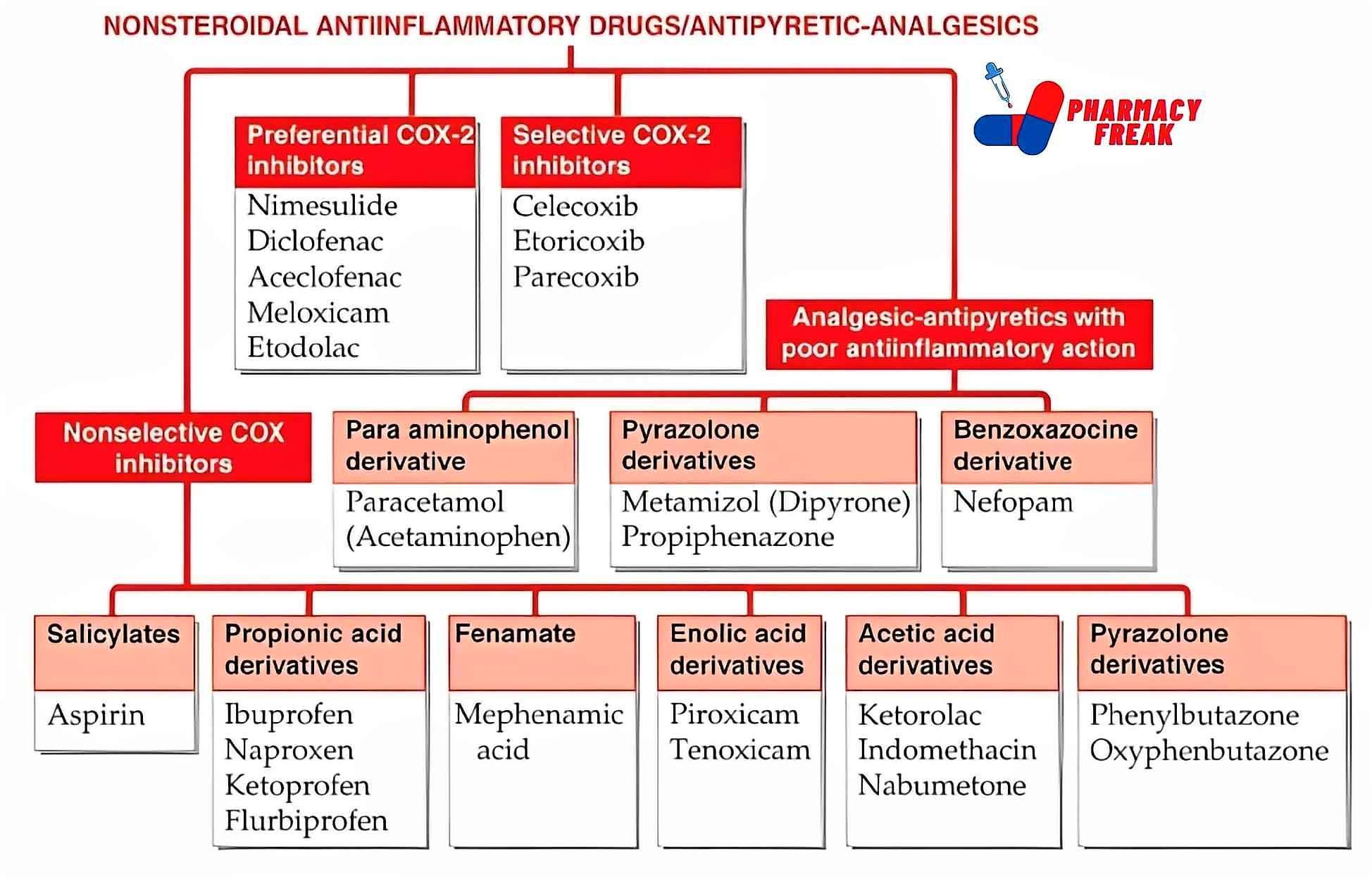
NONSTEROIDAL ANTIINFLAMMATORY DRUGS/ANTIPYRETIC-ANALGESICS
- Nonselective COX inhibitors
- Salicylates-Aspirin
- Propionic acid derivatives-Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Ketoprofen, Flurbiprofen
- Fenamate-Mephenamic acid
- Enolic acid derivatives-Piroxicam, Tenoxicam
- Acetic acid derivatives-Ketorolac, Indomethacin, Nabumetone
- Pyrazolone derivatives-Phenylbutazone, Oxyphenbutazone
- Preferential COX-2 inhibitors– Nimesulide, Diclofenac, Aceclofenac, Meloxicam, Etodolac
- Selective COX-2 inhibitors– Celecoxib, Etoricoxib, Parecoxib
- Analgesic-antipyretics with poor antiinflammatory action
- Para aminophenol derivative-Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
- Pyrazolone derivatives– Metamizol (Dipyrone), Propiphenazone
- Benzoxazocine derivative– Nefopam
Related Links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com