Glaucoma drugs
Glaucoma drugs is a group of eye diseases that cause damage to the optic nerve, often as a result of high intraocular pressure. Glaucoma can be treated with a variety of medications, including:
- Beta blockers- These medications, such as timolol and betaxolol, reduce the production of fluid in the eye, which aids in the reduction of eye pressure.
- Alpha agonists– These medications, which include brimonidine and apraclonidine, reduce fluid production in the eye while increasing fluid outflow, thereby lowering eye pressure.
- Prostaglandin analogs– These medications, which include latanoprost, bimatoprost, and travoprost, are typically used as the first line of glaucoma treatment. They function by increasing the outflow of fluid from the eye, which aids in the reduction of eye pressure.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors-These medications, which include latanoprost, bimatoprost, and travoprost, are typically used as the first line of glaucoma treatment. They function by increasing the outflow of fluid from the eye, which aids in the reduction of eye pressure.
- Miotics– Netarsudil, for example, increases the outflow of fluid from the eye and can be used in conjunction with other glaucoma medications.
Classification
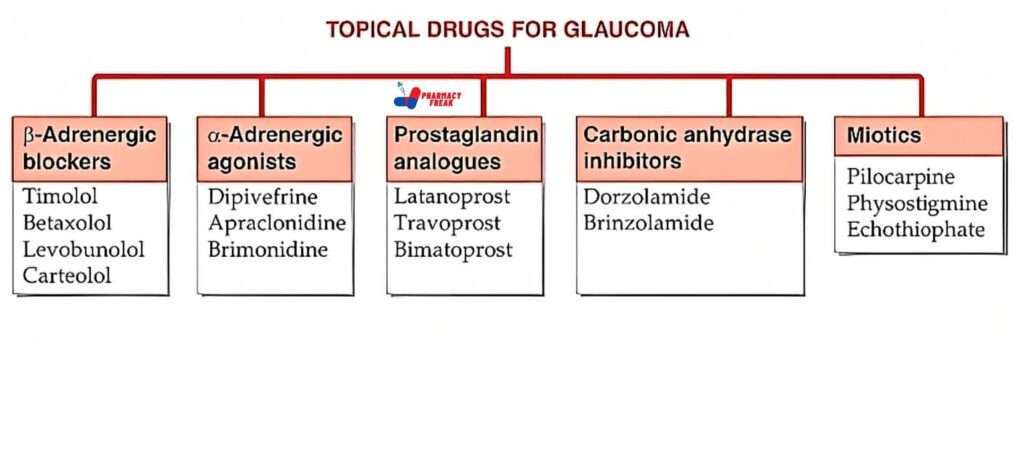
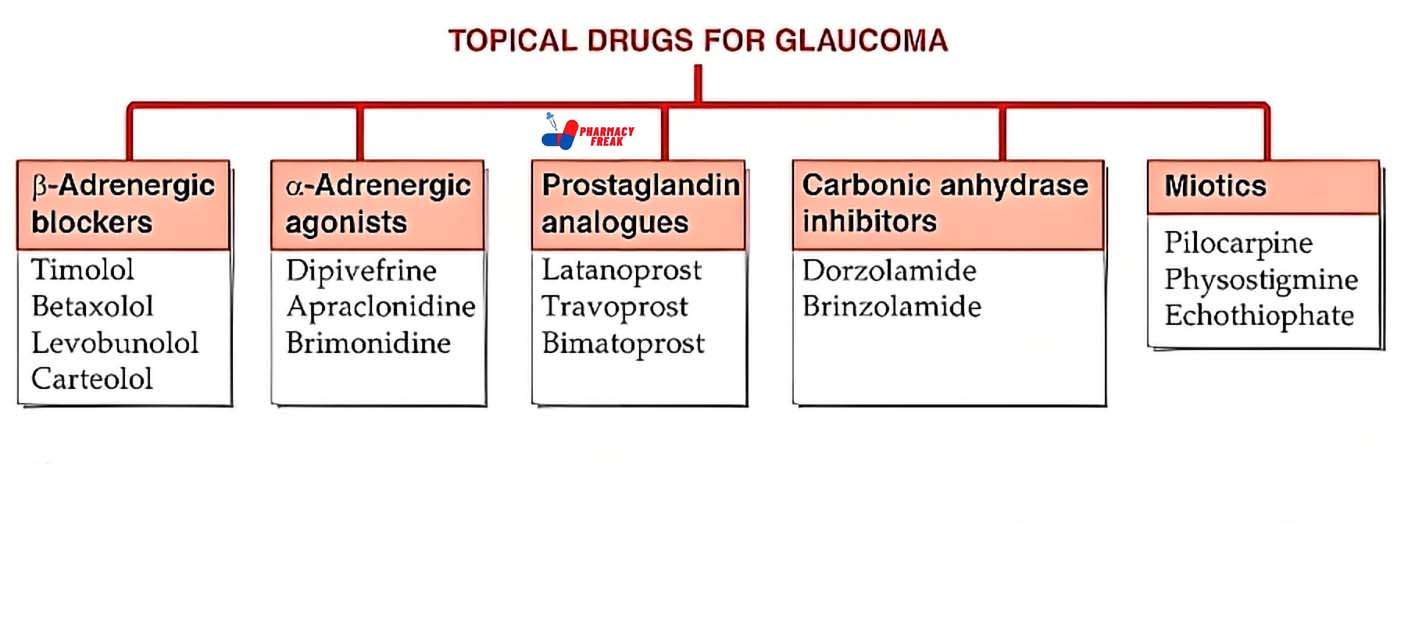
TOPICAL DRUGS FOR GLAUCOMA
- B-Adrenergic blockers-Timolol, Betaxolol, Levobunolol, Carteolol
- a.-Adrenergic agonists-Dipivefrine, Apraclonidine, Brimonidine
- Prostaglandin| analogues-Latanoprost, Travoprost, Bimatoprost
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors-Dorzolamide, Brinzolamide
- Miotics-Pilocarpine, Physostigmine, Echothiophate
Related Links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Antiglaucoma pharmacotherapy

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com