Beta(β) blockers
Beta(β) blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, are blood pressure medications. The hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is inhibited by beta blockers.
Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and forcefully, lowering blood pressure. Beta blockers also aid in the widening of veins and arteries, which improves blood flow.
Examples of beta (β) blockers
- Acebutolol
- Atenolol (Tenormin)
- Bisoprolol (Zebeta)
- Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL)
- Nadolol (Corgard)
- Nebivolol (Bystolic)
- Propranolol (Inderal, InnoPran XL)
Classification
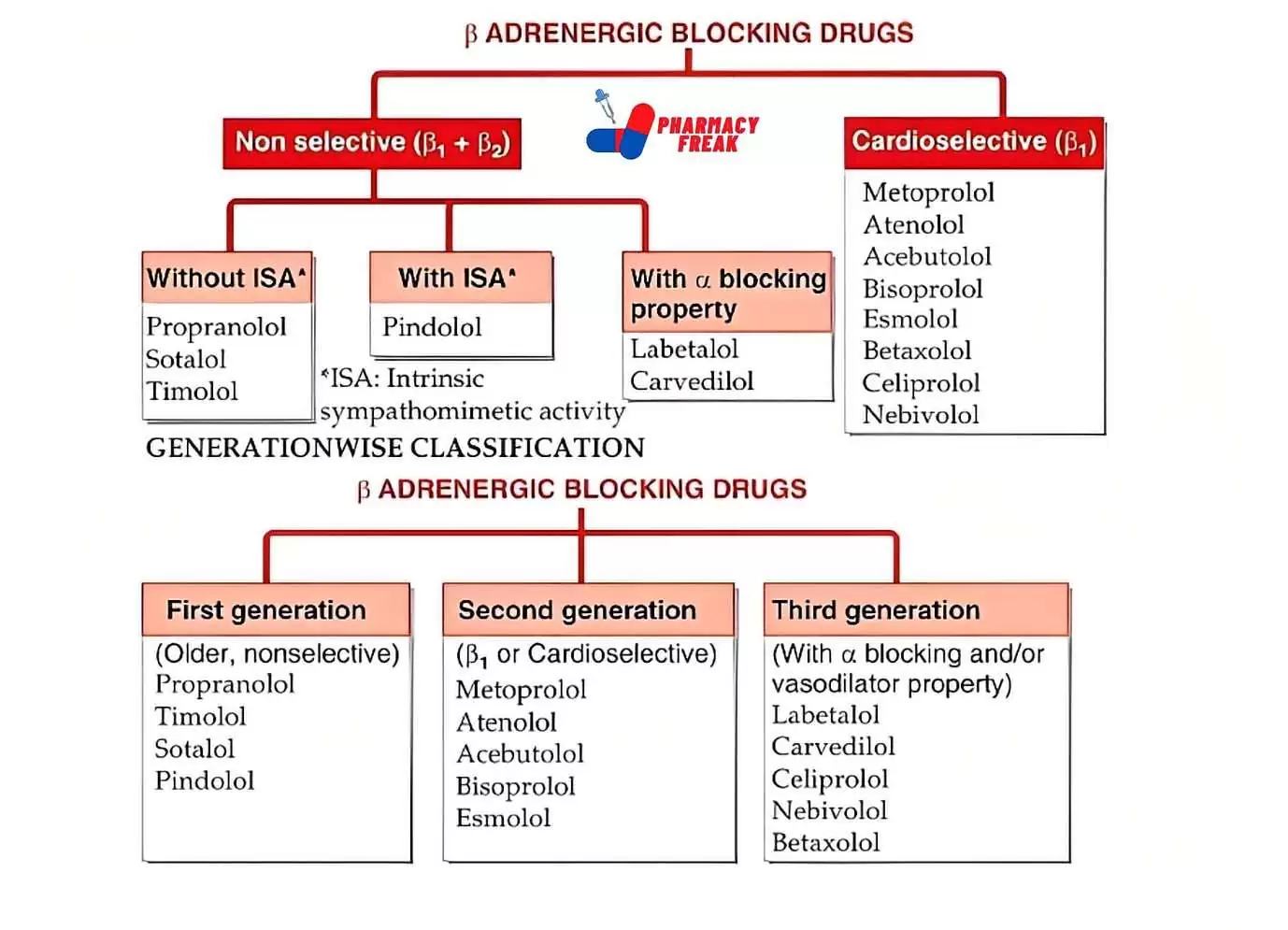
(β)Beta-ADRENERGIC BLOCKING DRUGS
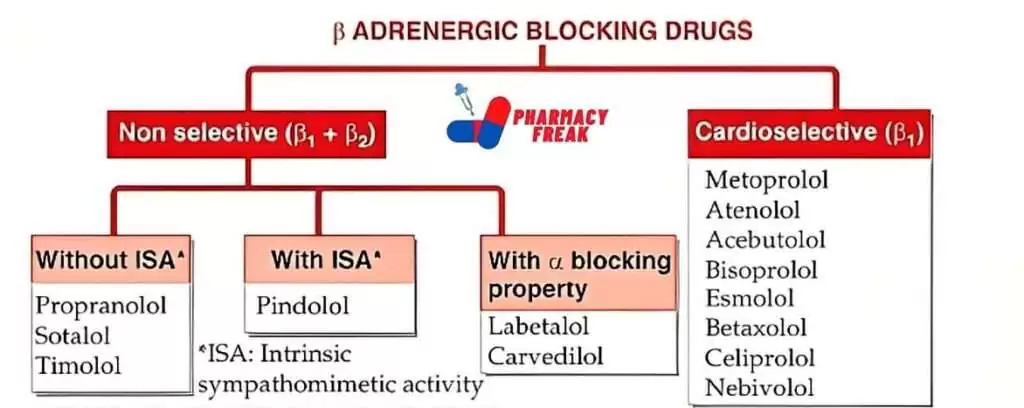
- Non selective (β₁ + β₂)
- Without ISA-Propranolol, Sotalol, Timolol
- With ISA-Pindolol
- With α blocking property-Labetalol, Carvedilol
- Cardioselective (β₁)– Metoprolol, Atenolo, Acebutolol, Bisoprolol, Esmolol, Betaxolol, Celiprolol, Nebivolol
(β)Beta-ADRENERGIC BLOCKING DRUGS (Generation wise)
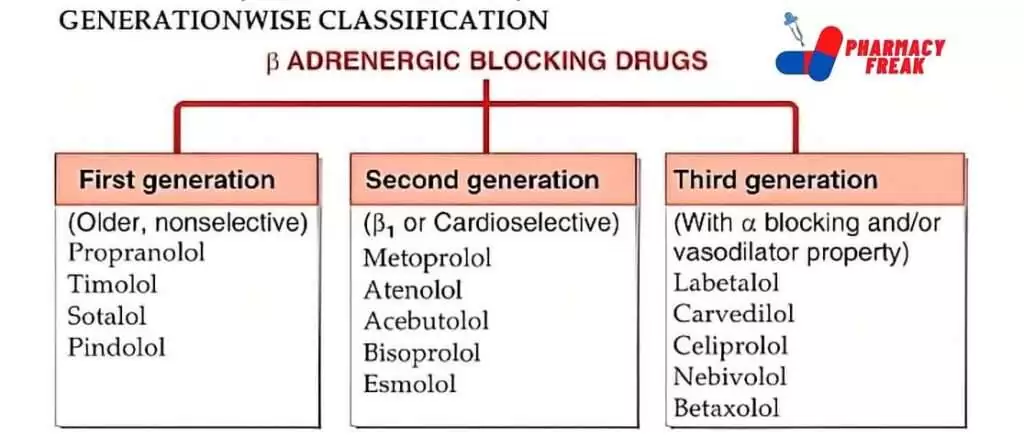
- First generation (Older, nonselective)- Propranolol, Timolol, Sotalol, Pindolol
- Second generation(β₁ or Cardioselective)- Metoprolol, Atenolol, Acebutolol, Bisoprolol, Esmolol
- Third generation(With α blocking and/or vasodilator property)- Labetalol, Carvedilol, Celiprolol, Nebivolol, Betaxolol
Related Links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Beta Adrenergic Blocking Agents

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com