Ganglionic blocking agents
A family of medications known as ganglionic blocking agents, also referred to as ganglionic blockers, affects the autonomic nervous system by preventing the transmission of nerve impulses at ganglia, which are collections of nerve cell bodies outside the central nervous system. Ganglionic blockers were once used to address conditions like hypertension, angina, and some forms of autonomic dysfunction, but they are no longer frequently prescribed.
Classification
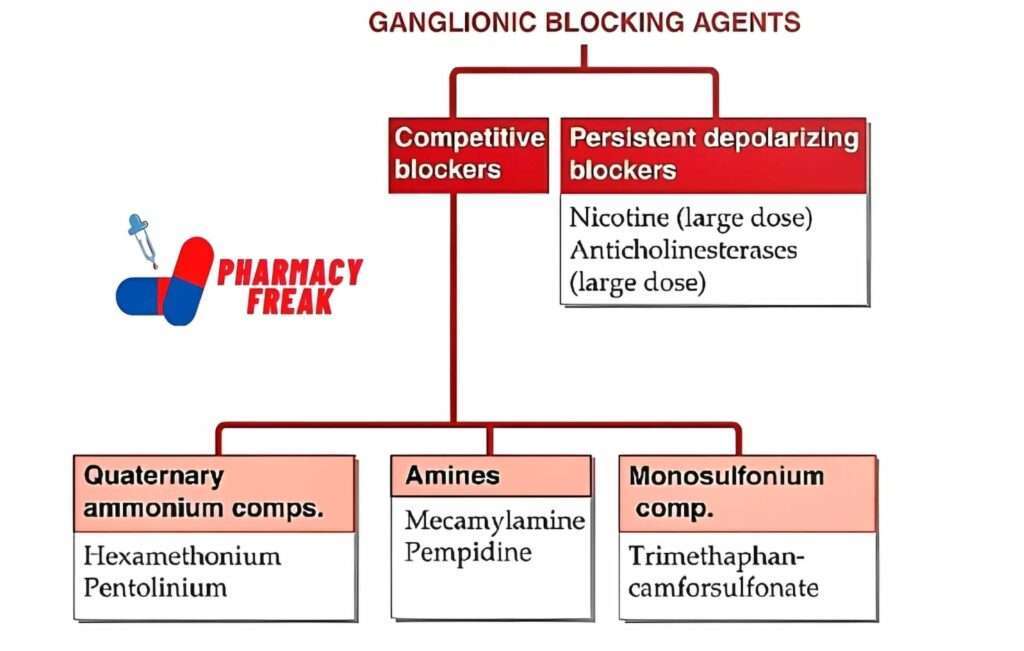
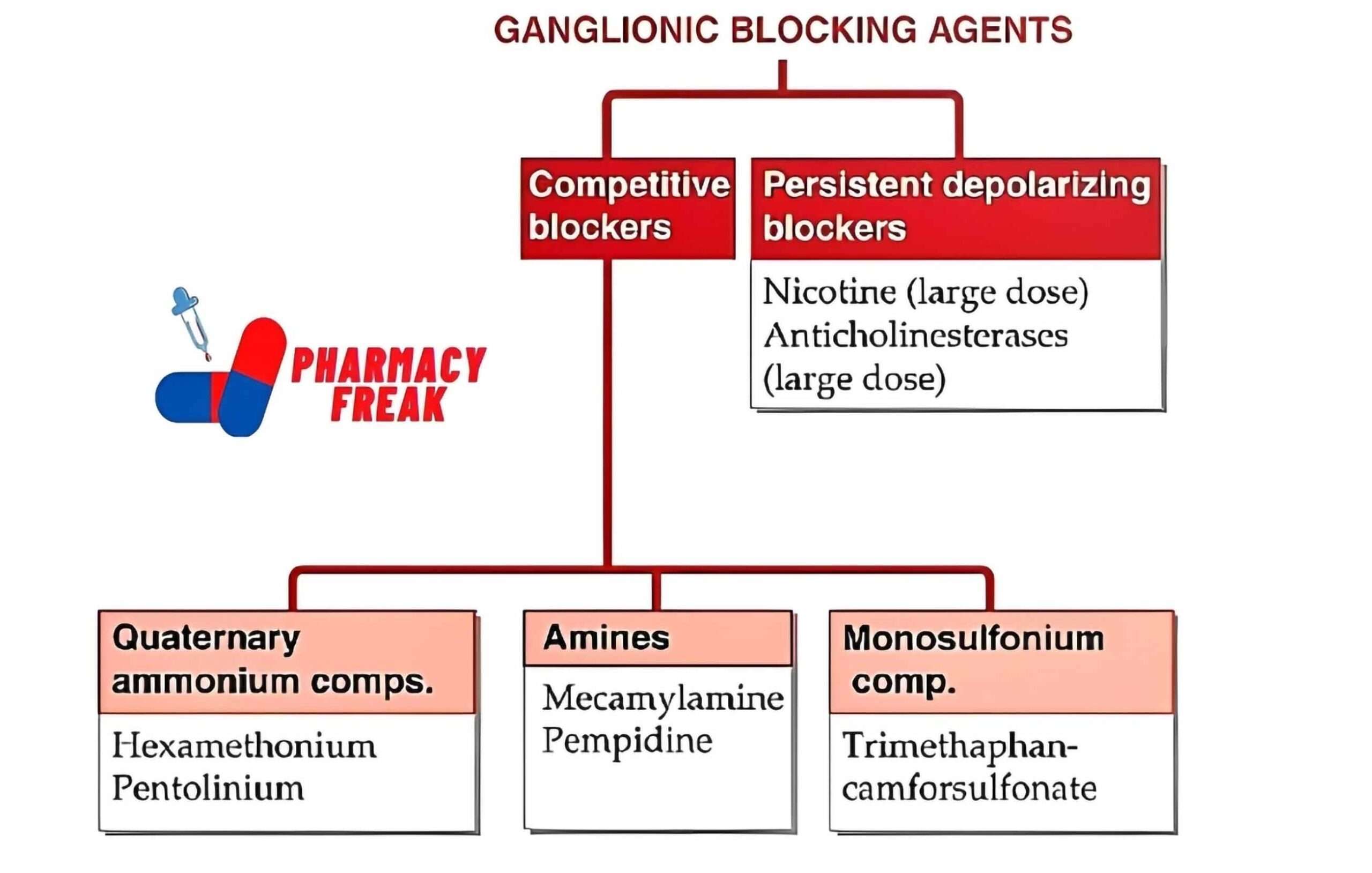
GANGLIONIC BLOCKING AGENTS
- Competitive blockers
- Quaternary ammonium comps.– Hexamethonium, Pentolinium
- Amines– Mecamylamine, Pempidine
- Monosulfonium comp.- Trimethaphan-camforsulfonate
- Persistent depolarizing blockers– Nicotine (large dose), Anticholinesterases (large dose)
Related links
- Classification of Ganglionic Stimulants
- Classification Of Anticholinargic Drugs
- Classification of Cholinergic drugs
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Nicotinic Ganglionic Blocker (Suraj Kaushal; Prasanna Tadi).

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com