Anticholinergic drugs
Anticholinergic drugs are a class of medications that block the actions of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, in the central and peripheral nervous system.
Uses
They are used to treat a variety of conditions including:
- Overactive bladder syndrome
- Urinary incontinence
- Gastrointestinal conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Parkinson’s disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Motion sickness
- Allergic rhinitis
- Asthma
- Alcohol withdrawal symptoms
Classification
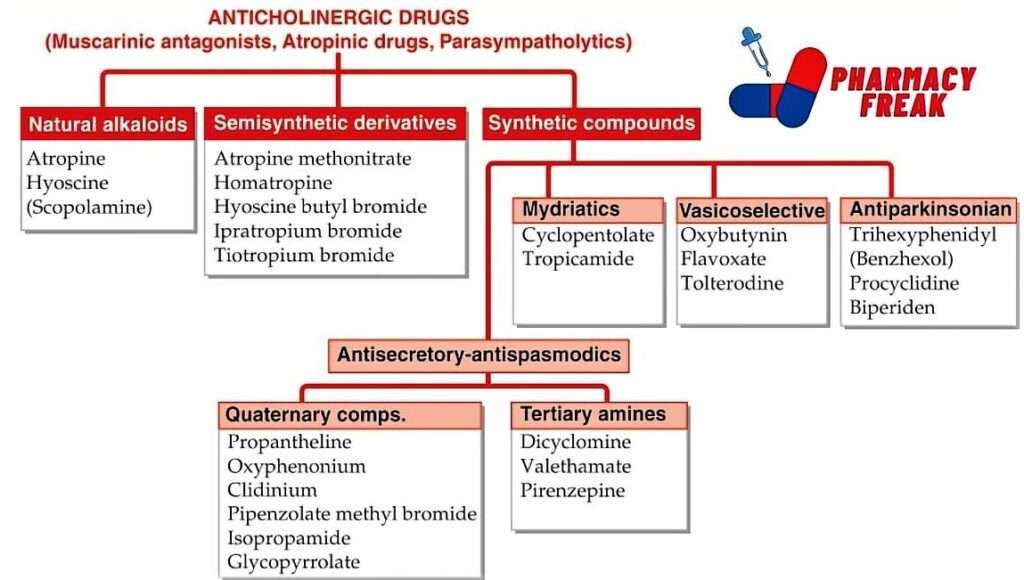
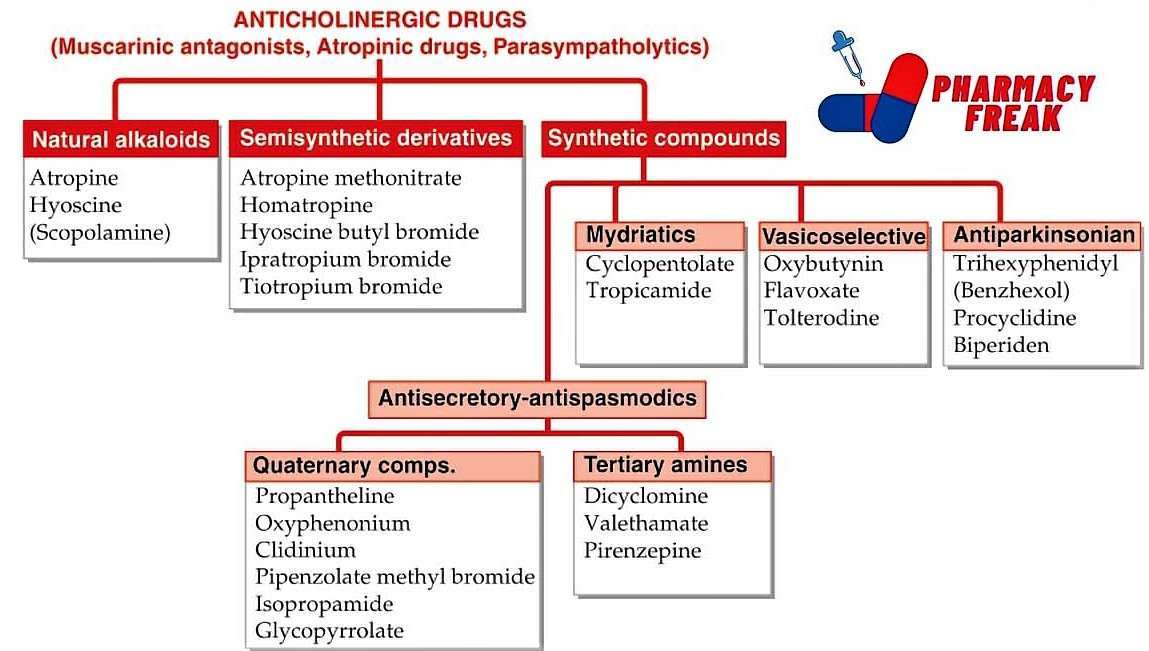
ANTICHOLINERGIC DRUGS (Muscarinic antagonists, Atropinic drugs, Parasympatholytics)
- Natural alkaloids– Atropine, Hyoscine (Scopolamine)
- Semisynthetic derivatives– Atropine methonitrate, Homatropine, Hyoscine butyl bromide, Ipratropium bromide, Tiotropium bromide
- Synthetic compounds
- Mydriatics– Cyclopentolate, Tropicamide
- Vasicoselective– Oxybutynin, Flavoxate, Tolterodine
- Antiparkinsonian– Trihexyphenidyl (Benzhexol), Procyclidine, Biperiden
- Antisecretory-antispasmodics
- Quaternary comps.– Propantheline, Oxyphenonium, Clidinium, Pipenzolate methyl bromide, Isopropamide, Glycopyrrolate,
- Tertiary amines– Dicyclomine, Valethamate, Pirenzepine
Related Links
Reference
- CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- ANTICHOLINERGIC DRUGS (Noah Ghossein; Michael Kang; Anand D. Lakhkar.)

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com