Table of Contents
Introduction
Topiramate is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug (AED) known for its use in treating partial and generalized seizures, migraine prophylaxis, and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. It has a multi-modal mechanism, acting on sodium channels, GABA-A receptors, glutamate receptors, and carbonic anhydrase. Its wide range of targets makes it effective in both epilepsy and mood disorders, though side effects like cognitive dulling and weight loss are notable.
This drug is frequently tested in USMLE, NCLEX, GPAT, and NEET-PG due to its multiple mechanisms and clinical uses.
Stepwise Mechanism of Action of Topiramate
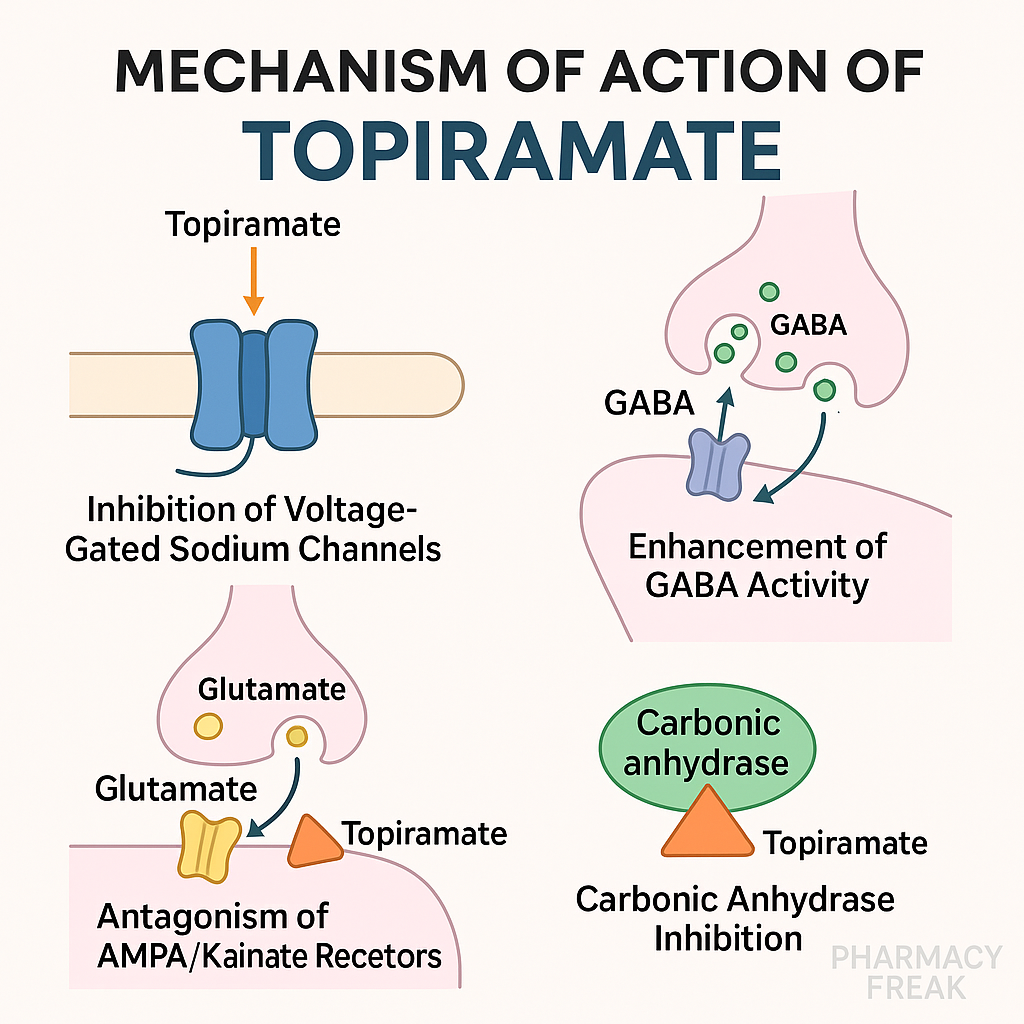
- Blockade of voltage-gated sodium channels
Topiramate inhibits voltage-gated Na⁺ channels, stabilizing neuronal membranes and preventing sustained repetitive firing. - Enhancement of GABAergic activity
It enhances the action of GABA-A receptors, increasing inhibitory neurotransmission in the CNS. - Inhibition of AMPA/kainate glutamate receptors
Topiramate blocks excitatory glutamate receptors, particularly AMPA and kainate, reducing excitatory synaptic transmission. - Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase
It weakly inhibits carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes, leading to mild metabolic acidosis, which may contribute to anticonvulsant activity. - Neuroprotective effects
Through multiple channels, topiramate may protect neurons from excitotoxic damage, especially in chronic epilepsy.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Topiramate
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | ~80% (oral) |
| Half-life | 20–30 hours |
| Protein binding | ~15% (low) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (partial), majorly renal excretion |
| Excretion | Renal (~70% unchanged) |
| Therapeutic range | Not routinely monitored |
Clinical Uses of Topiramate
- Focal (partial) seizures
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizures
- Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Weight loss (in combination with phentermine)
- Off-label use in bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence
Adverse Effects of Topiramate
- Cognitive slowing (“Dopamax” effect)
- Weight loss
- Paresthesias
- Kidney stones (due to carbonic anhydrase inhibition)
- Metabolic acidosis
- Glaucoma (angle-closure)
- Taste perversion
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Teratogenicity – cleft lip/palate
Comparative Analysis: Topiramate vs Lamotrigine
| Feature | Topiramate | Lamotrigine |
|---|---|---|
| Na⁺ channel inhibition | Yes | Yes |
| GABA enhancement | Yes | No |
| Glutamate inhibition | Yes (AMPA/kainate) | No |
| Carbonic anhydrase | Yes (mild inhibition) | No |
| Cognitive effects | Common (slowing) | Minimal |
| Rash (SJS risk) | Low | High (if titrated quickly) |
Practice MCQs
Q1. Topiramate enhances activity at which receptor?
a. AMPA
b. GABA-A ✅
c. NMDA
d. GABA-B
Q2. Which ion channel is blocked by topiramate?
a. K⁺ channels
b. Cl⁻ channels
c. Na⁺ channels ✅
d. Ca²⁺ channels
Q3. One side effect of topiramate is:
a. Weight gain
b. Memory improvement
c. Cognitive slowing ✅
d. Diarrhea
Q4. Topiramate inhibits which of the following enzymes?
a. MAO
b. Acetylcholinesterase
c. Carbonic anhydrase ✅
d. Tyrosine hydroxylase
Q5. Topiramate affects which excitatory receptors?
a. GABA-A
b. AMPA/kainate ✅
c. GABA-B
d. Glycine
Q6. Risk of kidney stones in topiramate is due to:
a. Sodium loss
b. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition ✅
c. Calcium retention
d. Water retention
Q7. Which psychiatric use is off-label for topiramate?
a. Depression
b. Bipolar disorder ✅
c. Schizophrenia
d. OCD
Q8. Topiramate is used for prophylaxis of:
a. Cluster headaches
b. Migraine ✅
c. Tension headaches
d. Sinus headaches
Q9. One serious ocular complication of topiramate is:
a. Retinopathy
b. Open-angle glaucoma
c. Angle-closure glaucoma ✅
d. Cataracts
Q10. What fetal defect is associated with topiramate?
a. Neural tube defect
b. Cleft palate ✅
c. Cardiac anomaly
d. Clubfoot
FAQs
Q1: Is topiramate used as monotherapy for seizures?
Yes, it can be used as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy for various seizures.
Q2: Why does topiramate cause weight loss?
Due to appetite suppression and mild metabolic changes.
Q3: Can topiramate be used in bipolar disorder?
Yes, off-label, especially in patients who are overweight or resistant to other mood stabilizers.
Q4: What monitoring is required?
Serum bicarbonate, renal function, and ocular pressure should be checked periodically.
Q5: Is topiramate safe in pregnancy?
No, it’s associated with teratogenic effects, including cleft lip/palate.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Review of Pharmacology – Sparsh Gupta
- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554529/

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com