Table of Contents
Introduction
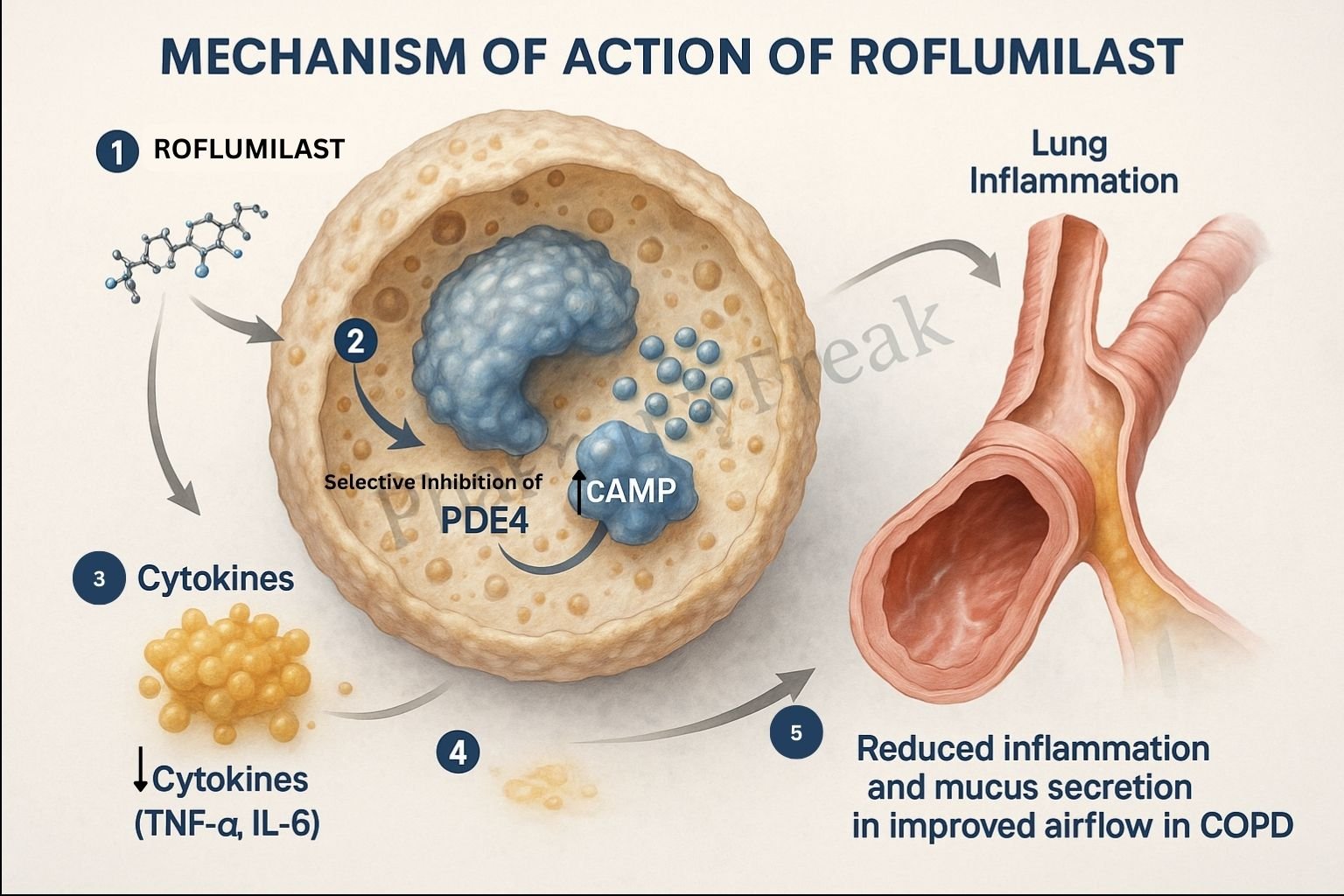
Roflumilast is an oral selective phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor used in the long-term management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) associated with chronic bronchitis. Unlike bronchodilators that target airway smooth muscle, roflumilast works primarily through anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Its distinct pharmacological action makes it a valuable adjunct in reducing the frequency of exacerbations in COPD patients.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)

1. Selective PDE4 Inhibition
Roflumilast selectively inhibits the PDE4 enzyme found in inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, eosinophils, and macrophages.
2. Elevated Intracellular cAMP
PDE4 inhibition prevents the breakdown of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), increasing its intracellular concentration.
3. Activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA)
Higher cAMP levels activate PKA, a key signaling molecule that regulates transcription of inflammatory genes.
4. Suppression of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
PKA activation leads to downregulation of inflammatory mediators including TNF-α, IL-8, and leukotriene B4.
5. Reduced Neutrophilic Inflammation
By limiting neutrophil infiltration and activation, roflumilast helps reduce airway inflammation.
6. No Bronchodilation
Roflumilast does not cause airway smooth muscle relaxation and should not be used for acute symptom relief.

Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: High oral bioavailability (~80%)
- Distribution: Plasma protein binding ~99%
- Metabolism: Hepatic metabolism via CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 to active metabolite roflumilast N-oxide
- Half-life:
- Roflumilast: ~17 hours
- Roflumilast N-oxide: ~30 hours
- Excretion: Renal elimination of metabolites
Clinical Uses
- Maintenance therapy in severe COPD with chronic bronchitis
- Reduces the risk of exacerbations in patients with a history of frequent flare-ups
- Not used for acute bronchospasm or as a rescue medication
Adverse Effects
- Common: Diarrhea, nausea, weight loss, headache, insomnia
- Serious: Depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts
- Precautions: Monitor weight and mental health status regularly
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Roflumilast | β2-Agonists | Inhaled Corticosteroids |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | PDE4 Inhibition | β2-Receptor Activation | Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation |
| Action | Anti-inflammatory | Bronchodilation | Anti-inflammatory |
| Route | Oral | Inhalation | Inhalation |
| Use | Maintenance | Rescue or maintenance | Maintenance |
| Onset | Delayed | Rapid | Variable |
| Side Effects | GI, psychiatric | Tremor, palpitations | Hoarseness, oral thrush |
Roflumilast is best used alongside bronchodilators and corticosteroids for full therapeutic benefit.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is the primary target of roflumilast?
a) V1 receptor
b) Beta-2 receptor
c) PDE4 enzyme
d) Alpha-1 receptor
Answer: c) PDE4 enzyme
2. Roflumilast primarily increases which second messenger?
a) cGMP
b) cAMP
c) Calcium
d) IP3
Answer: b) cAMP
3. Roflumilast is indicated for:
a) Asthma crisis
b) Acute bronchitis
c) Chronic bronchitis in COPD
d) Pneumonia
Answer: c) Chronic bronchitis in COPD
4. Which of the following is a common side effect of roflumilast?
a) Bradycardia
b) Hypokalemia
c) Diarrhea
d) Hypoglycemia
Answer: c) Diarrhea
5. What is the active metabolite of roflumilast?
a) Roflumilast sulfate
b) Roflumilast N-oxide
c) Roflumilast carboxylate
d) Roflumilast-glucuronide
Answer: b) Roflumilast N-oxide
6. Which cytochrome enzyme metabolizes roflumilast?
a) CYP2D6
b) CYP3A4
c) CYP2E1
d) CYP2C19
Answer: b) CYP3A4
7. Roflumilast lacks which of the following actions?
a) Anti-inflammatory
b) Bronchodilation
c) PDE4 inhibition
d) Cytokine suppression
Answer: b) Bronchodilation
8. The protein kinase involved in roflumilast’s action is:
a) PKC
b) PKA
c) AMPK
d) JAK2
Answer: b) PKA
9. Roflumilast is contraindicated in:
a) Asthma with eosinophilia
b) Severe depression
c) Bacterial pneumonia
d) Allergic rhinitis
Answer: b) Severe depression
10. How is roflumilast administered?
a) Intravenous
b) Subcutaneous
c) Inhalation
d) Oral
Answer: d) Oral
FAQs
Q1. How does roflumilast differ from bronchodilators?
Roflumilast reduces inflammation, not bronchoconstriction, and thus complements rather than replaces bronchodilators.
Q2. Can roflumilast be used in asthma?
It is not currently approved for asthma treatment.
Q3. How long does it take for roflumilast to work?
Effects are usually seen after several weeks of daily use.
Q4. What precautions should be taken during therapy?
Monitor weight, mood, and symptoms of gastrointestinal distress.
Q5. Is roflumilast used during acute COPD exacerbations?
No, it is for long-term maintenance therapy only.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- FDA Drug Label for Roflumilast
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com