Sedative-hypnotic drugs are a group of medications that can help to calm nerves, induce sleep, or even cause relaxation. They are commonly prescribed for conditions like insomnia or anxiety. Let’s break down this classification.
Table of Contents
Classification
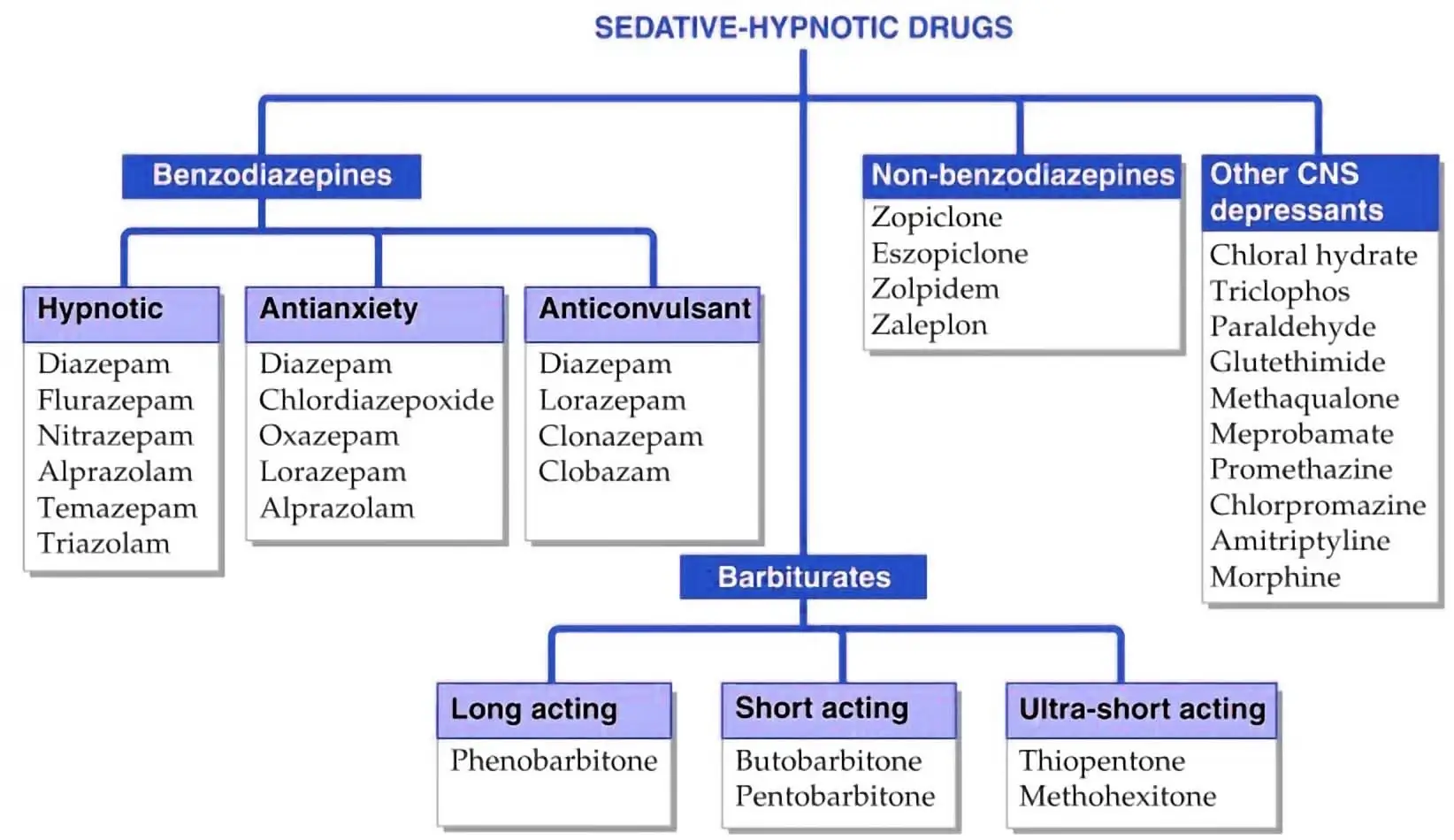
SEDATIVE-HYPNOTIC DRUGS
- Benzodiazepines
- Hypnotic– Diazepam,Flurazepam, Nitrazepam, Alprazolam, Temazepam, Triazolam
- Antianxiety- Diazepam, Chlordiazepoxide, Oxazepam, Lorazepam, Alprazolam
- Anticonvulsant– Lorazepam, Clonazepam, Diazepam, Clobazam
- Barbiturates
- Long-acting- Phenobarbitone
- Short-acting- Butobarbitone, Pentobarbitone
- Ultra-short acting– Thiopentone, Methohexitone
- Non-benzodiazepines- Zopiclone, Eszopiclone, Zolpidem, Zaleplon
- Other CNS depressants- Methaqualone, Chloral hydrate, Triclophos, Paraldehyde, Glutethimide, Meprobamate, Promethazine, Chlorpromazine, Amitriptyline, Morphine
Benzodiazepines
- Short-acting Benzodiazepines: These are fast-acting and have a short duration of action. Examples include alprazolam (Xanax) and lorazepam (Ativan).
- Intermediate-acting Benzodiazepines: These have a moderate duration of action. Examples include diazepam (Valium) and clonazepam (Klonopin).
- Long-acting Benzodiazepines: These have a prolonged duration of action. Examples include diazepam (Valium) and chlordiazepoxide (Librium).
Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics (Z-drugs)
- These drugs are structurally different from benzodiazepines but have a similar mechanism of action. Examples include zolpidem (Ambien), zaleplon (Sonata), and eszopiclone (Lunesta).
Barbiturates
- These are older sedative-hypnotic drugs that are rarely prescribed due to their potential for dependence and overdose. Examples include phenobarbital and secobarbital.
Melatonin Receptor Agonists
- These drugs work by targeting melatonin receptors in the brain and are used to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Examples include ramelteon (Rozerem).
Antihistamines
- Some over-the-counter antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and doxylamine (found in certain sleep aids) have sedative effects and can be used for short-term sleep problems.
Herbal and Natural Remedies
- Certain herbal supplements and natural products like valerian root, chamomile, and lavender oil are used as mild sedatives or sleep aids. However, their effectiveness varies from person to person.
Other Sedative-Hypnotic Medications
- This category includes miscellaneous drugs like quetiapine (Seroquel), which is an atypical antipsychotic sometimes used off-label for its sedative properties.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- The classification and mechanism of the hypnotics
Related Links

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com