Antihypertensive drugs are medications used to manage high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. They play a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing complications associated with elevated blood pressure. Understanding the types and mechanisms of action of antihypertensive drugs is essential for those dealing with hypertension or interested in how they work.
Table of Contents
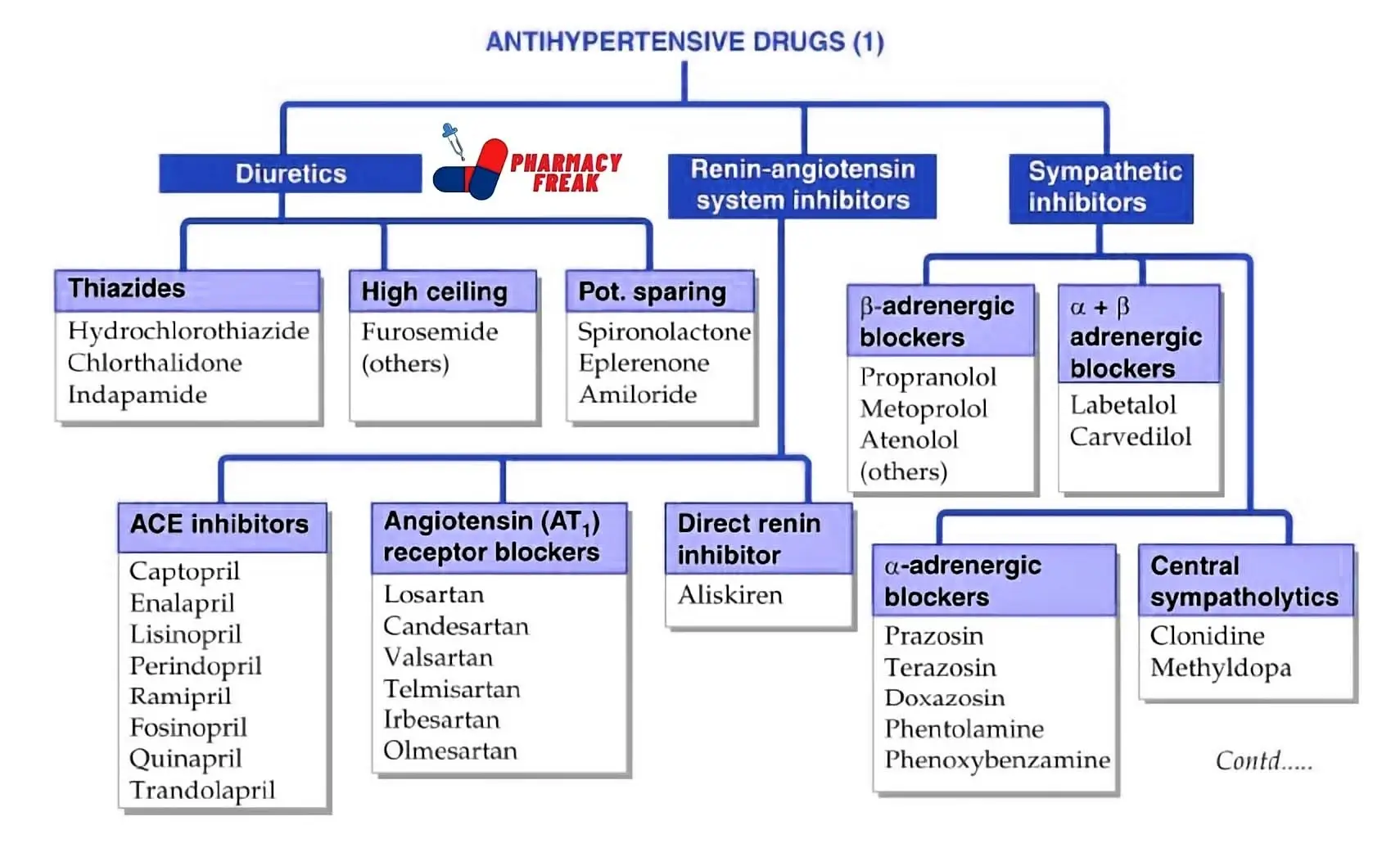
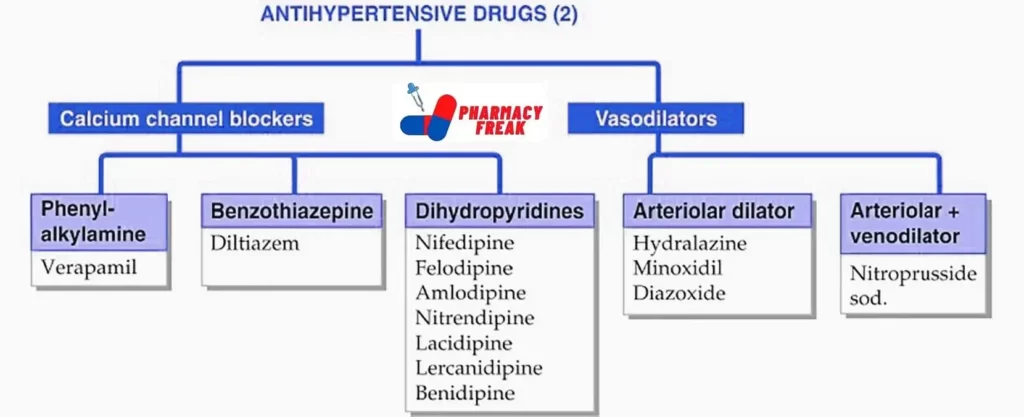
Classification of Antihypertensive Drugs
Antihypertensive drugs can be categorized into several classes based on their mechanisms of action:
- Diuretics
- Thiazides– Hydrochlorothiazide, Chlorthalidone, Indapamide
- High ceiling– Furosemide (others)
- Pot. sparing- Spironolactone, Eplerenone, Amiloride
- Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors
- ACE inhibitors- Captopril, Enalapril, Lisinopril, Perindopril, Ramipril, Fosinopril, Quinapril, Trandolapril
- Angiotensin (AT₁) receptor blockers- Losartan, Candesartan, Valsartan, Telmisartan, Irbesartan, Olmesartan
- Direct renin inhibitor- Aliskiren
- Sympathetic inhibitors
- β-adrenergic blockers- Propranolol, Metoprolol, Atenolol, (others)α+β adrenergic blockers– Labetalol, Carvedilol
- α-adrenergic blockers- Prazosin, Terazosin, Doxazosin, Phentolamine, Phenoxybenzamine
- Central sympatholytics- Clonidine, Methyldopa
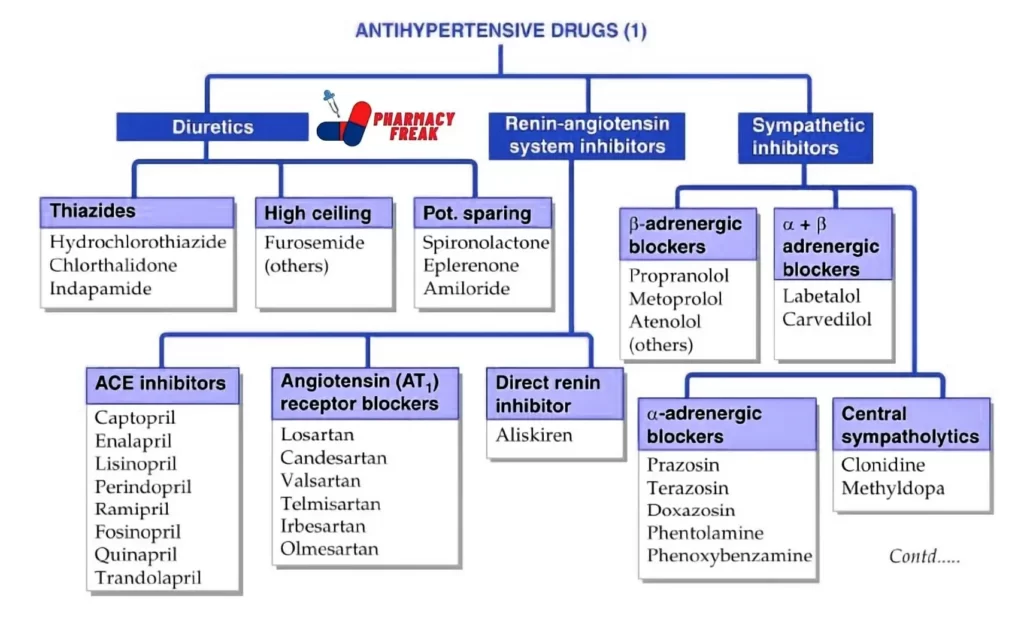
- Calcium channel blockers
- Phenyl-alkylamine– Verapamil
- Benzothiazepine- Diltiazem
- Dihydropyridines- Nifedipine, Felodipine, Amlodipine, Nitrendipine, Lacidipine, Lercanidipine, Benidipine
- Vasodilators
- Arteriolar dilator- Hydralazine, Minoxidil, Diazoxide
- Arteriolar + venodilator– Nitroprusside sod.
- Diuretics:
- Diuretics, also known as water pills, help reduce blood pressure by increasing urine production, which leads to decreased fluid volume in the bloodstream.
- Common diuretics include hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and chlorthalidone.
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors:
- ACE inhibitors block the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a substance that constricts blood vessels. By doing so, they reduce blood vessel constriction and lower blood pressure.
- Common examples are enalapril, lisinopril, and ramipril.
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs):
- ARBs, like ACE inhibitors, target angiotensin II but work by blocking its receptors. This action results in blood vessel dilation and reduced blood pressure.
- Well-known ARBs include losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan.
- Calcium Channel Blockers:
- Calcium channel blockers prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel muscle cells, leading to reduced blood vessel constriction and lower blood pressure.
- Amlodipine, verapamil, and diltiazem are examples of calcium channel blockers.
- Beta-Blockers:
- Beta-blockers reduce blood pressure by blocking the effects of adrenaline. This slows the heart rate and reduces the force of heart contractions.
- Common beta-blockers include metoprolol, atenolol, and propranolol.
- Alpha-Blockers:
- Alpha-blockers relax certain muscles in blood vessel walls, resulting in blood vessel dilation and lower blood pressure.
- Doxazosin and prazosin are examples of alpha-blockers.
- Central Alpha Agonists:
- These drugs stimulate receptors in the brain that reduce nerve signals, leading to lower blood pressure.
- Clonidine and methyldopa fall into this category.
- Vasodilators:
- Vasodilators relax blood vessel muscles directly, causing blood vessels to expand and blood pressure to decrease.
- Hydralazine and minoxidil are vasodilators used to manage hypertension.
Common Uses of Antihypertensive Drugs
Antihypertensive drugs are primarily used for the following conditions:
- Hypertension:
- The most common use of these medications is to treat high blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
- Heart Conditions:
- Antihypertensives are often prescribed to individuals with heart-related conditions like heart failure or after a heart attack to relieve strain on the heart.
- Kidney Diseases:
- Some kidney diseases are associated with high blood pressure, and antihypertensive drugs help protect the kidneys.
- Migraine Prevention:
- Beta-blockers are occasionally used to prevent migraines, although they are not primary migraine medications.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Antihypertensive Medications
Related Links

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com