
Here, we have combined more than 200 MCQs and sets of pharmacognosy MCQs. We provide MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) for the preparation for GPAT, B.pharma, D.pharma, and M.pharma. Please visit our site pharmacyfreak.com for any type of information and study material required for B.pharm, M.pharm, and GPAT.
MCQs set of pharmacognosy
1. Quinone on treatment with amynitrate in presence of hydrochloric acid gives oxime. This concludes the presence of characteristic moiety. Identify it
- (a) -CHCO
- (b) -CH-NO
- (c) —CH,–CO
- (d) -CH₂-CH=CH₂
Answer- (b) -CH-NO
2. Which aldehyde undergoes Cannizaro reaction?
- (a) Acetaldehyde
- (b) Benzeldehyde
- (c) Phenyl acetaldehyde
- (d) Propionaldehyde
Answer-(b) Benzeldehyde
3. Cephaeline differs from emetine in possessing
- (a) Heterocyclic ring
- (b) Hydroxy group in place of methoxy group, present in emetine
- (c) Double bond
- (d) N-CH, group
Answer-(b) Hydroxy group in place of methoxy group, present in emetine
4. Morphine on distillation with zinc dust yield
- (a) a-codeimethine
- (b) Morphenol
- (c) Morphol
- (d) Phenanthrene
Answer-(d) Phenanthrene
5. Ergotamine on alkaline hydrolysis gives
- (a) Isolysergic acid and alanine
- (b) Lysergic acid and a-hydroxy alanine
- (c) Lysergic acid and a-hydroxy phenylalanine
- (d) Lysergic acid and a-hydroxy alanine and proline
Answer-(b) Lysergic acid and a-hydroxy alanine
6. Brucine and Strychnine are isolated from strynes nuxvomica. Brucine is
- (a) Dealkaly derivative of strychnine
- (b) Dimethoxy derivative of strychnine
- (c) Saturated analogue of strychnine
- (d) demethylated derivative of strychnine
Answer-(b) Dimethoxy derivative of strychnine
7. The saponification value is defined as
- (a) number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids and saponify the ester contain in 1 gms of fats
- (b) number of grams of same as above
- (c) number of grams of same as above
- (d) None of the above
Answer- (a) number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize the free acids and saponify the ester contain in 1 gms of fats
8. Borneol on oxidation gives
- (a) Camphor
- (b) a-pinene
- (c) Borneone
- (d) ISO borneol
Answer-(a) Camphor
9. The sugar lactulose is
- (a) disaccharide,
- (b) aldohexose, an epimer of glucose
- (c) polysaccharide, a derivative of starch
- (d) monosaccharide, an epimer of fructose
Answer-(a) disaccharide
10. Which one of these is known as wood sugar?
- (a) Xylose
- (b) Cellulose
- (c) Amylose
- (d) Maltose
Answer-(b) Cellulose
11. Which one of these structures is related to carvacol?
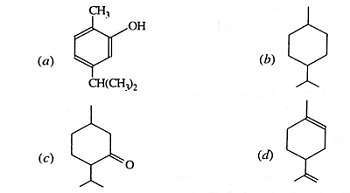
Answer-(A)
12. Penicillin on hydrolysis with alkali gives
- (a) Penicilloic acid
- (b) Penaldic acid
- (c) Penicillic acid
- (d) Penicillamine
Answer-
13. Which one of these is a B-lactamase inhibitor?
- (a) Chloramphenicol
- (b) Cefadroxil
- (c) Clavulanic acid
- (d) Ampicillin
Answer- (a) Chloramphenicol
14. The first hydrolytic product of STREPTOMYCIN with methanolic hydrochloric acid is given below. Identify the correct one
(a) Streptidine + Streptose + N-methyl glucosamine
- (b) Streptidine + Methyl strepto – biosaminide dimethyl acetal
- (c) Streptamine + Streptose + N-methyl glucosamine
- (d) Streptamine + Streptose dimethyl acetal + N-methyl glucosamine
Answer-(a) Streptidine + Streptose + N-methyl glucosamine
15. The levorotatory isomer of atropine is
- (a) Hyoscine.
- (b) Hyoscyamine
- (c) Tropine
- (d) Psudotropine
Answer-(a) Hyoscine.
16. In cephalosporins, the lactam ring is fused with
- (a) Thiazolidine system
- (b) 1, 3 dihydrothiazine system
- (c) Thiazine system
- (d) Dehydro thiazolidine system
Answer- (b) 1, 3 dihydrothiazine system
17. Gentamycin on hydrolysis gives
- (a) Garosamine + purpuroamine + 2-deoxy streptamine
- (b) Garosamine + streptose + purpurosamine
- (c) Garosamine + streptamine + 2-deoxy streptose
- (d) 3-amino, 2-deoxy – glucose + purpurosamim + 2-deoxy streptamine
Answer- (a) Garosamine + purpuroamine + 2-deoxy streptamine
18. Progesterone is commercially synthesized from
- (a) Stigmasterol
- (b) Sarsapogenin
- (c) Progenin
- (d) Estradiol
Answer-(a) Stigmasterol
19. Sonneuschein’s reagent is used for the detection of:
- (a) Tannins
- (b) Glycosides
- (c) Alkaloids
- (d) All of the above
Answer- (c) Alkaloids
20. Scheibler’s reagent is used for the detection of:
- (a) Glycosides
- (b) Alkaloids
- (c) Tannis
- (d) All of the above
Answer- (b) Alkaloids
21. Otto Reaction is used for the detection of
- (a) Brucine
- (b) Yohimlene
- (c) Strychnine
- (d) Referpine
Answer-
22. Ergotamine on alkaline hydrolysis gives :
- (a) d-lysergic acid + a-hydroxyalanine +1-phenylalanine + d-leucinac
- (b) d-lysergic acid + a-hydroxyvaline + Tryptophan
- (c) d-lysergic acid + a-hydroxylanine +1-pheylalanine + d-Proline
- (d) d-lysergic acid + a-hydroxyolanine +1-phenylalanine + d-proline
Answer-(c) d-lysergic acid + a-hydroxylanine +1-pheylalanine + d-Proline
23. Morphine on zinc dust or selenium distillation gives:
- (a) Phenanthrene
- (b) Napthacene
- (c) Quinoline
- (d) Isoquinlin
Answer- (d) Isoquinlin
24. Narcotine contains which of the following moiety?
- (a) Phenanthrene
- (b) Quinoline
- (c) Isoquinoline
- (d) Indole
Answer- (c) Isoquinoline
25. Papaverine on oxidation which hot conc. KMnO, gives:
- (a) 6,7-Dimthoxyisoquinoline -1- carloxylic acid + Veratic Acid
- (b) 6-methoxyisoquinoline -1- carloxylic acid + Isoveratic Acid
- (c) 5,6-Dimthoxyisoquinoline -1- carloxylic acid + Veratic Acid
- (d) 7-methoxyisoquinoline + Veratic
Answer- (a) 6,7-Dimthoxyisoquinoline -1- carloxylic acid + Veratic Acid
26. Acid Citral on oxidation with alkaline permangnate followed by chromic acid gives:
- (a) Laevulic acid + Acetone
- (b) Laevulic acid + oxalic acid + Acetone
- (c) 3-methyadipic acid + oxalic acid + Acetone
- (d) None of the above
Answer- (b) Laevulic acid + oxalic acid + Acetone
27. Citral-b is a
- (a) Cis isomer
- (b) Trans isomer
- (c) Cis-trans isomer
- (d) None of the above
Answer- (a) Cis isomer
28. On thermal decomposition, any terpenoid gives:
- (a) 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene
- (b) 3-methyl-1, 2-butadiene
- (c) 4-methyl-1-pentene
- (d) None of these
Answer-(a) 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene
29. Salkowski test is used to detect :
- (a) Terpenes
- (b) Alkaloids
- (c) Tannins
- (d) None of these
Answer-(a) Terpenes
30. Noller test is used to detect :
- (a) Alkaloids
- (b) Tannins
- (c) Terpenes
- (d) Rasins
Answer- (c) Terpenes
31. Liberman’s test is used to detect :
- (a) Terpenes
- (b) Steroius
- (c) Amino acids
- (d) None of these
Answer- (b) Steroius
32. Theophylline on oxidation gives:
- (a) Methylalloxan + Methylurea
- (b) Alloxan + Urea
- (c) Dimethylalloxan + Methylurea
- (d) Dimethylalloxan + Urea
Answer- (d) Dimethylalloxan + Urea
33. Citral on reaction with acetones gives :
- (a) Cyclocitral
- (b) Ionone
- (c) Pulegone
- (d) None
Answer- (b) Ionone
34. α -pinene on hydration is the presence of C₂H2OH/H₂SO4 gives :
- (a) Menthol
- (b) Geraniol
- (c) α-Terpineol
- (d) None
Answer-(c) α-Terpineol
35. Camplor on distillation with ZnCl₂. gives:
- (a) p-cymene
- (b) Limonene
- (c) Menthone
- (d) None of these
Answer- (a) p-cymene
36. Camphor on distillation with 1₂ gives:
- (a) Carvone
- (b) Carvacrol
- (c) Limonene
- (d) None of these
Answer- (b) Carvacrol
37. In stereochemistry of camphor which of the following isomers are known:
- (a) cis
- (b) trans
- (c) cis and trans both
- (d) None of these
Answer- (a) cis
38. Herzig Meyer method is used to detect :
- (a) N-alkyl group
- (b) N-aryl group
- (c) hydroxy-group
- (d) None of these.
Answer-(a) N-alkyl group
39. Zeigel method is used to estimate the number of
- (a) Aldehyde group
- (b) Ketone groups these
- (c) Alkoxyl group
- (d) None of these
Answer- (a) Aldehyde group
40. Ephedrine on heating with HCl gives
- (a) Acetone + Ethylamine
- (b) Acetophenone + Methylamine + Phenylacetone
- (c) Propiopheone + Methylamine + Phenylacetone
- (d) None of these
Answer- (c) Propiopheone + Methylamine + Phenylacetone
41. Thevetia nerrifolia contain
- (a) Anthraquinone glycoside
- (b) Flavonol glycoside
- (c) Cardiac glycoside
- (d) Triterperiod glycoside
Answer- (c) Cardiac glycoside
42. Which one of these is an immunomodulator
- (a) Ginseng
- (b) Campothica
- (c) Taxus
- (d) Guggul
Answer- (a) Ginseng
43. Which one of these are naturally occurring insecticides?
- (a) Chlordane
- (b) Rotenone
- (c) Phorate
- (d) Thimetor
Answer- (b) Rotenone
44. Which belongs to the category of auxins?
- (a) Indole-3-butyric acid
- (b) a-Napthyl acetic acid
- (c) Inapthyl acetamide
- (d) All of the above
Answer- (c) Inapthyl acetamide
45. The word ‘Gibbrellic acid’ denote
- (a) GA1
- (b) GA₂
- (c) GA3
- (d) GA7
Answer- (c) GA3
46. Which gas affects the ripening of fruits?
- (a) Ethylene
- (b) Phosphine
- (c) Acetylene
- (d) None of these
Answer- (a) Ethylene
47. The term ‘Garbling’ is defined as
- (a) removal of sand and dirt from the crude drug
- (b) removal of the stem in lobelia
- (c) removal of stalls in cloves
- (d) removal of entraneous matter, not constituting drug
Answer- (d) removal of entraneous matter, not constituting drug
48. ‘Peri-winkle’ is a common name for
- (a) Catharanthus roseus
- (b) Digitalis purpurea
- (c) Adhathoda vasaka
- (d) Hyoscyamus niger
Answer- (a) Catharanthus roseus
49. Isabgol is largely cultivated
- (a) Madhya Pradesh
- (b) Karnataka
- (c) Gujarat
- (d) Andhra Pradesh
Answer- (c) Gujarat
50. ‘Gudmar’ is a common name
- (a) Gymnema Sylvestre
- (b) Solanum nigrum
- (c) Solanum xanthocarpum
- (d) Embelica officinalis
Answer-(a) Gymnema Sylvestre
MCQs set of pharmacognosy
51. ‘Tejpatra’ is a common name
- (a) Cimmamomum zeylanicum
- (b) Cinnamomum Tamala
- (c) Eugenia caryophyllus
- (d) Eugenia zeylanicum
Answer- (d) Eugenia zeylanicum
52. Polyploidy may be induced by
- (a) Colchicine
- (b) Aconitine
- (c) Veratrine
- (d) Colchicine and veratrine
Answer-(a) Colchicine
53. ‘Chemodems’ are regarded as a group of plants
- (a) which differ in morphological character but possess the same chemical constituents
- (b) which differ in chemical nature but possess identical morphological character
- (c) which differ in both morpho-logical character and chemical nature
- (d) which differ only in the percentage of active constituents
Answer- (c) which differ in both morpho-logical character and chemical nature
54. ‘Tropane alkaloids’ are biosynthesized in the plant from
- (a) ornithine
- (b) lysine
- (c) tryptophan
- (d) phenylalanine
Answer-(a) ornithine
55. ‘T’ shaped trichomes are present in
- (a) Buchu leaves
- (b) Lobelia
- (c) Pyrethrum
- (d) Hamamelis
Answer- (c) Pyrethrum
56. Lignified trichomes are characteristic of
- (a) Nux vomica
- (b) Cannabis
- (c) Belladonna
- (d) Artemisia
Answer-(a) Nux vomica
57. Powdered ginger can be best analyzed with the help of
- (a) trichomes
- (b) chemical test
- (c) fiber
- (d) lycopodium spore method
Answer-(d) lycopodium spore method
58. The % moisture content in ‘Ergot’ should not be more than
- (a) 5%
- (b) 8%
- (c) 15%
- (d) 20%
Answer-(b) 8%
59. The Gentianose is a
- (a) Monosaccharide
- (b) Disaccharide
- (c) Trisaccharide
- (d) Polysaccharides
Answer-(b) Disaccharide
60. The drug ‘Pectin’ belongs to the category of
- (a) Polyuronide
- (b) Disaccharide
- (c) Alkaloid
- (d) Monosaccharide
Answer- (a) Polyuronide
61. ‘Arabin’ is a principal constituent of
- (a) Gum acacia
- (b) Tragacanth
- (c) Guar gum
- (d) Gum karaya
Answer-(a) Polyuronide
62. Gum ghatti is an adulterant for
- (a) Acacia
- (b) Starch
- (c) Exudates coming from stem
- (d) Bark
Answer- (a) Polyuronide
63. Guar gum is located in
- (a) Cotyledons
- (b) Endosperm
- (c) Tragacanth
- (d) Guggal
Answer- (b) Endosperm
64. Artificial invert sugar in honey can be detected on the basis of the presence of
- (a) Cotouring matter
- (b) Traces of succinic acid
- (c) Furfural
- (d) Enzymes
Answer- (c) Furfural
65. Tragacanth contain
- (a) 20% arabin
- (b) 60-70% bassorin
- (c) 20% bassorinin
- (d) Guaran
Answer- (b) 60-70% bassorin
66. Macrocystis pyrifera is a common source for
- (a) Tragacanth
- (b) Sodium polymannuronate
- (c) Honey
- (d) None of them
Answer- (b) Sodium polymannuronate
67. Which one of these forms copious precipitates with calcium chloride?
- (a) Sodium alginate
- (b) Pectin
- (c) Gum acacia
- (d) Guar gum
Answer- (a) Sodium alginate
68. Gum Ghatti is a gummy exudate obtained from
- (a) Sterculia urens
- (b) Citrus limon
- (c) Anogeissus latifolia
- (d) Astragalus gummifer
Answer- (c) Anogeissus latifolia
69. Chitosan is a
- (a) acetylated product of chitin
- (b) deacetylated product of chitin
- (c) sulphonated product of chitin
- (d) any of the above
Answer- (b) deacetylated product of chitin
70. Polyploid is defined as
- (a) addition of one chromosome
- (b) multiplication of entire chromosome
- (c) submicroscopic changes in DNA material
- (d) gross structural changes
Answer- (b) multiplication of entire chromosome
71. Colchicine is biogenetically derived from one of the following
- (a) Tyrosine and phenylalanine
- (b) Tryptophan and phenylalanine and phenylalanine
- (c) Ormithine and tryptophan
- (d) Ornithine
Answer- (a) Tyrosine and phenylalanine
72. Which statement is true about Bael fruits
- (a) Bael contains marmelosin
- (b) Bael is a mucilaginous fruit
- (c) Its pulp contains Vitamin C and Vitamin A
- (d) All of them
Answer-(d) All of them
73. Agar contains
- (a) Agarose.
- (b) Agaropection
- (c) Agarose and agaropectin
- (d) Galidin
Answer- (c) Agarose and agaropectin
74. Dextrin is produced from
- (a) hydrolysis of starch
- (b) acid treatment of honey
- (c) oxidation of starch
- (d) reduction of starch
Answer- (a) hydrolysis of starch
75. Which statement is true?
- (a) Amylose is water soluble
- (b) Amylose gives blue colour with iodine solution
- (c) Amylose is a polysaccharide
- (d) All of the above
Answer-(d) All of the above
76. Cascarosides are an example of
- (a) O-glycoside
- (b) C-glycoside
- (c) N-glycoside
- (d) S-glycoside
Answer- (b) C-glycoside
77. Hesperidin is a
- (a) Alkaloid
- (b) Flavonoid
- (c) Steroidal saponin
- (d) Coumarin
Answer- (b) Flavonoid
78. Bontrager test is performed to detect the presence of
- (a) Anthraquinone glycoside
- (b) Cardiac glycoside
- (c) Coumarin
- (d) Reduced form of Anthranols
Answer- (a) Anthraquinone glycoside
79. Senna is mainly cultivated in
- (a) Tamil Nadu
- (b) Kerala
- (c) Karnataka
- (d) Andhra Pradesh
Answer- (a) Tamil Nadu
80. Which statement about senna leave is not true?
- (a) Leaves are lanceolate
- (b) Leave contain paracytic stomata
- (c) Contain unicellular, conical thick walled trichomes
- (d) Senna leaves do not contain calcium oxalate crystal
Answer-(b) Leave contain paracytic stomata
81. The aglycone of Sennoside is designated as
- (a) 10, 10′-bis (9, 10 dihydro-1, 8-dihydroxy 9-oxoanthracene)-3-carboxylic acid
- (b) 10, 10′-bis (9, 10 dihydro-1, 8-dihydroxy 9-oxoanthracene)-2- carboxylic acid
- (c) 10, 10′-bis (8, 9 dihydro-1, 10-dihydroxy 9-oxoanthracene)-3-carboxylic acid
- (d) None of them
Answer- (a) 10, 10′-bis (9, 10 dihydro-1, 8-dihydroxy 9-oxoanthracene)-3-carboxylic acid
82. ‘Kumari’ is the common name for
- (a) Aloe
- (b) Senna pod
- (c) Rhubarb
- (d) None of them.
Answer- (a) Aloe
83. Indian rhubarb is
- (a) Rheum rhaponticum
- (b) Rheum webbianum
- (c) Rheum emodi
- (d) Rheum palmatum
Answer- (b) Rheum webbianum
84. Digitalis leaves should not contain
- (a) more than 1% moisture
- (b) more than 5% moisture
- (c) more than 10% moisture
- (d) more than 15% moisture
Answer-(b) more than 5% moisture
85. Purpurea glycoside A on hydrolysis gives
- (a) Digitoxigenin + glucose + 3 digitoxose
- (b) Gitoxigenin + glucose + 3 digitoxose
- (c) Digitoxin + glucose + 3 digitoxose
- (d) Digitoxin + 3 digitoxose
Answer- (a) Digitoxigenin + glucose + 3 digitoxose
86. Keller killiani test is performed to detect the presence of
- (a) digitoxin in digitalis leaves
- (b) digitoxose in digitalis leaves
- (c) digitoxigenin in digitalis leaves
- (d) glucose in digitalis leaves
Answer-(b) digitoxose in digitalis leaves
87. Thevetia nerrifolia contain
- (a) Anthraquinone nucleus
- (b) Flavonol nucleus
- (c) Steroid nucleus
- (d) Triterperiod nucleus
Answer- (c) Steroid nucleus
88. Lactone ring in cardiac glycoside in squill is
- (a) five-membered with one double bond
- (b) six-membered with one double bond
- (c) six-membered with two double bond
- (d) six-membered with no double bond
Answer- (d) six-membered with no double bond
89. Solasodine is a
- (a) Steroidal glycoalkaloid
- (b) Steroidal glycoside
- (c) Steroidal alkaloid
- (d) None of them
Answer- (a) Steroidal glycoalkaloid
90. Which of one these drugs contain lignified fibers?
- (a) Squill
- (b) Liquorice
- (c) Rhubarb
- (d) Shatmuli
Answer-(b) Liquorice
91. Glycyrrhizinic acid belongs to the category of
- (a) a-amyrin
- (b) B-amyrin
- (c) lupeol
- (d) None of them
Answer-(b) B-amyrin
92. Licorice contains
- (a) Triterpenoid glycoside
- (b) Flavonoid glycoside
- (c) Triterpenoid and flavonoid glycoside
- (d) Coumarin glycoside
Answer- (c) Triterpenoid and flavonoid glycoside
93. Shatavari is
- (a) dried roots of Asparagus recemosus belong to the family Liliaceae
- (b) dried leaves of Asparagus racemosus belong to the family Liliaceae
- (c) dried root, of Asparagus reacemosus belongs to family Apocyanace
- (d) dried root and leaves of Asparagus reacemosus belong to family Apocyanace
Answer- (d) dried root and leaves of Asparagus reacemosus belong to family Apocyanace
94. Sarsapogenin is an aglycone of
- (a) Shatavari
- (b) Brahmi
- (c) Centella Asiatica
- (d) Solanum khasianum
Answer- (a) Shatavari
95. Panax belongs to a family
- (a) Liliaceae
- (b) Apocynaceae
- (c) Araliaceae
- (d) Rubiaceae
Answer- (c) Araliaceae
96. Ginsenosides are
- (a) Saponin glycoside
- (b) Anthraquinone glycoside
- (c) Phenolic glycoside
- (d) Cardiac glycoside
Answer- (a) Saponin glycoside
97. Senega belongs to a family
- (a) Apocynaceae
- (b) Polygonaceae
- (c) Liliaceae
- (d) Rubiaceae
Answer- (b) Polygonaceae
98. Rhytidoma is present in
- (a) Cinchona bark
- (b) Quillaia bark
- (c) Cinnamomum bark
- (d) Kurchi bark
Answer- (b) Quillaia bark
99. Cyanogenetic glycoside is present in
- (a) Prunus communis
- (b) Prunus Amygdalus
- (c) Brassica nigra
- (d) None of them
Answer- (b) Prunus Amygdalus
MCQs set of pharmacognosy
100. Prunasin is a constituent of
- (a) Prunasin communis
- (b) Prunasin amygdalin
- (c) Prunus serotina
- (d) Prunus glabra
Answer-(c) Prunus serotina
101. Singrin is a
- (a) Cyanogenetic glycoside
- (b) Isocyanate glycoside
- (c) Flavonol glycoside
- (d) Phenolic glycoside
Answer- (c) Flavonol glycoside
102. Brassica nigra belongs to a family
- (a) Malvaceae
- (b) Rosaceae
- (c) Solanaceae
- (d) Cruciferae
Answer- (d) Cruciferae
103. “Our Lady’s Thistle’ is a synonym for
- (a) Cantharus roseus
- (b) Silybum marianum
- (c) Digitalis purpurea
- (d) Vinca rosea
Answer-(a) Cantharus roseus
104. Khelloside is a constituent of
- (a) Visnaga
- (b) Rutin
- (c) Ginkgo
- (d) Ammi
Answer- (a) Visnaga
105. Bavchi is a synonym for
- (a) Psoralea used in leucoderma
- (b) Visnaga used in cancer therapy
- (c) Psoralea used as a blood purifier
- (d) Black mustard, used as a blood purifier
Answer- (a) Psoralea used in leucoderma
106. Which one of these contains longitudinal annulation?
- (a) Rhubarb
- (b) Liquorice
- (c) Picrorrhiza
- (d) Gentian
Answer- (c) Picrorrhiza
107. Ophelic acid is present in
- (a) Gentian
- (b) Chirata
- (c) Quassia
- (d) Picrorrhiza
Answer- (b) Chirata
108. Quassia is a
- (a) root and rhizome of Picrasma excelsa belonging to the family Simaroubaceae
- (b) dried stem wood of Picrasma excelsa belonging to the family Simaroubaceae
- (c) dried stem wood of Picrasma excelsa belonging to the family Rubiaceae
- (d) the dried rhizome of Picrasma excelsa belonging to the family Simaroubaceae
Answer-(d) the dried rhizome of Picrasma excelsa belonging to the family Simaroubaceae
109. Andrographide is a
- (a) Triterpenoid
- (b) Diterperoid glycoside
- (c) Diterpenoid lactone
- (d) Bicyclic diterpenoid lactone
Answer-(a) Triterpenoid
110. The constituent lawsone is present in
- (a) Gymnema
- (b) Henna
- (c) Vasaka
- (d) Hing
Answer-(b) Henna
111. Goldbeater’s skin test is specific for
- (a) Tannin
- (b) Saponins
- (c) Triterpenoid
- (d) Steroids
Answer- (a) Tannin
112. Myrobalan is
- (a) fruits of Terminalia chebula, family combretaceae
- (b) fruits of Terminalia arjuna, family combretaceae.
- (c) fruits of Terminalia chebula, family Compositae
- (d) fruits of Terminalia catappa, family Combretaceae
Answer- (a) fruits of Terminalia chebula, family combretaceae
113. The ayurvedic preparation ‘Triphala’ contain
- (a) Myrobalan
- (b) Arjuna
- (c) Senna
- (d) Catechu
Answer-(a) Myrobalan
114. Black catechu contain
- (a) 5,7,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy flavan-3-ol
- (b) 3,5,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy flavan-3-ol
- (c) 3,8,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy flavan-3-ol
- (d) 3,7,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy flavan-3-ol
Answer- (a) 5,7,3′,4′-tetrahydroxy flavan-3-ol
115. Pale catechu is obtained from
- (a) Acacia catechu, family leguminosae
- (b) Uncaria gambier, family rubiaceae
- (c) Uncaria gambier, family leguminosae
- (d) Acacia catechu, family rubiaceae
Answer-(b) Uncaria gambier, family rubiaceae
116. The constituent gambier fluorescin is present in
- (a) Black Catechu
- (b) Katha
- (c) Pale Catechu
- (d) None of them
- Answer- (c) Pale Catechu
117. The popular ingredient of Chyavanprash is
- (a) Amla
- (b) Chebula
- (c) Tinospora
- (d) All of them
Answer- (a) Amla
118. Which one of these fatty acids possesses more iodine value?
- (a) Stearic acid
- (b) Oleic acid
- (c) Linoleic acid
- (d) Ligoseric acid
Answer- (c) Linoleic acid
119. Which oil in the hydrochloric acid solution reacts with ferric chloride giving a reddish brown crystal?
- (a) Sesame oil
- (b) Argemone oil
- (c) Linseed oil
- (d) Colton seed oil
Answer- (b) Argemone oil
120. The laxative action of castor oil is due to the presence of
- (a) Ricinoleic acid
- (b) Undecenoic acid
- (c) Isoricinoleic acid
- (d) Isoricinoleic acid
Answer- (a) Ricinoleic acid
121. Which one of these oils is antileprotic in nature?
(a) Olive oil
(b) Hydnocarpus oil
(c) Linseed oil.
(d) Olive oil
Answer- (b) Hydnocarpus oil
122. Cyanogenetic glycoside is present in
(a) Chaulmoogra oil
(b) castor oil
(c) linseed oil
(d) olive oil
Answer- (c) linseed oil
123. Sesame oil belongs to the family
(a) Leguminosae
(b) Graminae
(c) Pedialiaceae
(d) Euphorbiaceae
Answer- (c) Pedialiaceae
124. Kokum butter is obtained from
(a) Carthamus tinctorius
(b) Garcinia indica
(c) Sesamum indicum
(d) Pongamia glabra
Answer- (b) Garcinia indica
125. Melicyl cerolate is present in
(a) Beeswax
(b) Carnauba wax
(c) Kokum butter
(d) Cocoa butter
Answer- (b) Carnauba wax
126. Shark liver develops brownish color on adding chloroform and sulphuric acid. It is due to
(a) Fatty acid present in the oil
(b) Vitamin A
(c) Unsaturated fatty acid
(d) None of them
Answer- (b) Vitamin A
127. Myricyl palmitate is constituent of
(a) Carnuba wax
(b) Yellow bees wax
(c) Lard
(d) Spermaceti
Answer- (b) Yellow bees wax
128. Cetyl palmitate is a constituent of
(a) Carnuba wax
(b) Wool fat
(c) Spermaceti
(d) Bees wax
Answer- (c) Spermaceti
129. Cineole is a constituent of
(a) Caraway oil
(b) Peppermint oil
(c) Citronella oil
(d) Eucalyptus oil
Answer- (d) Eucalyptus oil
130. Ascaridole is present in
(a) Camphor oil
(b) Eucalyptus oil
(c) Geranium oil
(d) Chenopodium oil
Answer- (d) Chenopodium oil
131. Turpentine oil contain
(a) citral
(b) a-pinene
(c) carvone
(d) geraniol
Answer- (b) a-pinene
132. The main constituent of the volatile oil of Cuminum cyminum is
(a) Carvone
(b) Cuminic aldehyde
(c) Phellandrene
(d) None of them
Answer- (b) Cuminic aldehyde
133. The Elettaria cardamomum belongs to the family
(a) Umbelliferae
(b) Zingiberaceae
(c) Lauraceae
(d) Rubiaceae
Answer- (b) Zingiberaceae
134. The ‘Cremocarp’ type of fruit is characteristic of
(a) Umbelliferae
(b) Zingiberaceae
(c) Lauraceae
(d) Rubiaceae
Answer- (a) Umbelliferae
135. D-linalool is a major constituent of the volatile oil obtained from
(a) Fennel
(b) Cardamomum
(c) Clove
(d) Coriander
Answer-(b) Cardamomum
136. The expanded flower of the clove is known as
(a) Mother clove
(b) Blown clove
(c) Clove stalk
(d) None of them.
Answer- (b) Blown clove
137. Clove is
(a) dried flower buds of Eugenia Caryophyllus belonging to the family Meliaceae
(b) dried flower buds of Eugenia Caryophyllus belonging to the family Myrtaceae
(c) dried flower buds of Eugenia Caryophyllus belonging to the family Myrtaceae
(d) None of them
Answer- (b) dried flower buds of Eugenia Caryophyllus belonging to the family Myrtaceae
138. Jatamansi consist of
(a) dried rhizomes of lavender glabra belonging to family velerianaceae
(b) dried rhizomes of Nardostachis jatamansi belonging to family velerianaceae
(c) dried rhizomes of Centella Asiatica belonging to the family Apocynaceae
(d) dried rhizomes of Brahmi belonging to the family Lauraceae
Answer- (b) dried rhizomes of Nardostachis jatamansi belonging to family velerianaceae
139. Which one of these pairs of drugs exerts action on CNS?
(a) Jatamansi and Brahmi
(b) Jatamansi and Coriander
(c) Brahmi and Chinese Cinnamomum
(d) Nutmeg and Dill
Answer- (a) Jatamansi and Brahmi
140. Allicin is a constituent of
(a) Jangli Pyaz
(b) Onion
(c) Garlic
(d) Tulsi
Answer- (c) Garlic
141. Benafsha is obtained from
(a) Ocimum sanctum, family labiatae
(b) Viola odorata, family Violaceae
(c) Alpinia officinarum family Zingiberaceae
(d) Saussurea lappa, family compositae
Answer-(b) Viola odorata, family Violaceae
142. The alkaloid ‘odoratine’ is a constituent of
(a) Tulsi
(b) Rasna
(c) Banafsha
(d) Saffron
Answer-(c) Banafsha
143. A carotenoid glycoside is a constituent of
(a) Lavender
(b) Jatamansi
(c) Saffron
(d) Banafsha
Answer-(c) Saffron
144. Valproate is a constituent of
(a) Jatamansi
(b) Valerian
(c) Taxus
(d) Acorus
Answer-(b) Valerian
145. Artemisinin is
(a) diterpenoid glycoside possessing antimalarial activity
(b) sesquiterpene lactone possessing antimalarial activity
(c) sesquiterpene possessing anticancer activity
(d) alkaloid possessing antimalarial activity
Answer-(b) sesquiterpene lactone possessing antimalarial activity
146. Lavender oil is obtained from
(a) Lavandula officinalis, family labiatae
(b) Lavandula officinalis, family umbelliferae
(c) Lavandula cyminum, family labiatae
(d) None of them
Answer-(a) Lavandula officinalis, family labiatae
147. Which one of these oils is used in rheumatism?
(a) Lavender oil
(b) Gaultheria oil
(c) Anise oil
(d) Rosemary oil
Answer-(b) Gaultheria oil
148. Which one of these does not contain proteolytic activity?
(a) Diastase
(b) Chymotrypsin
(c) Papain
(d) Renin
Answer-(a) Diastase
149. The alkaloid ‘Vasicine’ contain
(a) Pyrrolidine nucleus
(b) Quinazoline nucleus
(c) Piperidine nucleus
(d) Purine nucleus
Answer-(b) Quinazoline nucleus
150. Ergot is
(a) dried sclerotium of fungus, Claviceps purpurea
(b) dried seed of Claviceps purpurea
(c) dried fruits of fungus of Claviceps purpurea
(d) None of them
Answer-(c) dried fruits of fungus of Claviceps purpurea
MCQs set of pharmacognosy
151. p-dimethylamino benzaldehyde gives blue color with
(a) Tropane alkaloid
(b) Opium alkaloid
(c) Ergot alkaloid
(d) Tobacco alkaloid
Answer-(c) Ergot alkaloid
152. Sarpagandha is common more for
(a) Nardactylchs
(b) Withania somnifera
(c) Viola odorata
(d) Rauwolfia
Answer-(d) Rauwolfia
153. The solution of crude opium develops red coloration with ferric chloride solution which is due to the presence of
(a) morphine
(b) codeine
(c) meconic acid
(d) papaverine
Answer-(c) meconic acid
154. The acidic solution of ipecacuanha gives yellow color with potassium chlorate due to the presence of
(a) cephaeline
(b) emetamine
(c) emetine
(d) ipecuanic acid
Answer- (c) emetine
155. Ipecacuanha is
(a) expectorant drug
(b) emetic drug
(c) expectorant and emetic drug
(d) antispasmodic and emetic drug
Answer-(c) expectorant and emetic drug
156. The alkaloid atropine is
(a) ievo form
(b) deutro form
(c) recemic form
(d) any of them
Answer-(c) recemic form
157. Phytolacca americana is adulterant for
(a) Vasaka leaves
(b) Hyoscyamus niger
(c) Atropa belladonna
(d) Lobelia
Answer-(c) Atropa belladonna
158. Thorn apple leaf is a synonym for
(a) Stramonium leaves
(b) Atropa belladonna
(c) Vinca rosea
(d) Datura
Answer-(a) Stramonium leaves
159. A Cuprea bark is
(a) Adulterant for cinchona bark
(b) Substitute for cinchona bark
(d) Not related to cinchona bark
(c) Allied drug of cinchona bark
Answer-(b) Substitute for cinchona bark
160. Lobeline is a alkaloid
(a) containing piperidine nucleus, used in asthma
(b) containing pyrrolidine nucleus, used in asthma
(c) containing piperidine nucleus, used as mydriatic
(d) containing piperidine nucleus, used as a cholinergic drug
Answer-(a) containing piperidine nucleus, used in asthma
161. Jaborandi is a common name for
(a) Pilocarpus, family rutaceae
(b) Pilocarpus, family leguminosae
(c) Neostigmus, family legminusae
(d) None of them
Answer-(a) Pilocarpus, family rutaceae
162. Which one of these drugs may be used in hypertension?
(a) Kurchi
(b) Veratrum
(c) Valerian
(d) Ephedra
Answer-(b) Veratrum
163. Multiseriate medullary rays and steroidal alkaloids are present in
(a) Veratrum
(b) Kurchi
(c) Ashwagandha
(d) None of them
Answer-(b) Kurchi
164. Ashwagandha belongs to the family
(a) Apocynaceae
(b) Liliaceae
(c) Solanaceae
(d) Compositae
Answer-(c) Solanaceae
165. Ashwagandha possess
(a) sedative activity
(b) immunomodulatory activity
(c) sex stimulant activity
(d) all the above activity
Answer-(d) all the above activity
166. Diterpene alkaloids are present in
(a) Ashwagandha
(b) Aconite
(c) Kurchi
(d) Vasaka
Answer-(b) Aconite
167. Adhatoda vasaka leaves belong to the family
(a) Ranunculaceae
(b) Acanthaceae
(c) Solanaceae
(d) Rutaceae
Answer-(b) Acanthaceae
168. Which one of these is not acidic resins?
(a) Colophony
(b) Myrrh
(c) Shellac
(d) Storax
Answer-(d) Storax
169. The pungency of capsicum is destroyed by
(a) boiling with dilute sodium hydroxide solution
(b) treatment with potassium permangnate solution
(c) treatment with sodium thiosulphate solution
(d) any of the above method
Answer-(b) treatment with potassium permangnate solution
170. Indian saffron is obtained from
(a) Crocus sativus, family Acanthaceae
(b) Curcuma longa, family Zingiberaceae
(c) Curcuma aromatica, family Zingiberacae
(d) None of them
Answer-(b) Curcuma longa, family Zingiberaceae
171. Devil’s drug is a synonym for
(a) Asafoetida
(b) Colophony
(c) Myrrh
(d) Cannabis
Answer-(a) Asafoetida
178. Free umbelliferone is present in oleo gum resin of
(a) Ferula asafoetida
(b) Ferula galbaniflua
(c) Styrax benzoin
(d) Commiphora molmol
Answer-(b) Ferula galbaniflua
179. Convolvulin is a constituent of
(a) Jalap
(b) Male fern
(c) Capsicum
(d) Colocynth
Answer-(a) Jalap
180. Etoposide is related with
(a) Kaladana
(b) Colocynth
(c) Podophyllum resin
(d) Jalap
Answer- (c) Podophyllum resin
181. Myrrh is an oleogum resin, obtained from
(a) Commiphora molmol, family Burseraceae
(b) Commiphora molmol, family Lauraceae
(c) Myrxnylon balsamum, family leguminosae
(d) Liquidamber Orientalis family lammelidaceae
Answer- (a) Commiphora molmol, family Burseraceae
182. Guggul is
(a) the acidic resin obtained from Commiphora weightii, family Burseraceae
(b) Oleo gum resin obtained from Commiphora weightii, family Burseraceae
(c) Oleo gum resin obtained from Commiphora molmol, family Burseraceae
(d) None of them
Answer- (b) Oleo gum resin obtained from Commiphora weightii, family Burseraceae
183. Which of these resins has hypocholesteremic action?
(a) Asafoetida
(b) Turmeric
(c) Guggul
(d) Sallaki guggul
Answer-(c) Guggul
184. Shilajit is a
(a) Mineral drug
(b) Herbal drug
(c) Semisynthetic drug
(d) Herbo-mineral drug
Answer-(d) Herbo-mineral drug
185. Azadirachin is
(a) Tri terperoid
(b) Tetra terperoid
(c) Sesquiterpend
(d) Diterpene alkaloid
Answer-(b) Tetra terperoid
186. Pyrethrum, insecticide is obtained from
(a) Chrysantheum cineriaefolium, family compositae
(b) Cantharus roseus, family Apocynaceae
(c) Chrysanthemum occineum, family compositae
(d) None of them
Answer-(a) Chrysantheum cineriaefolium, family compositae
188. Picrotoxin is a
(a) Analeptic, obtained from berries of Anamirta Cocculus
(b) Analeptic, obtained from seeds of Strychnos sps
(c) Analeptic, obtained from seeds of Anamirta Cocculus
(d) Sedative, obtained from fruits of Anamirta Cocculus
Answer-(a) Analeptic, obtained from berries of Anamirta Cocculus
189. Papaverine is a
(a) Cholinergic drug
(b) Peripheral vasodilator
(c) Cardiac depressant
(d) Anticholinergic drug
Answer-(b) Peripheral vasodilator
190. Which one of these drugs acts on the male reproductive organ?
(a) Papaverine
(b) Yohimbine
(c) Reserpine
(d) Ajmalicine
Answer-(b) Yohimbine
191. Which one of these is a precursor for auxin, indole acetic acid?
(a) Phenylalanine
(b) Tyrosine
(c) Tryptophan
(d) None of them
Answer-(c) Tryptophan
192. From which one of these, polyploidy can be induced
(a) Brucine
(b) Strychnine
(c) Carabine
(d) Colchicine
Answer-
193. Keller-Killiani test is specific for
(a) Reducing sugar
(b) Non-reducing sugar
(c) Desoxy sugar
(d) Steroidal aglycone
Answer-
194. Pyraxylin is a
(a) cellulose acetate
(b) oxidized cellulose
(c) cellulose nitrate
(d) methylcellulose
Answer-(d) methylcellulose
195. Inulin is obtained from
(a) tubers of Dahlia variabilis
(b) tubers of Ricinus communis
(c) tubers Olea Europa
(d) tubers of Commiphora molmol
Answer-(c) tubers Olea Europa
196. Carrageenans are
(a) fructosan
(b) Galatians
(c) glucose
(d) xylan
Answer-(a) fructosan
198. Which one of these is rich in phloroglucinol derivatives?
(a) Acacia
(b) Asafoetida
(c) Copaiba
(d) Male fern
Answer-(b) Asafoetida
199. Capsaicin is a
(a) Vanillyl amide of dodecanoic acid
(b) Vanillyl ester of dodecanoic acid
(c) Ethylamide of isodecenoic acid
(d) Methyl amide isodecenoic acid
Answer-(d) Methyl amide isodecenoic acid
200. Umbelliferone is a derivative of
(a) xanthone
(b) coumarin
(c) a-pyrone
(d) hydroquinone
Answer-(b) coumarin
201. The average stomatal index number for Tinnevally senna leaves in
(a) 10.5
(b) 8.5
(c) 17.5
(d) 21.5
Answer-(c) 17.5
202. Vein-islet number of Alexandrian senna leaves is
(a) 10.0-15.0
(b) 25-29.5
(c) 17-19
(d) 15-17
Answer-(b) 25-29.5
203. The cochineal contain
(a) Umbellic acid
(b) Angelic acid
(c) Ellagotanins
(d) Carminic acid
Answer-(c) Ellagotanins
204. The flavolignan ‘Silybin’ is a
(a) Anticancer drug
(b) Hepatoprotective drug
(c) Immunomodulatory drug
(d) Approdisie drug
Answer-(b) Hepatoprotective drug
205. Carminic acid is a
(a) Coumarin derivative
(b) C-glycoside
(c) O-glycoside
(d) Xanthone
Answer-(b) C-glycoside
206. Linalol is an important constituent of
(a) Lavender
(b) Peppermint oil
(c) Thyme oil
(d) Dill oil
Answer-(a) Lavender
207. Which one of these oils are obtained from the heartwood of the plant?
(a) Sandal oil
(b) Cardamom oil
(c) Cinnamon oil
(d) Anise oil
Answer-(a) Sandal oil
208. Which one of these is known as soap bark?
(a) Kurchi bark
(b) Cacara bark
(c) Quillaia bark
(d) Wildcherry bark
Answer-(c) Quillaia bark
209. Quassia wood contain
(a) Quassin, (terpenoid)
(b) Quassin, (allaloid)
(c) Quassin, (phenolic glycoside)
(d) Quassin, (coumarins)
Answer-(a) Quassin, (terpenoid)
210. Rubber is
(a) Complex sesquiterpenes
(b) Complex diterpenes
(c) Polyterpenes
(d) Sesquiterpene lactone polymer
Answer-(c) Polyterpenes
211. Alkana tinctures are used to locate
(a) oil containing cell
(b) calcium oxalate containing cell
(c) starch containing cell
(d) collenchymatous cell
Answer-(a) oil containing cell
212. The average stomatal index number of digitalis purpurea is
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 16
(d) 19
Answer-(b) 12
213. A rhamno glucoside on complete hydrolysis gives
(a) Aglycone + Fructose + Rhamnose
(b) Aglycone + Ribose + Rhamnose
(c) Aglycone + Rhamnose + ghicose
(d) Rhamnose + Fructose
Answer-(c) Aglycone + Rhamnose + ghicose
214. Wagner’s test is used to detect the presence of
(a) Steroid
(b) Alkaloid
(c) Glycoside
(d) Terplane
Answer-(b) Alkaloid
215. Stratified, i.e., forked corks are characteristic diagnostic features of
(a) Apocynaceae]
(b) Scrophulariaceae
(c) Gentianaceae
(d) Polygonaceae
Answer-(d) Polygonaceae
216. Claviceps purpurea yield’s after infecting ovaries of Gramimaceous plant
(a) Digitoxin
(b) Lysergic acid derivatives
(c) Reserpine
(d) Polypeptides
Answer-(b) Lysergic acid derivatives
217. Idioblasts of crystal of calcium
(a) Hyosyamus niger
(b) Deadly nightshade leaves
(c) Cinchona bark
(d) Senna leaves.
Answer-(b) Deadly nightshade leaves
218. Anamocytic type of stomata are found in leaves of
(a) Foxglove
(b) Urginea maritima
(c) Cassia acutifolia
(d) Atropa belladona
Answer-(a) Foxglove
219. Peroxidase enzyme present in acacia is identified by
(a) Brontrager test
(b) Molisch’s test
(c) Oxidation and extraction in benzidine
(d) Oxidation and treatment with benzidine
Answer-(d) Oxidation and treatment with benzidine
220. Reserpine on hydrolysis gives
(a) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy cinnamic acid
(b) Reserpic acid + Acetic acid + trimethoxy benzaldehyde
(c) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy benzoic acid
(d) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy cinnamaldehyde
Answer-(c) Reserpic acid + methyl alcohol + trimethoxy benzoic acid
MCQs set of pharmacognosy
Report any error on our collection of MCQs. Contact Us

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com

Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.