Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Widely used non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic for mild–moderate pain and fever; centrally acting with minimal peripheral anti-inflammatory effects.
Brand Names
Examples: Tylenol, Panadol, Calpol (brands vary by country).
Name
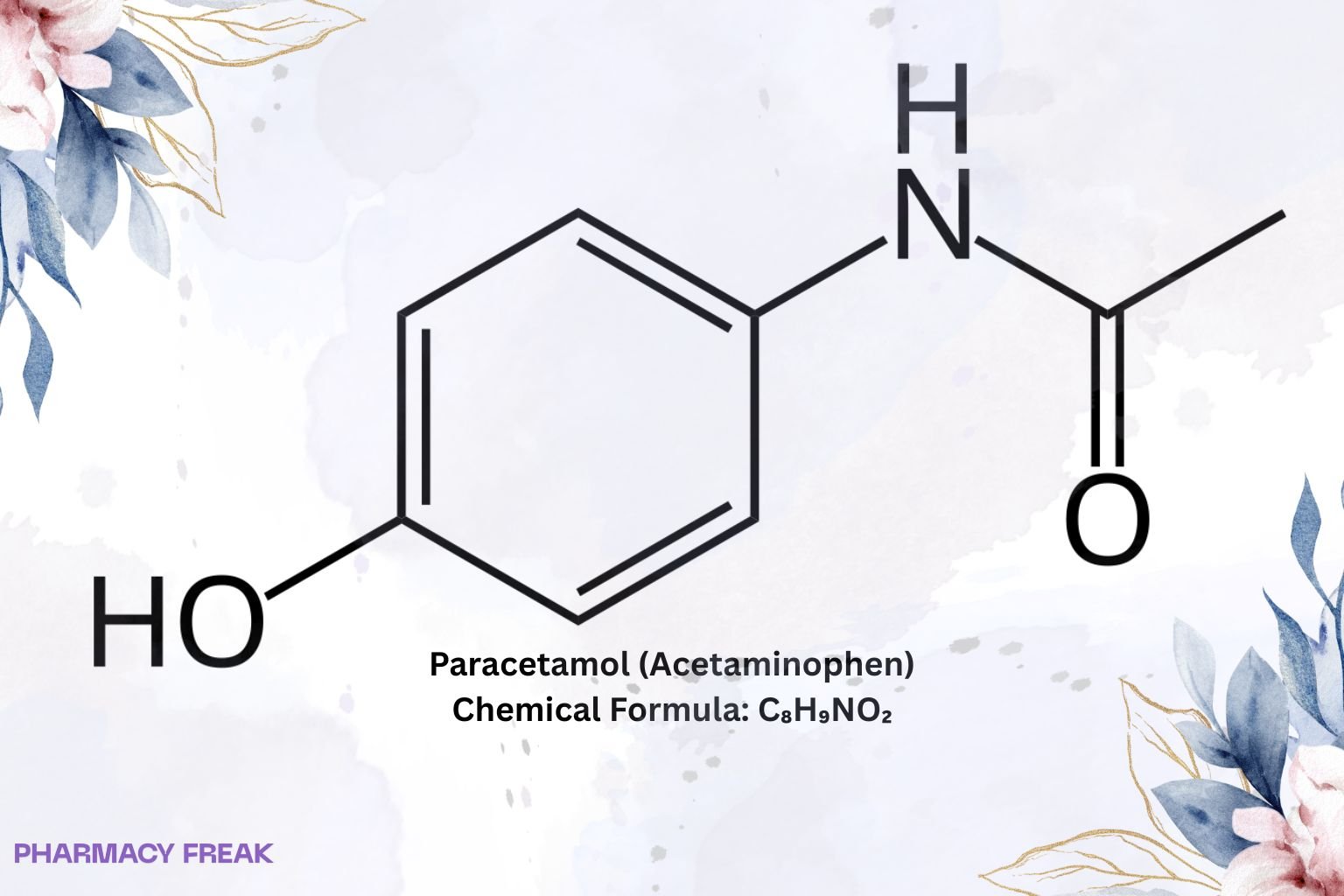
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
Background
Discovered in the late 19th–early 20th century and adopted globally as a first-line antipyretic/analgesic. Included in many mono- and combination products across OTC and prescription channels (jurisdiction-dependent).
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; OTC (region-dependent)
Structure

Weight
~151.16 g/mol (relative molecular mass)
Chemical Formula
C₈H₉NO₂
Synonyms
Acetaminophen; N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide; N-acetyl-p-aminophenol (APAP)
External IDs
CAS: 103-90-2; PubChem CID: 1983; UNII: 362O9ITL9D; DrugBank: DB00316; KEGG: D00217 / C06804; ChEMBL: CHEMBL112; ChEBI: 46195; RxCUI: 161
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Relief of mild–moderate pain (e.g., headache, dental, musculoskeletal, dysmenorrhoea) and reduction of fever; widely used in primary care and hospital settings.
Associated Conditions
Fever, tension-type headache, osteoarthritis-related pain flares, peri-procedural analgesia as part of multimodal regimens.
Associated Therapies
Commonly co-administered within multimodal analgesia (e.g., with NSAIDs or opioids where indicated), and in fixed-dose combinations for cold/flu symptoms (region-dependent labeling).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Hypersensitivity to paracetamol/acetaminophen; serious risk of dose-dependent hepatotoxicity with overdose or when total daily intake from multiple products exceeds recommended limits. Alcohol use disorder and chronic alcohol intake elevate risk.
Pharmacodynamics
Analgesic and antipyretic actions mainly via central prostaglandin pathway modulation; negligible peripheral anti-inflammatory effect at therapeutic doses.
Mechanism of Action
Central cyclooxygenase/prostaglandin synthesis modulation with additional proposed central mechanisms (e.g., serotonergic/endocannabinoid involvement). A minor oxidative pathway forms NAPQI, detoxified by hepatic glutathione under normal dosing.
Absorption
Rapid oral absorption; food may delay time to peak without meaningfully altering overall exposure for standard immediate-release products.
Volume of Distribution
Approximately ~0.9 L/kg (range reported across studies).
Protein Binding
~10–25% at therapeutic concentrations (higher in overdose).
Metabolism
Predominantly hepatic phase II conjugation (glucuronidation and sulfation); a small fraction via CYP-mediated oxidation (notably CYP2E1) to NAPQI.
Route of Elimination
Renal excretion, chiefly as glucuronide and sulfate conjugates; <~5% unchanged.
Half-life
~1.5–2.5 hours at therapeutic doses; prolonged (e.g., 4–8 h) in overdose or hepatic injury.
Clearance
Typical adult systemic clearance reported around ~0.27 L/h/kg following IV dosing; age-dependent in pediatrics.
Adverse Effects
Usually well tolerated at labeled doses; possible nausea, rash. Rare but serious reactions include severe cutaneous adverse reactions and acute liver failure with overdose or risk factors.
Toxicity
Overdose causes glutathione depletion and NAPQI accumulation → hepatocellular injury. Management follows time-based nomograms and N-acetylcysteine protocols.
Pathways
Conjugation pathways (UGT, SULT) dominate; minor oxidative bioactivation with downstream glutathione conjugation.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Variability in UGT/SULT activity and CYP2E1 induction (e.g., with alcohol) can influence metabolite patterns and risk profiles.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
- Warfarin (chronic/high-dose acetaminophen): potential enhancement of anticoagulant effect; monitor INR if regular use is necessary.
- Enzyme inducers/inhibitors & chronic alcohol: may shift metabolic balance toward/toxic pathways.
- Anticholinergics: may delay gastric emptying and slow absorption (usually limited clinical impact).
Food Interactions
Food can delay absorption (longer tₘₐₓ) without materially reducing total exposure for standard immediate-release products. Alcohol concomitance increases hepatotoxicity risk.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
N02BE01 (paracetamol; anilide analgesics)
Drug Categories
Analgesics (non-opioid); Antipyretics; Anilides; Phenolic derivatives; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Aromatic amide; Phenol; Anilide; Neutral, lipophilicity-balanced small molecule
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
362O9ITL9D
CAS number
103-90-2
InChI Key
RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,11H,1H3,(H,9,10)
IUPAC Name
N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide
SMILES
CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(O)C=C1
6. References
- PubChem Compound Summary: Acetaminophen (CID 1983) — structure, identifiers, physicochemical overview. PubChem+1
- StatPearls: Acetaminophen — clinical pharmacology, protein binding ~10–25%, distribution characteristics, toxicity summaries. Updated 2024. NCBI
- StatPearls: Acetaminophen Toxicity — half-life behavior in liver disease/overdose, toxicity management principles. NCBI
- DailyMed (multiple acetaminophen labels) — maximum daily dose warnings, alcohol cautions, OTC labeling language. DailyMed+2DailyMed+2
- WHO Model List of Essential Medicines — listing and status of paracetamol/acetaminophen on the EML (2025 update resources). World Health Organization+1
- ATC/DDD Index (N02BE01) — classification and DDD context for paracetamol. atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
- Medscape Drug Reference (Acetaminophen IV / Tylenol) — clearance (~0.27 L/h/kg), Vd ≈ 1 L/kg, protein binding 10–25%. Medscape Reference+1
- Food-effect literature — food delays absorption (↑tₘₐₓ) with minimal impact on extent for common analgesics including paracetamol. PubMed+1
- KEGG (D00217; C06804) — external ID cross-references and molecular data. Genome.jp+1
- NIST WebBook (CAS 103-90-2) — InChIKey and registry confirmation. NIST WebBook
- ChEMBL (CHEMBL112) — external database cross-link for acetaminophen. EMBL-EBI
- RxNav / RxNorm — RxCUI references for acetaminophen ingredient and selected products. mor.nlm.nih.gov+2NCBO BioPortal+2

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com