Table of Contents
Introduction
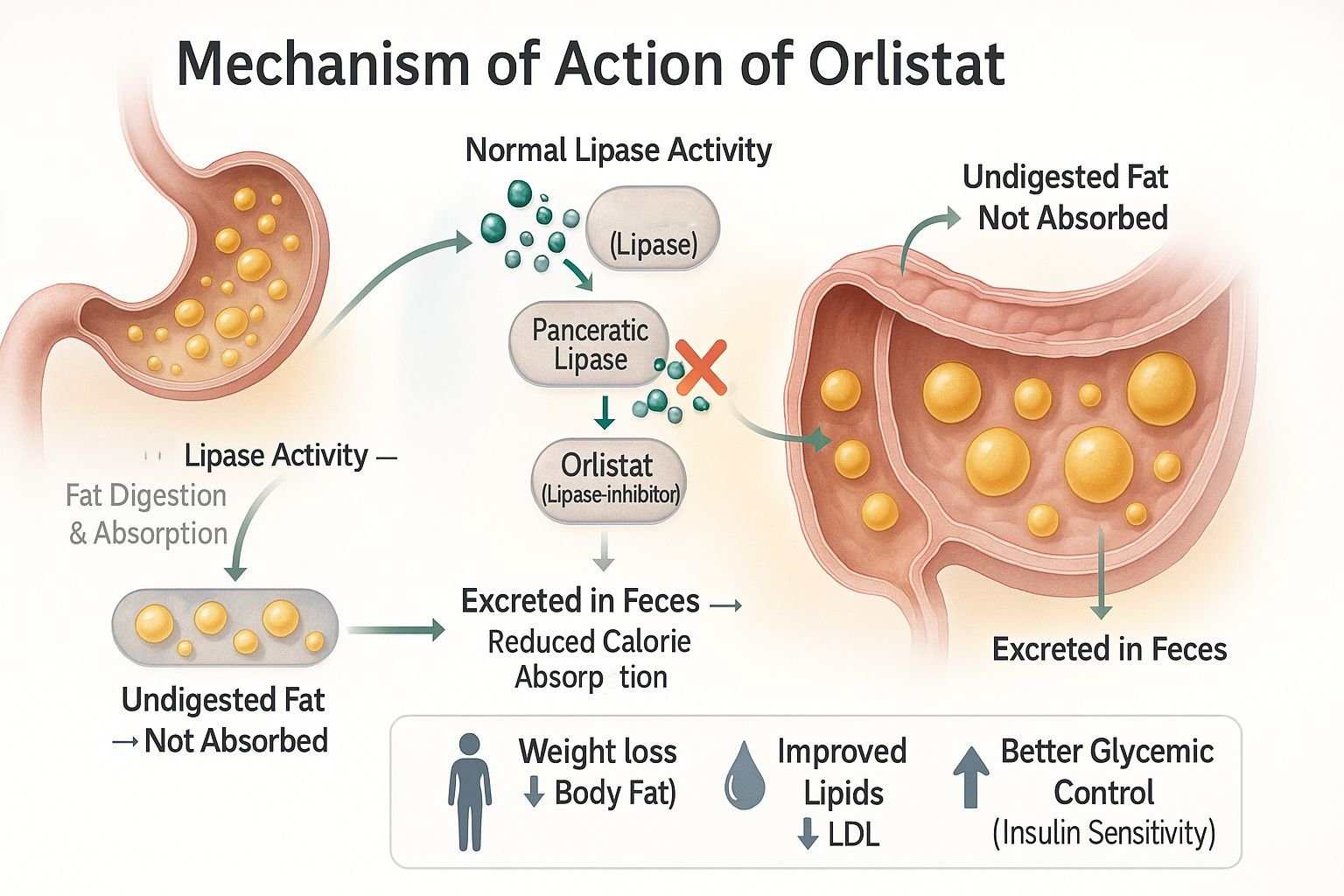
Orlistat is a lipase inhibitor used primarily as an anti-obesity agent. It acts locally within the gastrointestinal tract to reduce the absorption of dietary fats. Unlike centrally acting appetite suppressants, orlistat exerts its effect peripherally without affecting the central nervous system. This makes it a valuable pharmacologic option for long-term weight management in obese individuals, especially when combined with dietary modification.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
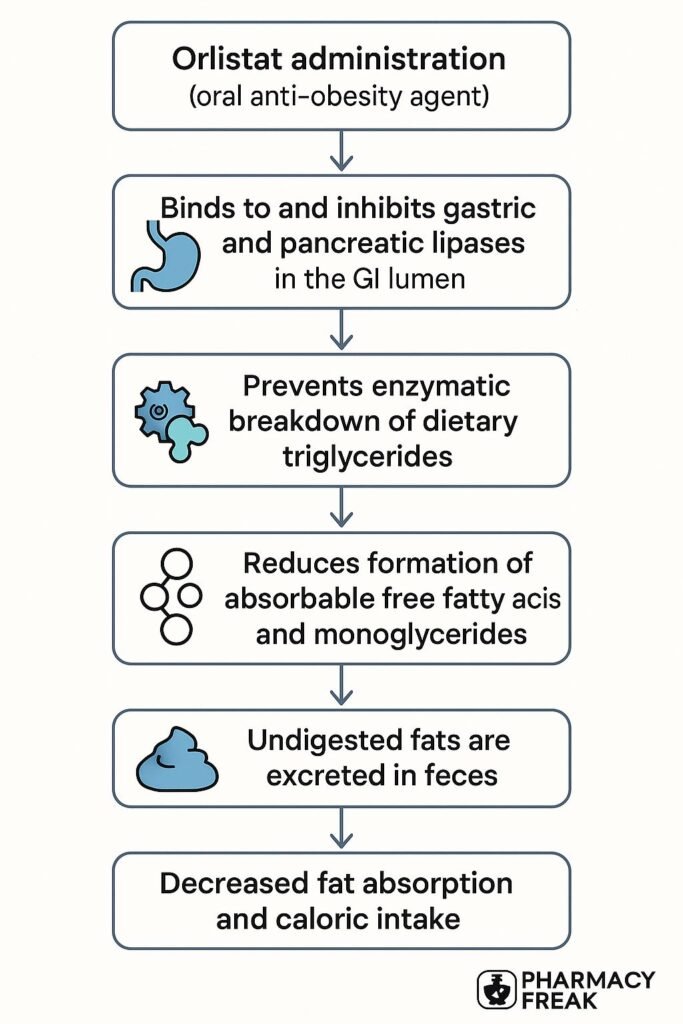
1. Inhibition of Gastric and Pancreatic Lipases
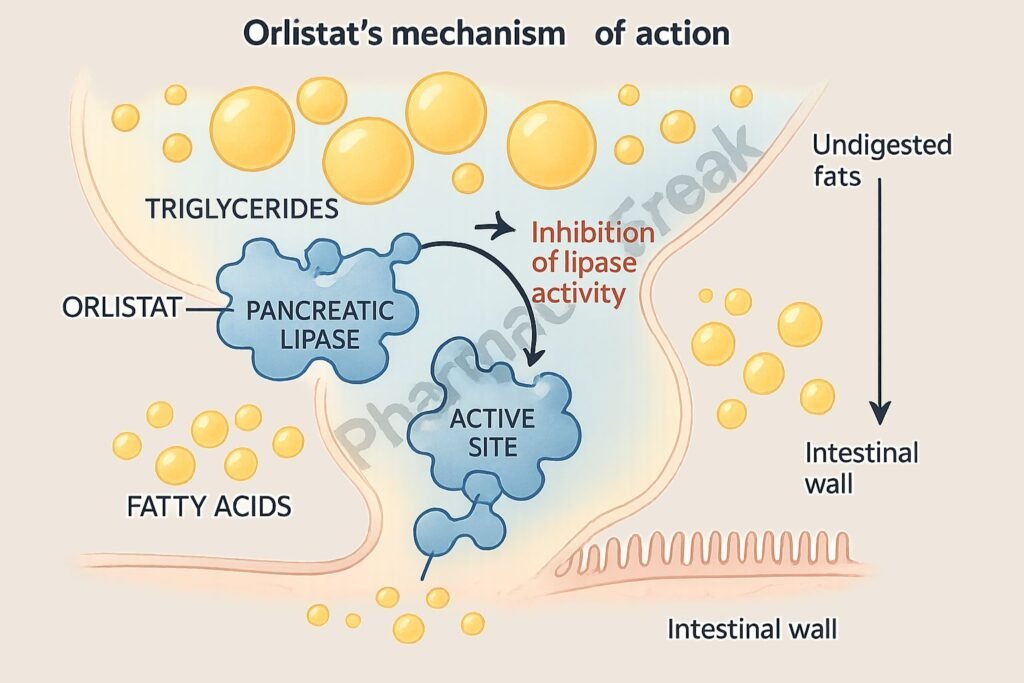
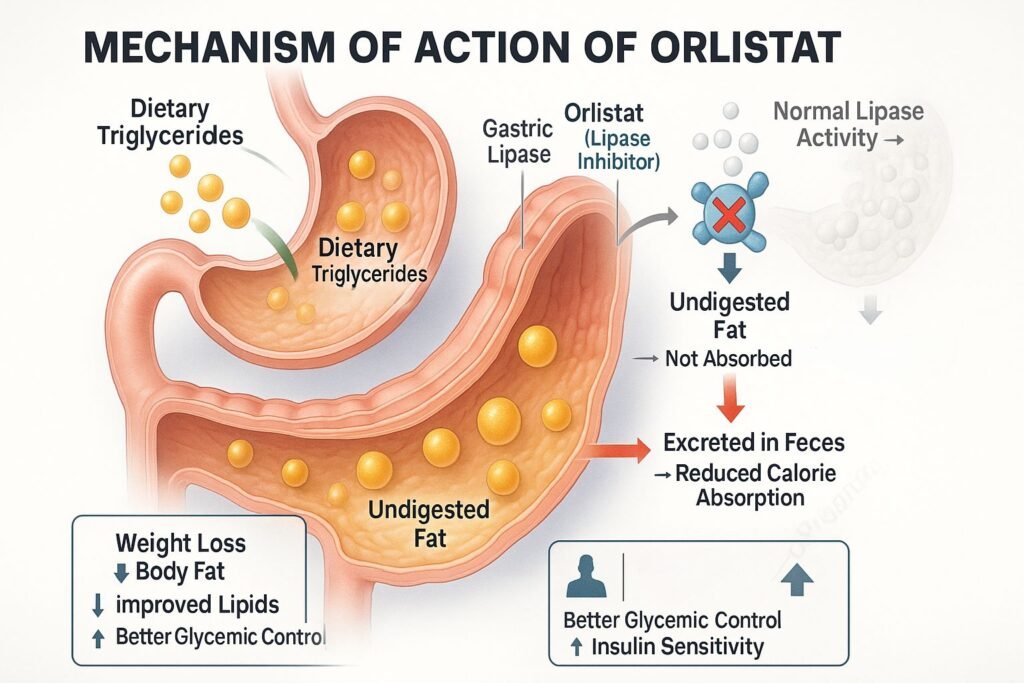
Orlistat irreversibly binds to the active serine site of gastric and pancreatic lipases in the lumen of the stomach and small intestine.
2. Prevention of Triglyceride Hydrolysis
These enzymes are essential for the hydrolysis of dietary triglycerides into absorbable free fatty acids and monoglycerides. Orlistat inhibits this step.
3. Reduced Fat Absorption
As a result, approximately 30% of dietary fat remains unabsorbed and is excreted unchanged in the feces.
4. Caloric Deficit and Weight Loss
The unabsorbed fat leads to a caloric deficit, promoting gradual and sustained weight loss.
5. Minimal Systemic Absorption
Orlistat acts locally within the GI tract and has negligible systemic absorption, minimizing systemic side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
- Route of Administration: Oral
- Bioavailability: Negligible systemic absorption
- Time to Peak Plasma: ~8 hours (for trace systemic levels)
- Half-Life: Not well-defined due to minimal absorption
- Protein Binding: >99%
- Metabolism: Minimal; metabolized in GI wall if absorbed
- Excretion: Fecal (~97% as unchanged drug)
Clinical Uses
- Obesity management (BMI ≥30 or ≥27 with risk factors)
- Weight maintenance and prevention of regain
- Adjunct to reduced-calorie diet
- Potential use in metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes (off-label)
Adverse Effects
- Gastrointestinal: Steatorrhea, oily spotting, flatulence with discharge, fecal urgency
- Fat-soluble vitamin deficiency (A, D, E, K)
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Rare hepatic injury
- Contraindications: Chronic malabsorption syndrome, cholestasis, pregnancy
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Orlistat | Liraglutide |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Lipase inhibition | GLP-1 receptor agonist |
| Site of Action | GI lumen | CNS and pancreas |
| Appetite Suppression | No | Yes |
| Weight Loss Mechanism | Fat malabsorption | Appetite suppression & delayed gastric emptying |
| Systemic Side Effects | Minimal | Present |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is the primary mechanism of action of orlistat?
a) Appetite suppression
b) Lipase inhibition
c) Beta-adrenergic stimulation
d) Serotonin modulation
Answer: b) Lipase inhibition
2. Orlistat reduces absorption of:
a) Carbohydrates
b) Proteins
c) Fats
d) Vitamins only
Answer: c) Fats
3. The major route of orlistat excretion is:
a) Renal
b) Pulmonary
c) Fecal
d) Biliary
Answer: c) Fecal
4. A common adverse effect of orlistat is:
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Oily rectal discharge
c) Bradycardia
d) Renal stones
Answer: b) Oily rectal discharge
5. Orlistat is contraindicated in:
a) Obese diabetic patients
b) Pregnancy
c) Hypertension
d) Hyperlipidemia
Answer: b) Pregnancy
FAQs
Q1. Can orlistat be used long-term?
Yes, it is approved for long-term use when combined with lifestyle modification.
Q2. Does orlistat cause hypoglycemia?
No, it does not directly affect blood glucose levels.
Q3. Should fat-soluble vitamins be supplemented with orlistat?
Yes, especially vitamins A, D, E, and K, due to impaired absorption.
Q4. How soon do the GI side effects appear?
Typically within the first few days of therapy, especially if dietary fat intake is high.
Q5. Is a prescription required for orlistat?
Yes for 120 mg strength; 60 mg is available over-the-counter in some countries.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Orlistat Prescribing Information
- Clinical guidelines for obesity treatment
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com