Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
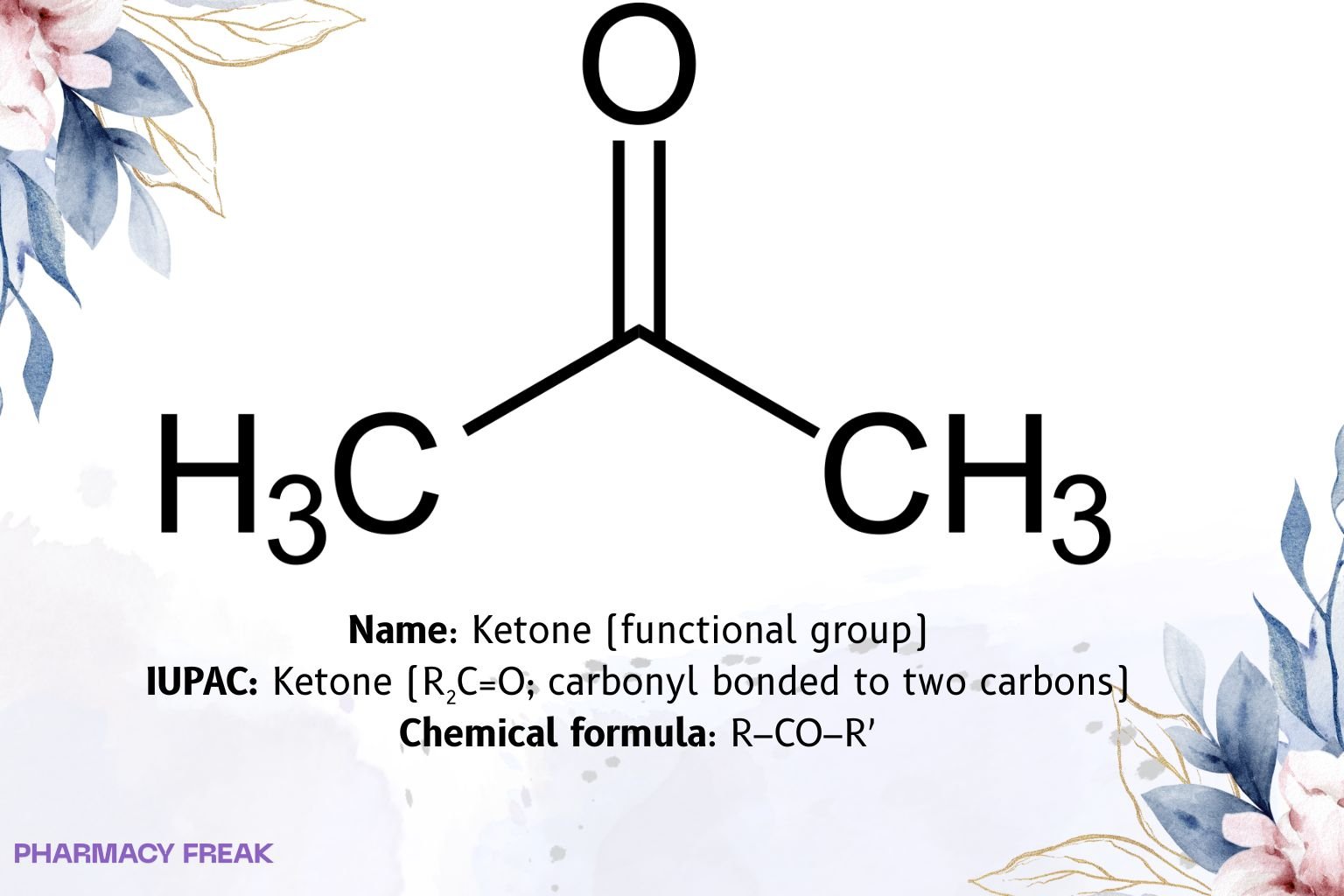
Ketone is a carbonyl functional group in which the carbonyl carbon is bonded to two carbons (R₂C=O; neither R is H). The carbonyl is sp², trigonal planar, strongly electrophilic, and shows a characteristic C=O IR band near ~1715 cm⁻¹ for simple aliphatic ketones (conjugation/substitution shifts lower). α-Hydrogens adjacent to the carbonyl are acidic (pKₐ ≈ 19–20) and form enol/enolate tautomers that drive much of ketone chemistry (aldol, halogenation, Michael additions).
Typical preparations include oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones, Friedel–Crafts acylation (aryl ketones), and Markovnikov hydration of terminal alkynes → methyl ketones. Reductions (e.g., NaBH₄, LiAlH₄, catalytic H₂) give secondary alcohols; methyl ketones undergo the haloform reaction under basic halogenation.
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
Ketone (functional group)
Background
Core motif across organic synthesis, medicinal chemistry, polymers, and natural products; found in solvents (e.g., acetone) and as masked handles for C–C bond construction.
Modality
Functional group (small-molecule chemistry)
Groups
Endogenous/exogenous chemicals (not a therapeutic agent)
Structure
Weight
Not applicable (class)
Chemical Formula
R–CO–R′ (R, R′ = carbon substituents)
Synonyms
Carbonyl (ketone), alkanone/alkan-2-one (nomenclature family)
External IDs
Not applicable (class)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not applicable (functional group).
Associated Conditions
Not applicable.
Associated Therapies
Not applicable.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable.
Pharmacodynamics
Chemical behavior: electrophilic C=O undergoes nucleophilic addition (e.g., hydride, organometallics), and α-deprotonation to enol/enolate that participates in aldol and related reactions.
Mechanism of action
Reactivity arises from π(C=O)–π* polarization; conjugation and substituents modulate carbonyl IR frequency and electrophilicity; keto–enol tautomerism is equilibrium- and solvent-dependent.
Absorption
Not applicable.
Volume of distribution
Not applicable.
Protein binding
Not applicable.
Metabolism
Not applicable at class level (scaffold-dependent).
Route of elimination
Not applicable.
Half-life
Not applicable.
Clearance
Not applicable.
Adverse Effects
Not applicable (class).
Toxicity
Not applicable (class).
Pathways
Representative synthetic/transformational pathways:
- Oxidation of secondary alcohols → ketones (e.g., PCC, Swern/DMP).
- Friedel–Crafts acylation of arenes → aryl ketones.
- Hydration of alkynes (Hg²⁺/acid) → ketones (terminal → methyl ketone).
- Reduction of ketones → secondary alcohols (hydride/catalytic).
- Haloform reaction for methyl ketones under basic halogenation.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Not applicable.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Not applicable (functional group).
Food Interactions
Not applicable.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None.
Drug Categories
Functional group; Carbonyl compound
Chemical Taxonomy
R₂C=O carbonyl; sp² trigonal planar; C=O IR ~1715 cm⁻¹ (simple aliphatic; conjugation lowers); α-C–H pKₐ ≈ 19–20; keto–enol tautomerism.
Affected organisms
Not applicable.
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
Not applicable (class)
CAS number
Not applicable (class). Example (context): acetone 67-64-1.
InChI Key
Not applicable (class)
InChI
Not applicable (class)
IUPAC Name
Ketone functional group (R₂C=O)
SMILES
Generic: R–C(=O)–R′
6. References
IUPAC Gold Book — definition of ketone: carbonyl bonded to two carbons (R₂C=O; neither R is H). old.goldbook.iupac.org+3goldbook.iupac.org+3goldbook.iupac.org+3
ChemLibreTexts — IR region 1660–1770 cm⁻¹ for carbonyls; spectroscopic features of aldehydes/ketones. Chemistry LibreTexts+1
MSU (Reusch) IR tutorial — ketone C=O ~1710–1740 cm⁻¹, conjugation lowers frequency. Michigan State University Chemistry
ChemLibreTexts — α-hydrogen acidity pKₐ ≈ 19–20, enolate stabilization; keto–enol tautomerism overview. Chemistry LibreTexts+1
ChemLibreTexts — haloform reaction of methyl ketones under basic halogenation; mechanistic notes. Chemistry LibreTexts+2Chemistry LibreTexts+2
ChemLibreTexts — oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones (PCC and related); formation overview. Chemistry LibreTexts
ChemLibreTexts — hydration of alkynes → ketones (terminal → methyl ketone; Hg²⁺/acid), Markovnikov tautomers. Chemistry LibreTexts+4Chemistry LibreTexts+4Chemistry LibreTexts+4
ChemLibreTexts/UCLA pages — Friedel–Crafts acylation gives aryl ketones (method and example). Chemistry LibreTexts+2Chemistry LibreTexts+2
Organic-Chemistry.org — Dess–Martin oxidation as a mild route to aldehydes/ketones (context). organic-chemistry.org

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com