Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Glucose (D-glucose; dextrose) is a naturally occurring aldohexose monosaccharide that serves as a primary cellular energy source and a key metabolic substrate in humans. In clinical use, glucose solutions treat hypoglycemia, provide calories and fluid in parenteral nutrition, and are used in diagnostic tests (e.g., OGTT).
Brand Names
Generic glucose/dextrose products; region-dependent examples exist (tablets, gels, oral solutions, IV infusions).
Name
Glucose (D-glucose; dextrose)
Background
Endogenous nutrient central to glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the pentose phosphate pathway. Pharmaceutical forms include oral tablets/gel and sterile IV solutions (various strengths).
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Nutrient; OTC/Rx (product-dependent)
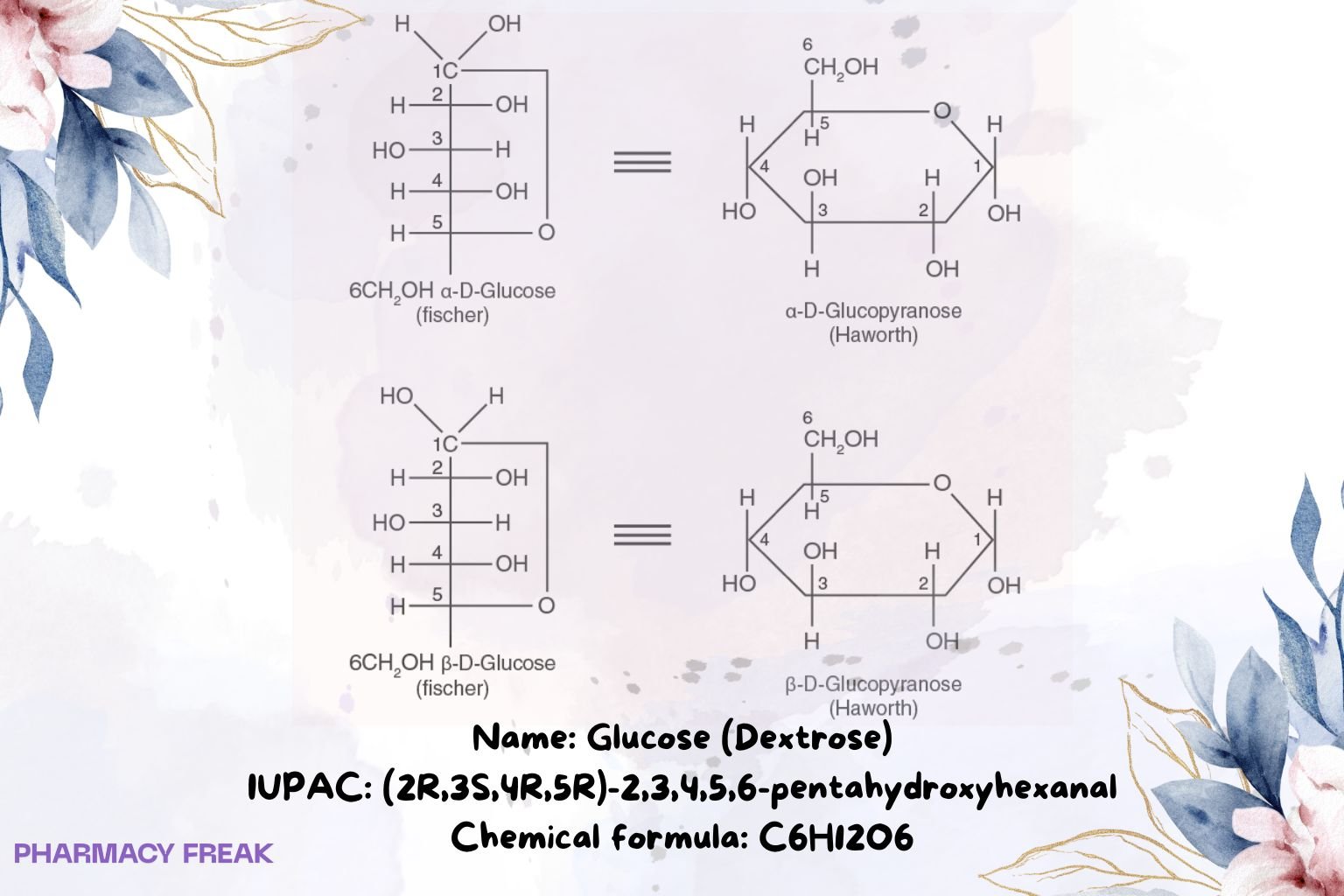
Structure
Weight
~180.16 g/mol (anhydrous); 198.17 g/mol (monohydrate)
Chemical Formula
C₆H₁₂O₆ (anhydrous); C₆H₁₂O₆·H₂O (monohydrate)
Synonyms
Dextrose; D-glucose; grape sugar; β-D-glucopyranose (cyclic form)
External IDs
CAS (D-glucose/anhydrous): 50-99-7; CAS (monohydrate): 5996-10-1
PubChem CID: 5793 (D-glucose)
UNII (anhydrous dextrose): 5SL0G7R0OK; UNII (monohydrate): LX22YL083G; UNII (dextrose, unspecified): IY9XDZ35W2
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Treatment of hypoglycemia; caloric and fluid source in parenteral nutrition; component of oral rehydration; carbohydrate load for oral glucose tolerance testing.
Associated Conditions
Hypoglycemia (diabetes therapy–related or spontaneous), dehydration, perioperative or critical-care caloric needs, diagnostic use.
Associated Therapies
With insulin (e.g., to prevent hypoglycemia during insulin therapy for hyperkalemia); combined with electrolytes in IV fluids; used in standardized OGTT protocols.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
No boxed warning. Avoid/use caution in severe hyperglycemia, intracranial/intraspinal hemorrhage where hyperosmolar fluids are contraindicated, and in patients at risk of fluid overload. Check product-specific labeling.
Pharmacodynamics
Raises plasma glucose concentration; supplies substrate for ATP generation; high concentrations exert osmotic effects (diuresis, shifts in water balance).
Mechanism of action
Transport via SGLT/GLUT transporters → intracellular metabolism through glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation; storage as glycogen; entry into pentose phosphate pathway and biosynthetic routes.
Absorption
Oral absorption is rapid and efficient via SGLT1 in the small intestine; IV administration results in immediate systemic availability.
Volume of distribution
Distributes into total body water and tissues; rapid cellular uptake driven by insulin-regulated and basal GLUT transporters (value depends on physiologic state and dosing).
Protein binding
Negligible
Metabolism
Widespread cellular metabolism to pyruvate/CO₂ + H₂O; incorporation into glycogen, lipids, and other biomolecules.
Route of elimination
Ultimately exhaled as CO₂ (metabolic); urinary excretion of intact glucose occurs when renal threshold is exceeded (e.g., marked hyperglycemia).
Half-life
Not fixed (endogenous substrate with rapid turnover); pharmacodynamic effect depends on dose, route, and metabolic demand.
Clearance
Predominantly metabolic utilization; apparent clearance varies with endocrine and nutritional status.
Adverse Effects
Hyperglycemia, glycosuria, fluid/electrolyte disturbances (especially with hypertonic IV solutions), vein irritation/phlebitis (IV), and rare extravasation injury with hyperosmolar solutions.
Toxicity
Excessive dosing may cause severe hyperglycemia, hyperosmolar states, and electrolyte shifts; management is supportive and may require insulin and careful fluid/electrolyte correction.
Pathways
Glycolysis (Embden–Meyerhof); pentose phosphate pathway; glycogen synthesis/breakdown; numerous anabolic pathways.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No routine pharmacogenomic considerations; physiologic response depends on endocrine milieu (e.g., insulin/glucagon dynamics).
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
- Insulin and insulin secretagogues: antagonistic effect on blood glucose; dosing balance required.
- Sodium–glucose cotransporter inhibitors (SGLT2): may alter glycosuria thresholds and glycemic profiles.
- Hyperkalemia therapy: glucose is co-administered with insulin to mitigate hypoglycemia risk.
Food Interactions
Oral absorption is efficient; gastric emptying and mixed-meal composition can modulate timing of peak glucose levels.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
V06DC01 (carbohydrates; nutrients)
V04CA02 (tests for diabetes)
B05CX01 (other irrigating solutions)
Drug Categories
Nutrient; Diagnostic agent; Parenteral solution component; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Aldohexose; monosaccharide; typically β-D-glucopyranose in solution; multiple tautomers/anomers
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic/nutritional use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
5SL0G7R0OK (anhydrous dextrose); LX22YL083G (dextrose monohydrate); IY9XDZ35W2 (dextrose, unspecified)
CAS number
50-99-7 (D-glucose); 5996-10-1 (D-glucose monohydrate)
InChI Key
GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-SLPGGIOYSA-N (D-glucose/anhydrous dextrose)
InChI
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6-/m0/s1 (β-D-glucopyranose)
IUPAC Name
(2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal (open-chain D-glucose)
SMILES
OC[C@H]1OC@@HC@@HC@H[C@H]1O (β-D-glucopyranose; one valid isomeric representation)
6. References
- KEGG COMPOUND C00031 (D-Glucose) — formula, exact mass, aliases. KEGG
- KEGG DRUG D00009 (Glucose) — ATC codes B05CX01, V04CA02, V06DC01; drug classification. KEGG
- ATC/DDD Index (FHI) — V04CA02 (glucose; tests for diabetes); B05CX01 (glucose; other irrigating solutions); V06DC01 (carbohydrates—glucose). atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
- UNII (FDA GSRS) — anhydrous dextrose 5SL0G7R0OK (InChIKey GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-SLPGGIOYSA-N); dextrose unspecified IY9XDZ35W2; monohydrate LX22YL083G. precisionFDA+3precisionFDA+3precisionFDA+3
- DailyMed — glucose/dextrose injection solutions; monohydrate formula C₆H₁₂O₆·H₂O and MW 198.17. DailyMed+2DailyMed+2
- NIST WebBook / Cheminformatics sources — β-D-glucopyranose InChI/InChIKey; representative SMILES. NIST WebBook+2chemeo.com+2

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com