Drugs for erectile dysfunction (ED) can be classified into several categories based on their mechanism of action and mode of administration.
Table of Contents
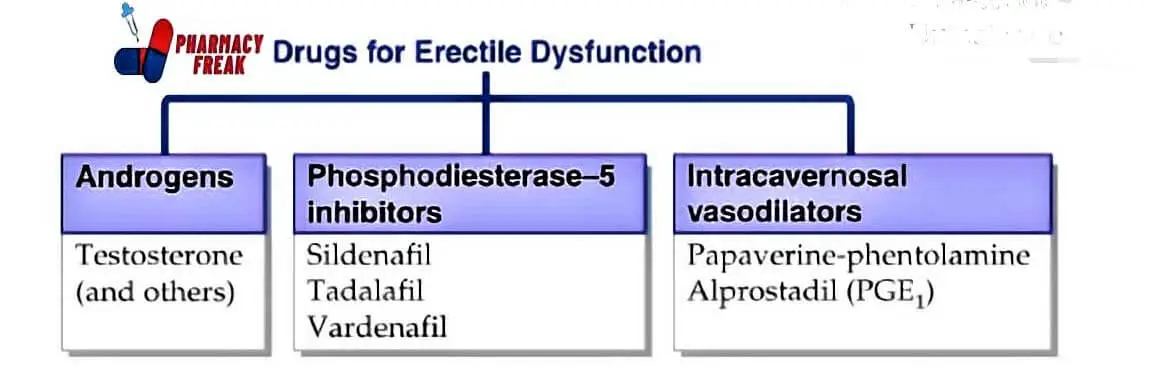
Here is a classification of drugs commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction
Drugs for Erectile Dysfunction
- Androgens- Testosterone (and others)
- Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors– Sildenafil, Tadalafil, Vardenafil
- Intracavernosal vasodilators- Papaverine-phentolamine, Alprostadil (PGE₁)
Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors
PDE5 inhibitors are the most common and widely used medications for treating ED. They work by increasing blood flow to the penis, helping to achieve and maintain an erection.
Examples include
- Sildenafil (Viagra): This medication is typically taken as needed and has a rapid onset of action.
- Tadalafil (Cialis): Tadalafil has a longer duration of action, allowing for a more spontaneous sexual activity. It is available in a daily low-dose form.
- Vardenafil (Levitra, Staxyn): Vardenafil works similarly to sildenafil and is available in different formulations.
Intracavernosal Injections
These drugs are injected directly into the base of the penis before sexual activity. They cause the blood vessels in the penis to dilate, producing an erection.
Examples include
- Alprostadil (Caverject, Edex): Alprostadil is a prostaglandin E1 analog used as an injectable medication for ED.
Intraurethral Suppositories
These are small suppository pellets that are inserted into the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder). They help relax the penile muscles and increase blood flow.
Examples include
Alprostadil (MUSE): MUSE stands for “medicated urethral system for erections.”
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
In cases where ED is associated with low testosterone levels, TRT may be prescribed to restore hormonal balance.
Examples include testosterone gels, patches, and injections.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Pharmacologic Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com