Table of Contents
What Are Antianxiety Drugs?
Antianxiety drugs, also referred to as anxiolytics, are medications designed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety disorders. These conditions can include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder (SAD), and specific phobias, among others. These drugs work by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, resulting in a calming and relaxing effect.
Classification of Antianxiety Drugs
Antianxiety drugs can be categorized into several classes based on their mechanism of action and chemical structure. Let’s explore these classifications in more detail:
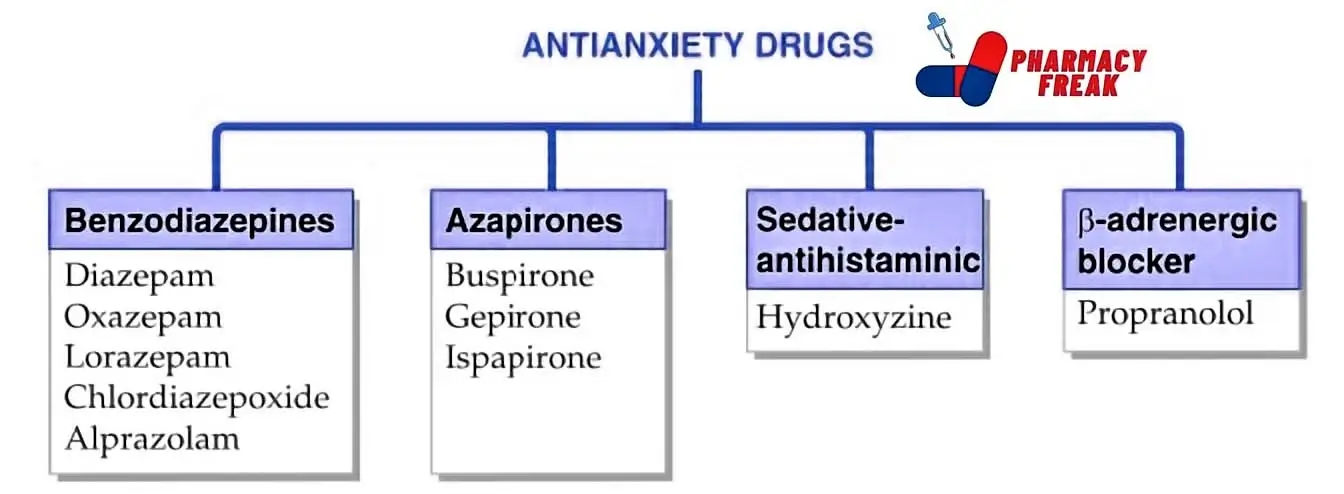
- Benzodiazepines– Diazepam, Oxazepam, Lorazepam, Chlordiazepoxide, Alprazolam
- Azapirones– Buspirone, Gepirone, Ispapirone
- Sedative-antihistaminic– Hydroxyzine
- B-adrenergic blocker– Propranolol
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are one of the most well-known and widely used classes of antianxiety drugs. They work by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that inhibits brain activity. This leads to a sedative and calming effect. Common benzodiazepines include:
- Alprazolam (Xanax): Used to treat panic disorder and GAD.
- Diazepam (Valium): Prescribed for various anxiety disorders, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal.
- Lorazepam (Ativan): Effective for treating acute anxiety, including panic attacks.
Despite their efficacy, benzodiazepines can be habit-forming, leading to potential addiction and withdrawal symptoms.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are primarily known as antidepressants, but they are also used to treat anxiety disorders. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, in the brain. Some SSRIs prescribed for anxiety include:
- Sertraline (Zoloft): Effective for various anxiety disorders, including social anxiety disorder and panic disorder.
- Escitalopram (Lexapro): Used for GAD and SAD.
- Fluoxetine (Prozac): Prescribed for panic disorder and OCD, among other conditions.
SSRIs are considered safer than benzodiazepines in the long term and have a lower risk of dependence.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are another class of antidepressants that can help manage anxiety disorders. They work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. Common SNRIs include:
- Venlafaxine (Effexor): Used for GAD.
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta): Prescribed for GAD and sometimes panic disorder.
Buspirone (Buspar)
Buspirone is a unique antianxiety medication that doesn’t belong to the benzodiazepine or antidepressant classes. Its exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to affect serotonin and dopamine receptors. Buspirone is primarily used for GAD and has a lower risk of dependence than benzodiazepines.
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are not traditional antianxiety drugs but can help manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heart rate and trembling. They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline. Propranolol is a commonly used beta-blocker for anxiety.
Antihistamines
Certain antihistamines, such as hydroxyzine (Vistaril), can have sedative effects and are sometimes prescribed for anxiety. They are generally considered safe but can cause drowsiness.
Off-Label Medications
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications not specifically approved for anxiety but found to be effective. These can include antipsychotic medications, mood stabilizers, and even certain blood pressure medications.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Pharmacotherapy of Anxiety Disorders
Related Links

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com