Table of Contents
Introduction
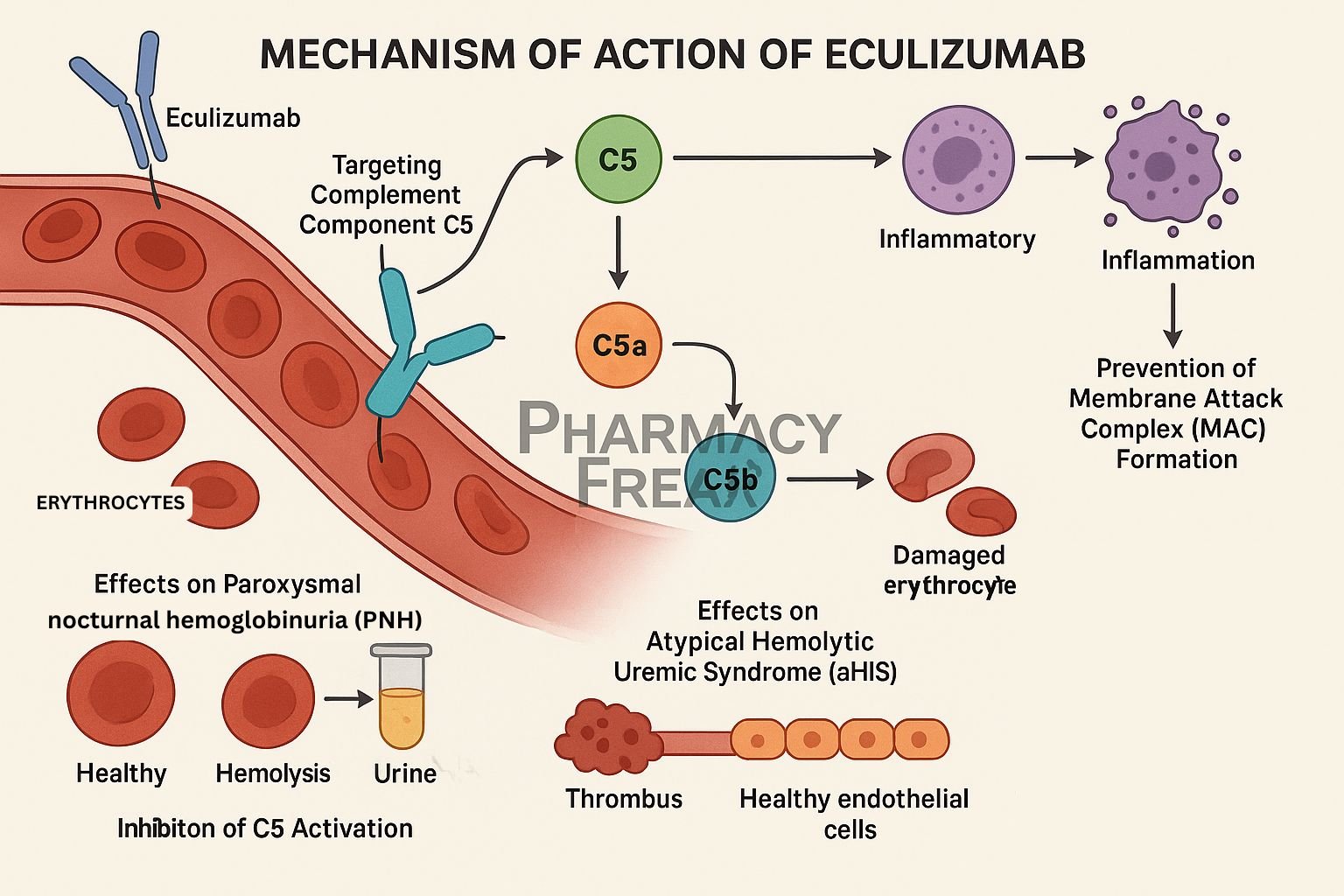
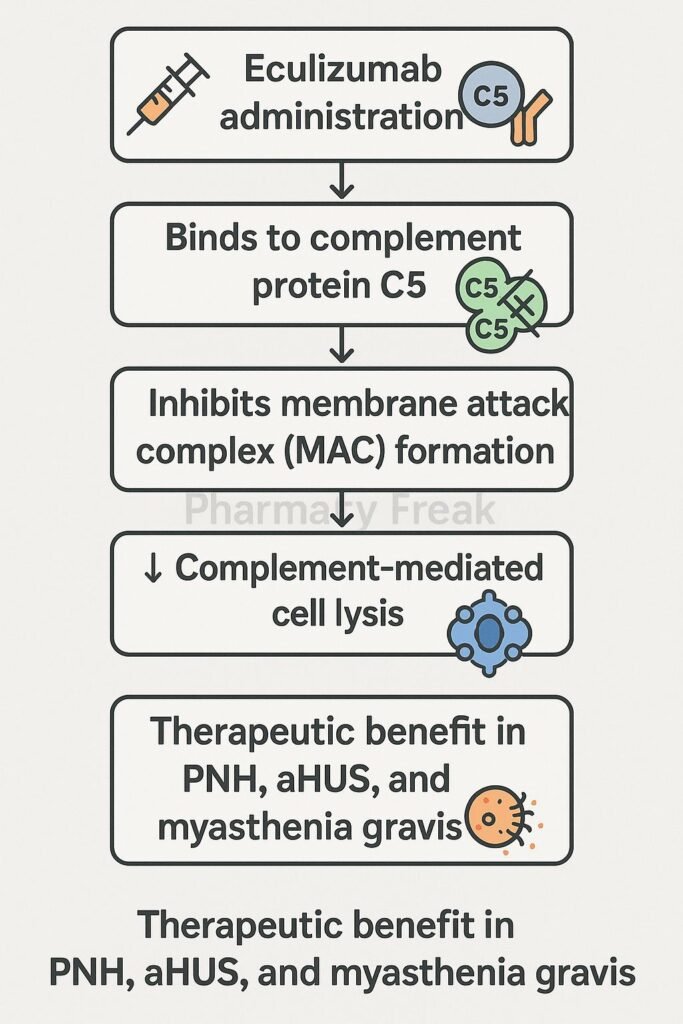
Eculizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to complement protein C5, inhibiting its cleavage and preventing terminal complement complex formation. It is approved for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG), and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD).
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Binding to complement C5
Eculizumab attaches with high affinity to C5, blocking its activation by C5 convertase. - Prevents formation of C5a and C5b
This inhibition stops generation of the potent anaphylatoxin C5a and C5b. - Blocks membrane attack complex
By preventing C5b formation, it stops assembly of the membrane attack complex (C5b–C9), thus avoiding cell lysis. - Reduces hemolysis and inflammation
In PNH and aHUS, this reduces intravascular hemolysis, endothelial damage, and inflammatory tissue injury. - Modulates immune response
Lower levels of C5a decrease neutrophil and macrophage activation, reducing inflammation and tissue damage in autoimmunity.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Intravenous infusion (every 2 weeks) |
| Distribution | Extracellular fluid, limited tissue penetration |
| Half-life | ~11 days |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic degradation |
| Excretion | None—cleaved by proteolysis into amino acids |
Clinical Uses
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH)
- Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)
- Generalized myasthenia gravis with anti-AChR antibodies
- Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD)
Adverse Effects
- Increased risk of meningococcal infections (vaccination required)
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Headache, nausea, diarrhea
- Rare infusion reactions
Comparative Analysis
| Drug | Target | Dosing Frequency | Main Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eculizumab | C5 | Every 2 weeks IV | PNH, aHUS, gMG, NMOSD |
| Ravulizumab | C5 | Every 8 weeks IV | Similar indications, longer dosing |
| C3 inhibitors | C3 | Under investigation | PNH, C3 glomerulopathy |
MCQs
- Eculizumab binds to which complement protein?
a) C3 b) C5 c) C7 d) C9
Answer: b) C5 - It prevents formation of which complex?
a) C3 convertase b) MAC (C5b–C9) c) Anaphylatoxin C3a d) C4b2a
Answer: b) MAC (C5b–C9) - Which potent inflammatory mediator is reduced?
a) C3a b) C5a c) IL‑6 d) TNF‑α
Answer: b) C5a - Main risk with eculizumab therapy is:
a) Hepatitis b) Meningococcal infection c) Pancreatitis d) Cardiomyopathy
Answer: b) Meningococcal infection - Primary route of clearance is:
a) Renal b) Hepatic CYP c) Proteolysis d) Biliary
Answer: c) Proteolysis - Typical dosing interval is:
a) Weekly b) Every 2 weeks c) Monthly d) Daily
Answer: b) Every 2 weeks - Which enzyme activates C5?
a) C3 convertase b) C5 convertase c) Factor D d) Thrombin
Answer: b) C5 convertase - Eculizumab reduces which symptom in PNH?
a) Thrombocytopenia b) Hemolysis c) Hypertension d) Diabetes
Answer: b) Hemolysis - Complement activation blocked stops:
a) TNF production b) MAC formation c) IgG binding d) T-cell activation
Answer: b) MAC formation - Vaccination required before initiation is directed against:
a) Pneumococcus b) Meningococcus c) Influenza d) Varicella
Answer: b) Meningococcus
FAQs
1. Why is meningococcal vaccination necessary?
Blocking C5 impairs complement-mediated bacterial defense; vaccination reduces meningococcal risk.
2. How is eculizumab administered?
Given as an intravenous infusion every two weeks.
3. Can therapy be paused if infection occurs?
Clinical judgment needed—treatment may be paused or continued with antibiotic coverage.
4. Are there alternatives with longer dosing intervals?
Yes—ravulizumab targets C5 with 8-week dosing intervals.
5. Is renal function affected?
No—excretion is proteolytic; no dose adjustment in renal impairment.
References

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com