Antipsychotic drugs, also known as neuroleptics or antipsychotics, are a class of medications primarily used to manage and alleviate the symptoms of psychotic disorders. These disorders often involve disruptions in thinking, emotions, and perceptions. Understanding the types and uses of antipsychotic drugs is essential for those who may be prescribed these medications or are interested in their effects.
Table of Contents
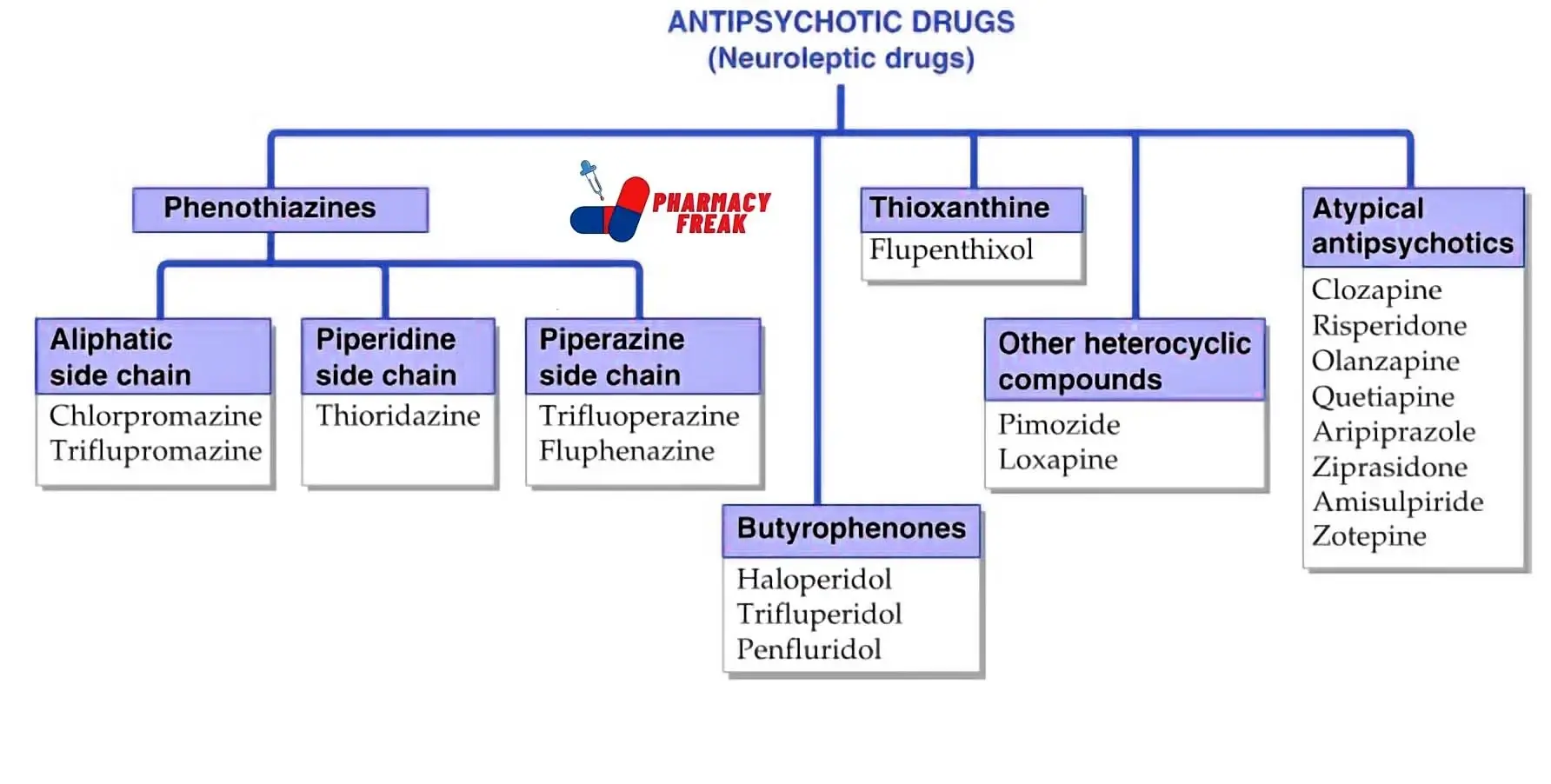
Classification of Antipsychotic Drugs
- Phenothiazines
- Aliphatic side chain- Chlorpromazine, Triflupromazine
- Piperidine side chain– Thioridazine
- Piperazine side chain- Trifluoperazine, Fluphenazine
- Butyrophenones- Haloperidol, Trifluperidol, Penfluridol
- Thioxanthine– Flupenthixol
- Other heterocyclic compounds- Pimozide, Loxapine
- Atypical antipsychotics- Clozapine, Risperidone, Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Aripiprazole, Ziprasidone, Amisulpiride, Zotepine
Antipsychotic drugs can be classified into two major categories based on their mechanisms of action:
- Typical Antipsychotics (First-Generation Antipsychotics):
- Typical antipsychotics are the older class of antipsychotic medications.
- They primarily work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, which helps alleviate symptoms of conditions like schizophrenia.
- Common examples include haloperidol (Haldol), chlorpromazine (Thorazine), and fluphenazine (Prolixin).
- Atypical Antipsychotics (Second-Generation Antipsychotics):
- Atypical antipsychotics are newer medications that have a broader mechanism of action compared to typical antipsychotics.
- They not only affect dopamine but also influence other neurotransmitters like serotonin, which can be more effective in managing psychotic symptoms.
- Common examples include aripiprazole (Abilify), olanzapine (Zyprexa), and risperidone (Risperdal).
Common Uses of Antipsychotic Drugs
Antipsychotic drugs have various medical and non-medical uses:
- Schizophrenia Treatment:
- Antipsychotics are the primary treatment for schizophrenia, a mental disorder characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
- Bipolar Disorder:
- In bipolar disorder, which involves extreme mood swings, antipsychotics are sometimes used alongside mood stabilizers to manage manic episodes.
- Major Depressive Disorder:
- Some atypical antipsychotics are prescribed as adjunctive treatments for major depressive disorder, especially when other antidepressants are ineffective.
- Psychotic Disorders:
- Antipsychotic drugs are used in various psychotic disorders to reduce symptoms like hallucinations and paranoia.
- Non-Medical Use:
- Some individuals may misuse antipsychotic drugs to achieve sedative or calming effects, which is not recommended and can be dangerous.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Neuroleptic Medications
Related Links

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com