Central Nervous System (CNS) stimulants are a class of drugs that stimulate the CNS, increasing alertness, attention, and energy. They are commonly prescribed for medical conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Understanding the types and uses of CNS stimulants is essential for those who may be prescribed these medications or are interested in their effects.
Table of Contents
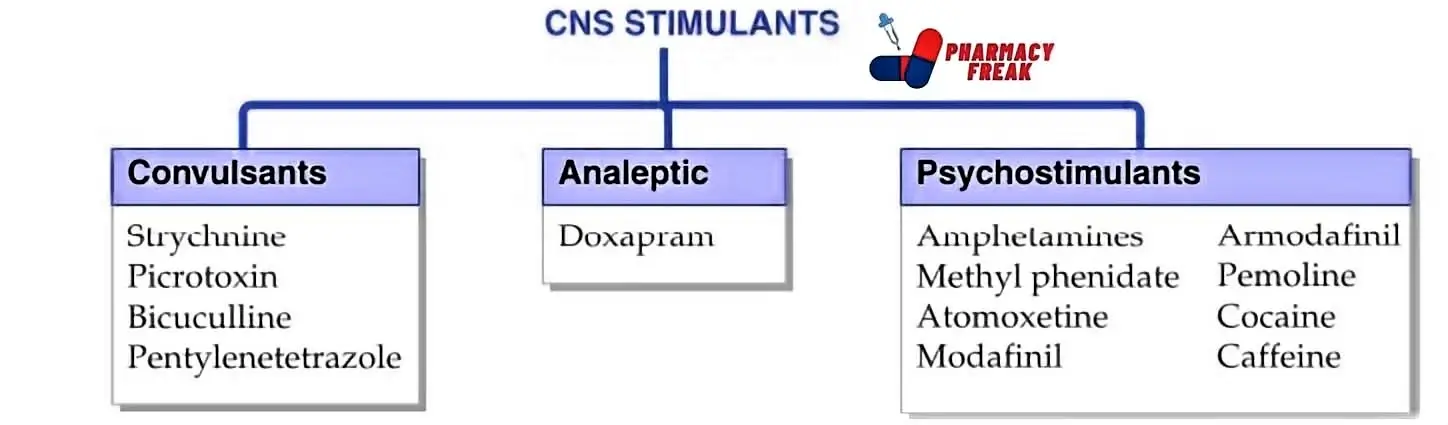
Classification of CNS Stimulants
CNS stimulants can be classified into several categories based on their mechanisms of action and medical applications. Here are some common types:
- Convulsants- Strychnine, Picrotoxin, Bicuculline, Pentylenetetrazole
- Analeptic– Doxapram
- Psychostimulants– Amphetamines, Methyl phenidate, Pemoline, Atomoxetine, Cocaine, Modafinil, Armodafinil, Caffeine
- Amphetamines:
- Amphetamines stimulate the release of certain neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, leading to increased alertness and focus.
- Examples include amphetamine (Adderall) and dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine).
- Methylphenidate:
- Methylphenidate-based stimulants work similarly to amphetamines but have a different chemical structure.
- Common medications are methylphenidate (Ritalin) and dexmethylphenidate (Focalin).
- Non-Amphetamine Stimulants:
- These stimulants have different mechanisms of action and are often used as alternatives to amphetamines or methylphenidate.
- Atomoxetine (Strattera) is an example of a non-amphetamine stimulant used for ADHD.
- Wakefulness-Promoting Agents:
- These stimulants are primarily used to treat sleep disorders like narcolepsy or shift work sleep disorder.
- Modafinil (Provigil) and armodafinil (Nuvigil) are common wakefulness-promoting agents.
- Dietary Supplements and Caffeine:
- Certain dietary supplements and caffeine-containing products are used by individuals to enhance alertness and energy.
- Examples include caffeine, guarana, and ephedra (in some dietary supplements).
Common Uses of CNS Stimulants
CNS stimulants have various medical and non-medical uses:
- ADHD Treatment:
- CNS stimulants like amphetamines and methylphenidate are commonly prescribed to manage the symptoms of ADHD, such as inattention and hyperactivity.
- Narcolepsy:
- Wakefulness-promoting agents are used to treat narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Shift Work Sleep Disorder:
- Individuals who work irregular hours may use wakefulness-promoting agents to stay alert during their shifts.
- Cognitive Enhancement:
- Some people use CNS stimulants off-label for cognitive enhancement, seeking improved focus and productivity.
Responsible Use of CNS Stimulants
When using CNS stimulants, whether prescribed or not, it’s important to follow responsible guidelines:
- Medical Supervision: If prescribed, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely. For non-prescription use, consider consulting a healthcare professional.
- Dosage and Timing: Stick to the recommended dosage and timing to avoid potential side effects and dependence.
- Legal Status: Be aware of the legal status of CNS stimulants in your area. Many are controlled substances and may have legal restrictions.
- Side Effects: Understand the potential side effects, which can include insomnia, increased heart rate, and anxiety.
- Avoid Alcohol and Other Substances: Some CNS stimulants may interact negatively with alcohol and other substances. It’s best to avoid these combinations.
- Non-Medical Use: Using prescription CNS stimulants without a medical need can be dangerous and illegal. Always use medications as prescribed.
Reference
- Classification of Progestins- KD Tripathi
- National Library of Medicine- Central Nervous System (CNS) Stimulants
Related Links

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com