Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Salbutamol (USAN: albuterol) is a short-acting β₂-adrenergic agonist (SABA) used for rapid bronchodilation in asthma, exercise-induced bronchospasm, and COPD; supplied mainly as the sulfate salt for inhalation, oral, and parenteral products.
Brand Names
Ventolin, ProAir, Proventil, Accuneb; numerous generics (region-dependent)
Name
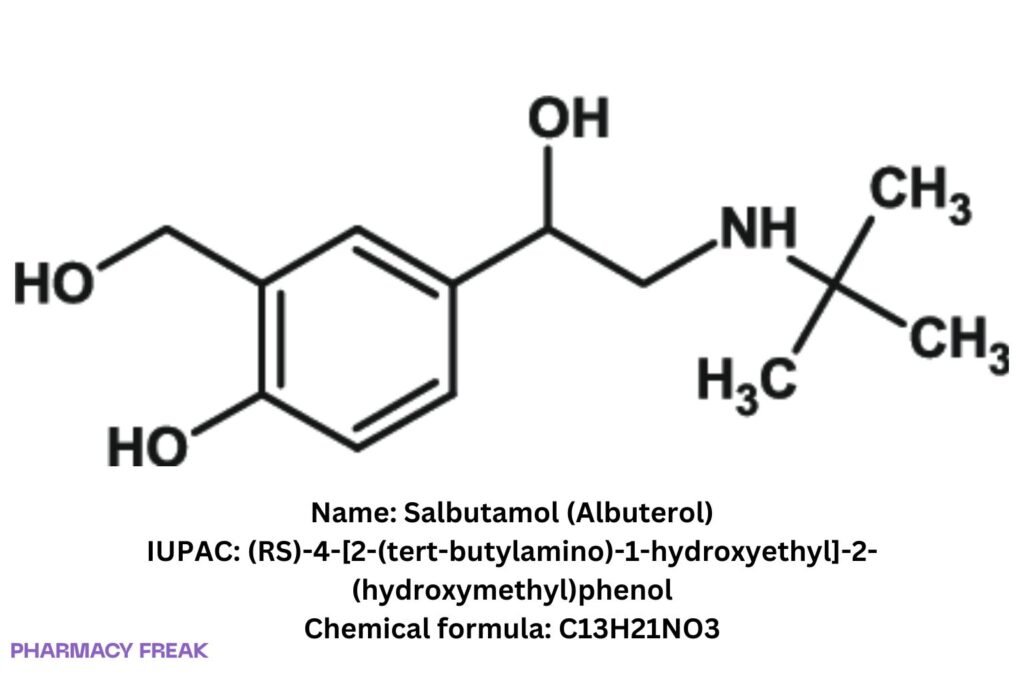
Salbutamol (Albuterol)
Background
Racemic (R/S) catecholamine derivative introduced in the late 1960s; (R)-salbutamol is the active eutomer. Available as metered-dose inhalers, dry-powder inhalers, nebulizer solutions, oral tablets/syrup, and IV.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; OTC/Rx status varies by jurisdiction and product
Structure
Weight
≈ 239.31 g/mol (free base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₃H₂₁NO₃ (free base)
Synonyms
Albuterol; (RS)-4-[2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol
External IDs
CAS (base): 18559-94-9; CAS (sulfate): 51022-70-9
PubChem CID (base): 2083; UNII (base): QF8SVZ843E; UNII (sulfate): 021SEF3731
ATC: R03AC02; KEGG: D02147
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Relief and prevention of bronchospasm in asthma and COPD; exercise-induced bronchospasm prophylaxis; adjunct in hyperkalemia management (off-label protocols).
Associated Conditions
Acute asthma, intermittent asthma, COPD with reversible component, EIB.
Associated Therapies
Combined with inhaled corticosteroids for control; with ipratropium in some acute care settings.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
No boxed warning. Contraindicated in severe hypersensitivity to components. Caution with significant cardiovascular disease, arrhythmias, seizure disorders, hyperthyroidism, and in patients on QT-prolonging agents.
Pharmacodynamics
Selective β₂-receptor agonism → ↑ cAMP in airway smooth muscle → bronchodilation, reduced mediator release, improved mucociliary clearance. Onset (inhaled) typically ≤15 min; duration 3–6 h.
Mechanism of action
Binds β₂-adrenergic receptors; Gs–adenylate cyclase activation increases cAMP; PKA-mediated phosphorylation lowers intracellular Ca²⁺ and relaxes bronchiolar smooth muscle.
Absorption
Inhaled: pulmonary + swallowed fractions; systemic exposure depends on device/technique. Oral: absorbed with first-pass metabolism; IV: immediate.
Volume of distribution
Large (order of ~2 L/kg), consistent with extensive tissue distribution.
Protein binding
Low (~10%).
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic to salbutamol 4′-O-sulfate (inactive); additional minor oxidative/conjugative routes.
Route of elimination
Predominantly renal as unchanged drug and sulfate conjugate; small fecal component.
Half-life
Inhaled ~4–6 h; oral ~5 h (formulation- and subject-dependent).
Clearance
Renal excretion of parent + metabolites; apparent clearance influenced by route, device, and co-medications.
Adverse Effects
Tremor, tachycardia, palpitations, nervousness, headache, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, nausea. Rare: paradoxical bronchospasm, QT prolongation, serious arrhythmias.
Toxicity
Overdose → marked tachycardia, tremor, hypokalemia, lactic acidosis; management is supportive with monitoring of electrolytes and ECG.
Pathways
β₂-receptor signaling; hepatic sulfation; renal elimination.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Variants in ADRB2 (e.g., Gly16Arg) may modulate response in some cohorts; no routine PGx testing recommended.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Nonselective β-blockers antagonize effect; MAO inhibitors/TCAs may potentiate cardiovascular effects; diuretics and other hypokalemia-inducing drugs increase hypokalemia risk; sympathomimetics add toxicity; caution with QT-prolonging agents.
Food Interactions
No clinically meaningful food effect on inhaled products; avoid excess caffeine if symptomatic tachycardia occurs.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
R03AC02 (selective β₂-agonists)
Drug Categories
Short-acting β₂-agonist; Bronchodilator; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Phenethylamine β-hydroxy scaffold; tert-butylamino side chain; phenolic diol motif.
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
QF8SVZ843E (salbutamol, base); 021SEF3731 (salbutamol sulfate)
CAS number
18559-94-9 (base); 51022-70-9 (sulfate)
InChI Key
NDAUXUAQIAJITI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C13H21NO3/c1-13(2,3)14-7-12(17)9-4-5-11(16)10(6-9)8-15/h4-6,12,14-17H,7-8H2,1-3H3
IUPAC Name
(RS)-4-[2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol
SMILES
CC(C)(C)NCC(C1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)CO)O
6. References
PubChem Compound Summary: Salbutamol (CID 2083) — identifiers, formula, MW, canonical SMILES/InChI. PubChem
DailyMed labeling (albuterol sulfate) — UNII codes, dosage forms, PK (half-life ≈4–6 h), interactions, warnings. DailyMed+2DailyMed+2
FDA GSRS/UNII — albuterol sulfate 021SEF3731, formula and InChIKey; base UNII cross-reference. precision.fda.gov
ATC/DDD Index — R03AC02 salbutamol classification. ATCDDD
StatPearls/peer-reviewed PK — low protein binding (~10%), clinical use overview; bioavailability/half-life ranges corroborated across labels. NCBI+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com