Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Pantoprazole is a substituted benzimidazole proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) used for short-term treatment and maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis due to GERD, and for pathological hypersecretory states (e.g., Zollinger–Ellison); oral bioavailability ~77%, terminal t½ ≈1 h, extensive CYP2C19-mediated metabolism, and ~98% protein binding.
Brand Names
Protonix; numerous generics
Name
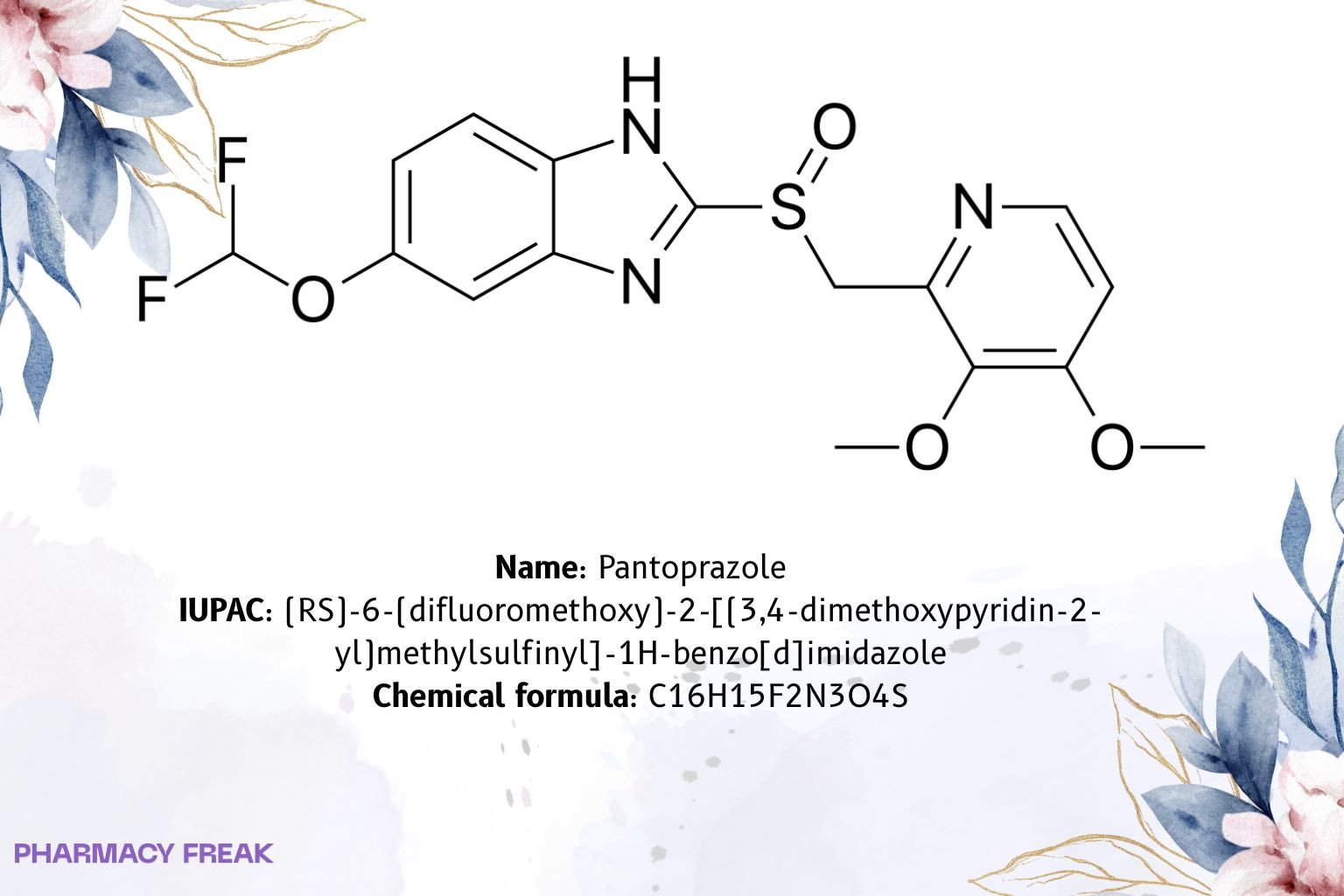
Pantoprazole
Background
Acid-labile prodrug; enteric-coated oral formulations and IV forms; activated in acidic canaliculi of gastric parietal cells to a sulfenamide that covalently binds the H⁺/K⁺-ATPase.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
![Pantoprazole 2D chemical structure (substituted benzimidazole sulfoxide). Formula C16H15F2N3O4S; IUPAC (RS)-6-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole; CAS 102625-70-7.](https://pharmacyfreak.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/panto2-1024x683.jpg)
Weight
~383.37 g/mol (base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₆H₁₅F₂N₃O₄S
Synonyms
(±)-Pantoprazole; BY-1029; SK&F-96022; 6-difluoromethoxy-2-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole
External IDs
CAS: 102625-70-7 (base); PubChem CID: 4679; UNII: D8TST4O562; ATC: A02BC02
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Healing/maintenance of erosive esophagitis associated with GERD; ZE and other hypersecretory conditions; part of H. pylori regimens per local guidance.
Associated Conditions
GERD with esophagitis, peptic disease requiring acid suppression, hypersecretory syndromes.
Associated Therapies
Triple/quadruple therapy for H. pylori (with antibiotics/bismuth per guideline).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
No boxed warning. Contraindicated in patients with known serious hypersensitivity to substituted benzimidazoles or formulation components. Class cautions include masking gastric malignancy, B-12 deficiency with long use, and label-specific warnings.
Pharmacodynamics
Irreversible inhibition of gastric H⁺/K⁺-ATPase; suppresses basal and stimulated acid secretion until new pumps are synthesized.
Mechanism of action
Prodrug accumulates in acidic canaliculi → converts to reactive sulfenamide → covalent disulfide bonds with cysteines on the proton pump → sustained acid suppression.
Absorption
Absolute bioavailability ~77%; t_max ~2.5 h; food may delay absorption without altering AUC.
Volume of distribution
~11–23.6 L (mainly extracellular fluid).
Protein binding
~98% (primarily albumin).
Metabolism
Extensive hepatic metabolism: CYP2C19 (major, demethylation→sulfation); CYP3A4 minor; metabolites lack significant activity.
Route of elimination
After labeled dosing: ~71% urine (metabolites), ~18% feces (biliary); no unchanged drug in urine.
Half-life
~1 hour (longer in CYP2C19 poor metabolizers and hepatic impairment).
Clearance
~7.6–14.0 L/h (IV data; extensive metabolizers).
Adverse Effects
Headache, diarrhea, nausea/abdominal pain; post-marketing/label class effects include hypomagnesemia, C. difficile-associated diarrhea, cutaneous lupus, AIN (see label).
Toxicity
Supportive care in overdose; consider electrolyte assessment and ECG if clinically indicated.
Pathways
Acid activation → covalent pump binding; hepatic biotransformation; renal/fecal elimination of metabolites.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
CYP2C19 polymorphism: poor metabolizers show higher AUC and prolonged t½ (adults ~3.5–10 h; higher exposure in pediatric PMs); dosing adjustment generally not required in adults; consider reduction in known pediatric PMs.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Do not co-administer with atazanavir or nelfinavir (marked ↓ antiviral exposure).
Warfarin: monitor INR.
pH-dependent absorption drugs (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, some TKIs): ↓ exposure.
Limited effect on probe substrates in studies (diazepam, phenytoin, midazolam, clarithromycin, metoprolol, diclofenac, naproxen, theophylline).
Food Interactions
Food may delay t_max; AUC unchanged. Tablets may be taken without regard to meals; follow product label.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
A02BC02 (proton-pump inhibitors)
Drug Categories
Proton-pump inhibitor; Acid-suppressant; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Substituted benzimidazole sulfoxide bearing difluoromethoxy aryl and 3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl methylsulfinyl substituents
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
D8TST4O562 (pantoprazole, base)
CAS number
102625-70-7
InChI Key
IQPSEEYGBUAQFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C16H15F2N3O4S/c1-23-13-5-6-19-12(14(13)24-2)8-26(22)16-20-10-4-3-9(25-15(17)18)7-11(10)21-16/h3-7,15H,8H2,1-2H3,(H,20,21)
IUPAC Name
(RS)-6-(difluoromethoxy)-2-[(3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzo[d]imidazole
SMILES
FC(F)Oc1ccc2[nH]c(nc2c1)S(=O)Cc3nccc(OC)c3OC
6. References
DailyMed (pantoprazole sodium delayed-release tablet): bioavailability ~77%, t_max ~2.5 h, t½ ~1 h, Vd 11–23.6 L, protein binding ~98%, hepatic metabolism via CYP2C19/3A4, urine 71% / feces 18% (no unchanged in urine); interaction bullets (atazanavir/nelfinavir, warfarin, pH-dependent drugs). DailyMed+1
PubChem (pantoprazole base): formula C16H15F2N3O4S, molar mass ~383.4 g/mol, identifiers (CAS, InChI/Key, SMILES). PubChem
FDA GSRS/UNII: Pantoprazole UNII D8TST4O562 (base); Pantoprazole sodium UNII 6871619Q5X (salt) and metadata. precisionFDA+1
ATC/DDD Index: A02BC02 classification (proton-pump inhibitors). atcddd.fhi.no

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com