Table of Contents
Introduction
Vonoprazan is a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB), introduced as a more potent and faster-acting alternative to proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It is primarily used for acid-related disorders such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Helicobacter pylori eradication.
Mechanism of Action (Stepwise Points)
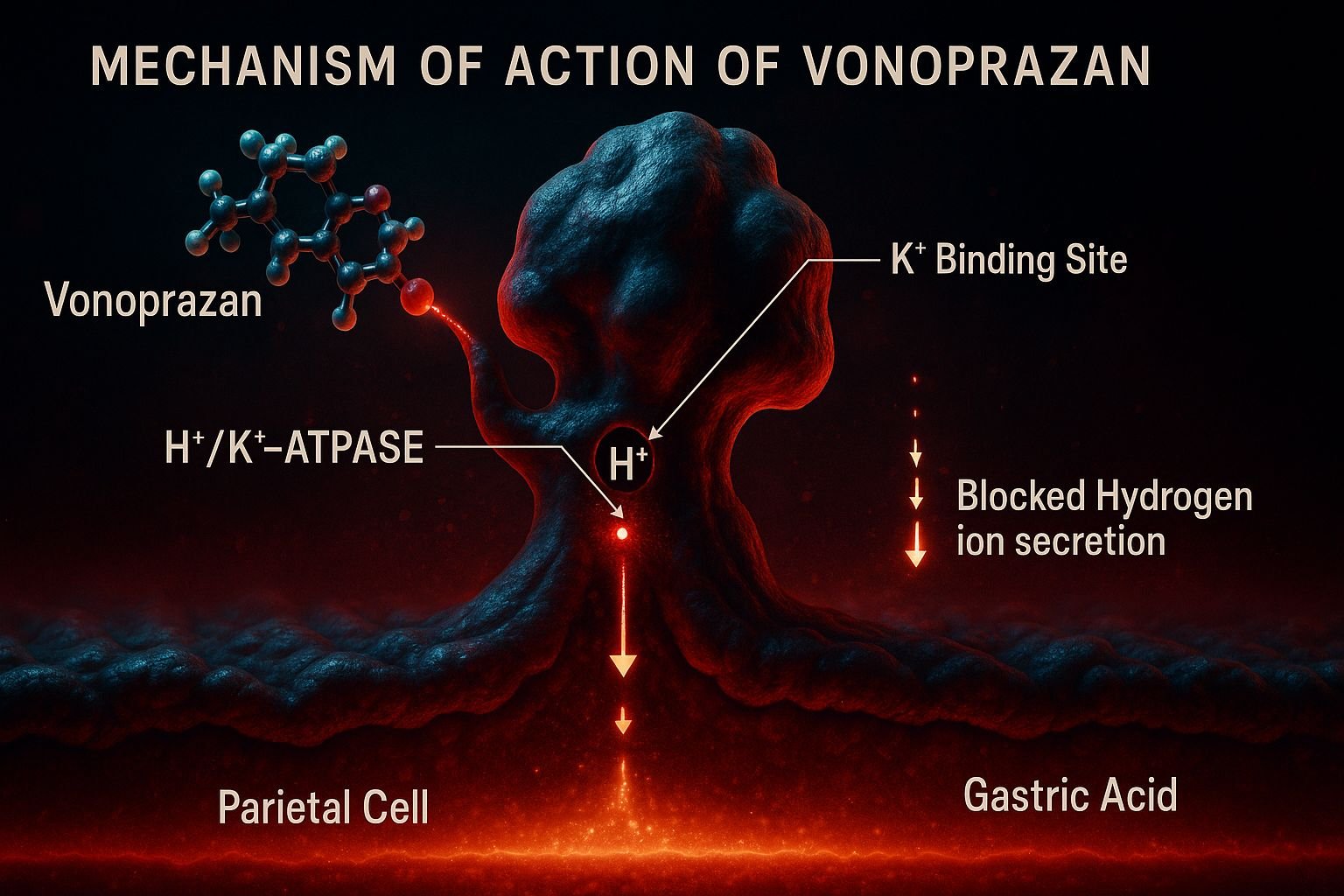
- Targeting the H⁺/K⁺-ATPase
Vonoprazan acts directly on the gastric H⁺/K⁺-ATPase enzyme (proton pump) in the parietal cells of the stomach. - Potassium-Competitive Inhibition
It competitively inhibits the K⁺ binding site of the enzyme, blocking the final step of acid secretion. - Acid-Independent Activation
Unlike PPIs, vonoprazan does not require acidic activation, allowing immediate onset of action. - Reversible Binding
Vonoprazan binds reversibly but tightly, offering prolonged and consistent acid suppression. - Stable Action
It maintains its effect regardless of circadian rhythms or food intake, making it more stable than traditional PPIs.


Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Rapid oral absorption with peak plasma concentrations within 2 hours.
- Bioavailability: High, with minimal influence from food.
- Metabolism: Primarily via CYP3A4; minor pathways include CYP2B6 and CYP2C19.
- Half-life: Approximately 7 hours.
- Elimination: Renal and fecal routes.
Clinical Uses
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
- Helicobacter pylori eradication (in combination regimens)
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (off-label use)
Adverse Effects
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Hypergastrinemia (with prolonged use)
- Elevated liver enzymes (rare)
- No significant CYP2C19 polymorphism effect
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Vonoprazan | Omeprazole | Pantoprazole |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | P-CAB | PPI | PPI |
| Acid Activation Required | No | Yes | Yes |
| Onset of Action | Fast (<2 hours) | Delayed (1–3 days) | Delayed (1–3 days) |
| CYP2C19 Influence | Minimal | Significant | Moderate |
| Binding | Reversible | Irreversible | Irreversible |
| Use in H. pylori Eradication | Yes (superior) | Yes | Yes |
Explanation: Vonoprazan provides more consistent and rapid acid suppression than PPIs, with fewer inter-individual variations due to genetic polymorphisms.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Vonoprazan belongs to which class of drugs?
a) PPI
b) Potassium-competitive acid blocker
c) H2 receptor antagonist
d) Prokinetic agent - Vonoprazan inhibits:
a) Gastrin receptors
b) H⁺/K⁺-ATPase enzyme
c) M3 receptors
d) Carbonic anhydrase - Vonoprazan differs from PPIs in that it:
a) Acts slowly
b) Requires acid activation
c) Acts immediately and reversibly
d) Causes more side effects - Which enzyme metabolizes vonoprazan?
a) CYP2C19 exclusively
b) CYP2D6
c) CYP3A4
d) UGT1A1 - Vonoprazan is preferred in:
a) Mild reflux only
b) Delayed acid suppression
c) Rapid and potent acid suppression
d) Antiemetic therapy - What makes vonoprazan superior for H. pylori treatment?
a) Longer half-life
b) Less absorption
c) More consistent acid suppression
d) Hepatic excretion - Binding nature of vonoprazan to proton pumps is:
a) Irreversible
b) Reversible
c) Allosteric
d) Covalent - Primary site of action of vonoprazan is:
a) Parietal cell nucleus
b) Parietal cell membrane H⁺/K⁺-ATPase
c) Chief cells
d) Enterochromaffin cells - Which adverse effect is least common with vonoprazan?
a) Diarrhea
b) Hypergastrinemia
c) Hepatotoxicity
d) Headache - Vonoprazan’s efficacy is least affected by:
a) Food intake
b) Genetic polymorphism
c) Circadian rhythm
d) All of the above
FAQs
Q1: Is vonoprazan available globally?
A1: Initially launched in Japan, it’s now available in several countries including the US and EU markets.
Q2: Can vonoprazan be used long-term?
A2: Yes, but monitoring for hypergastrinemia and mucosal changes is advised.
Q3: Does vonoprazan interact with clopidogrel?
A3: Minimal interaction due to less CYP2C19 dependency.
Q4: How soon does vonoprazan start working?
A4: Within 1–2 hours of the first dose.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Pharmacological Screening Methods & Toxicology by Avanapu Srinivasa Rao
- Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics by Thakur Publication
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com