Table of Contents
Introduction
Sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics that inhibit folic acid synthesis in bacteria. Because mammals obtain folate from the diet, while bacteria synthesize it de novo, sulfonamides offer selective toxicity. Commonly used sulfonamides include sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine, and sulfisoxazole — often combined with trimethoprim for synergistic effects.
This class is important in pharmacology exams like USMLE, NCLEX, GPAT, and NEET-PG, particularly when discussing antimetabolites, combination therapy, and resistance patterns.
Stepwise Mechanism of Action of Sulfonamides
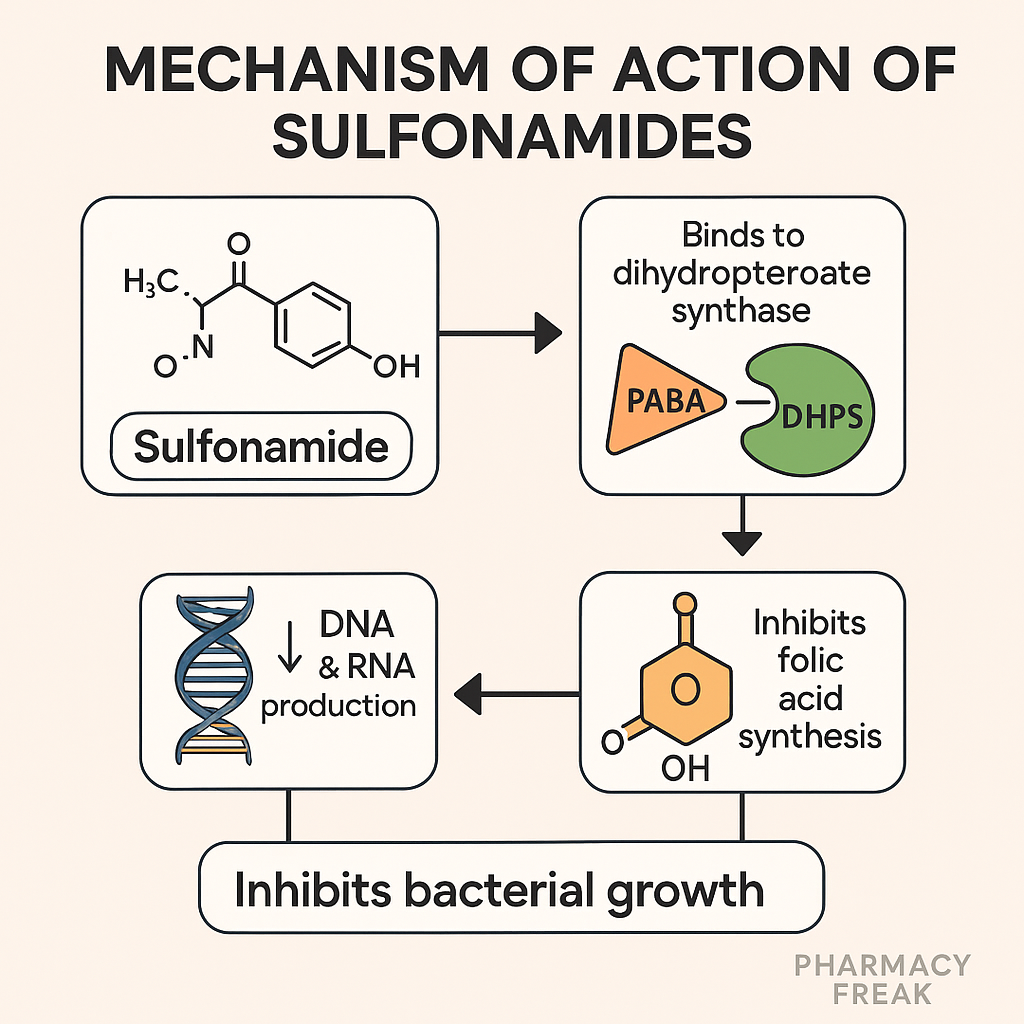
- Analog of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
Sulfonamides are structural analogs of PABA, a substrate for folic acid synthesis in bacteria. - Inhibition of dihydropteroate synthase
Sulfonamides competitively inhibit the dihydropteroate synthase enzyme, blocking the conversion of PABA to dihydropteroic acid. - Inhibition of folate synthesis
Without folic acid production, tetrahydrofolate (THF) is not formed, which is essential for DNA synthesis and repair in bacteria. - Bacteriostatic effect
Inhibition of DNA synthesis halts bacterial cell division, making sulfonamides bacteriostatic. - Selective toxicity
Humans lack dihydropteroate synthase and obtain folic acid from the diet, hence sparing host cells.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Sulfonamides (e.g., Sulfamethoxazole)
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | High (oral) |
| Half-life | ~10 hours (sulfamethoxazole) |
| Protein binding | ~70% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (acetylation) |
| Excretion | Renal |
| CNS penetration | Moderate (esp. sulfadiazine) |
Clinical Uses of Sulfonamides
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Nocardiosis
- Toxoplasmosis (sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine)
- Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (SMX-TMP)
- Shigellosis and traveler’s diarrhea
- Burn wound infections (topical silver sulfadiazine)
- Prophylaxis in HIV-positive patients (PJP, toxoplasma)
Adverse Effects of Sulfonamides
- Hypersensitivity reactions (rashes, Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
- Photosensitivity
- Hemolysis in G6PD deficiency
- Kernicterus in neonates (displacement of bilirubin)
- Crystalluria and nephrotoxicity
- Megaloblastic anemia (with long-term use)
Comparative Analysis: Sulfonamides Alone vs Cotrimoxazole (SMX-TMP)
| Feature | Sulfonamide Alone | Cotrimoxazole (SMX + TMP) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Dihydropteroate synthase inhibition | Dual blockade (folate pathway) |
| Effect | Bacteriostatic | Bactericidal |
| Spectrum | Narrower | Broader |
| Clinical use | Limited | Common in UTIs, PJP, toxoplasmosis |
Practice MCQs
Q1. Sulfonamides act by inhibiting which bacterial enzyme?
a. Dihydrofolate reductase
b. DNA gyrase
c. Dihydropteroate synthase ✅
d. Peptidoglycan synthase
Q2. Which bacterial pathway is blocked by sulfonamides?
a. Protein synthesis
b. Folic acid synthesis ✅
c. Cell wall synthesis
d. DNA repair
Q3. Sulfonamides are structurally similar to:
a. Tetrahydrofolate
b. Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) ✅
c. Thymidine
d. Ribose
Q4. A severe skin reaction caused by sulfonamides is:
a. Urticaria
b. Atopic dermatitis
c. Stevens-Johnson syndrome ✅
d. Lichen planus
Q5. Sulfonamides are contraindicated in:
a. Pregnancy
b. Neonates
c. G6PD deficiency
d. All of the above ✅
Q6. Why are sulfonamides bacteriostatic?
a. Inhibit protein formation
b. Block folate uptake
c. Arrest DNA synthesis ✅
d. Disrupt membranes
Q7. Which condition is treated with sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine?
a. Malaria
b. Toxoplasmosis ✅
c. Tuberculosis
d. Filariasis
Q8. Which adverse effect occurs in G6PD deficiency?
a. Hepatitis
b. Hemolysis ✅
c. Ototoxicity
d. Anaphylaxis
Q9. Which of the following increases sulfonamide crystalluria risk?
a. Acidic urine ✅
b. Alkaline urine
c. High protein diet
d. Low-fat diet
Q10. Cotrimoxazole exerts a bactericidal effect by:
a. DNA damage
b. Blocking 30S & 50S
c. Sequential folate synthesis blockade ✅
d. Protein denaturation
FAQs
Q1: Can sulfonamides be used in pregnancy?
They are not recommended, especially near term, due to risk of kernicterus in newborns.
Q2: Why are sulfonamides contraindicated in neonates?
They displace bilirubin from albumin, increasing the risk of kernicterus.
Q3: What is the most common side effect?
Hypersensitivity reactions like rashes are the most common.
Q4: Do sulfonamides cover anaerobes?
Coverage is limited — mostly aerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms.
Q5: What is the difference between sulfonamides and trimethoprim?
Sulfonamides inhibit dihydropteroate synthase, while trimethoprim inhibits dihydrofolate reductase — both in folate pathway.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Sparsh Gupta – Review of Pharmacology
- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547663/

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com