Table of Contents
Introduction
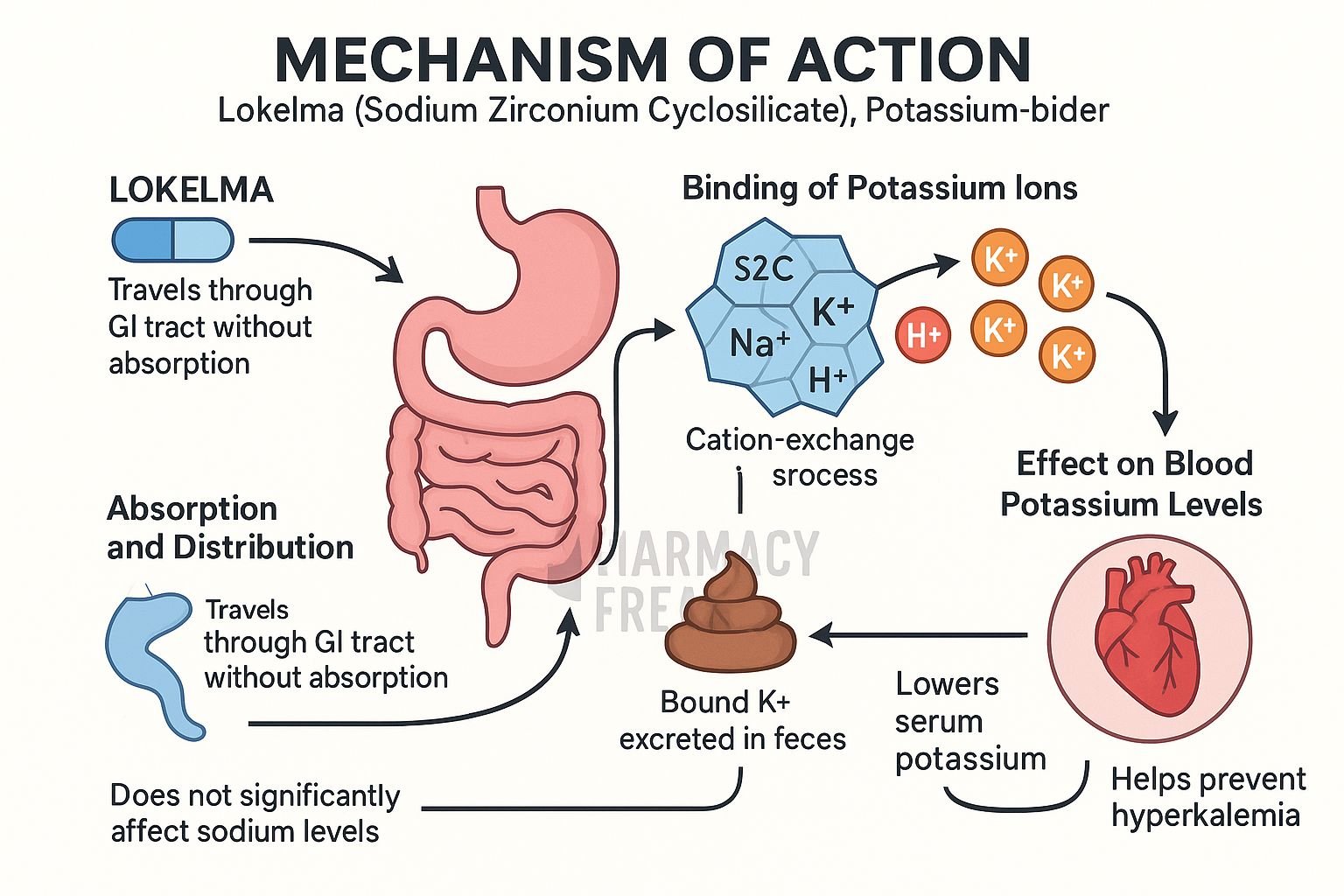
Lokelma is an oral, non-absorbed potassium binder used to treat hyperkalemia. It works by selectively trapping potassium ions in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby lowering serum potassium levels and promoting potassium excretion via feces.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Selective potassium capture
Lokelma is a crystalline inorganic compound with micropores that mimic potassium channels, enabling highly selective binding of K⁺ throughout the GI tract lokelma-hcp.com+7en.wikipedia.org+7ema.europa.eu+7go.drugbank.com+1ema.europa.eu+1. - Ion exchange process
While binding potassium, Lokelma exchanges sodium and hydrogen ions, maintaining its ion balance ema.europa.eu+2go.drugbank.com+2en.wikipedia.org+2. - Intra-luminal potassium reduction
By decreasing free GI potassium, it creates a gradient that draws potassium from the bloodstream into the gut lumen for binding pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+7go.drugbank.com+7myastrazeneca.co.uk+7. - Increased fecal excretion
The bound potassium is eliminated in feces, reducing serum levels. Normokalemia is often achieved within 24–48 hours, with effects beginning as early as 1 hour post-dose go.drugbank.com+1ema.europa.eu+1.

Pharmacokinetic Parameters
- Absorption: Not absorbed; acts locally within the GI tract pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+5go.drugbank.com+5ema.europa.eu+5
- Time to action: Begins reducing serum potassium ≈1 hour after administration pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+5go.drugbank.com+5ema.europa.eu+5
- Excretion: Eliminated completely in feces; no systemic metabolism go.drugbank.com+1ema.europa.eu+1
Clinical Uses
- Acute and chronic hyperkalemia management in patients with conditions like CKD, heart failure, or using RAAS inhibitors
- Not suitable for emergency hyperkalemia due to delayed onset
Adverse Effects
- Hypokalemia due to potassium over-elimination
- Edema, possibly related to sodium exchange en.wikipedia.org+4ema.europa.eu+4drugs.com+4drugs.com
- Gastrointestinal discomfort (e.g., edema, constipation, diarrhea)
Comparative Analysis
Lokelma offers higher selectivity and fewer systemic effects than older potassium binders like sodium polystyrene sulfonate. It provides rapid onset and predictable action, with lower risk of fluid shifts and electrolyte imbalances.
MCQs
- Lokelma acts by binding which ion?
a) Calcium b) Potassium c) Magnesium d) Sodium
Answer: b) Potassium - The primary route of potassium elimination with Lokelma is:
a) Renal b) Pulmonary c) Fecal d) Sweating
Answer: c) Fecal - Which ions are exchanged when Lokelma binds potassium?
a) Calcium & sodium b) Sodium & hydrogen c) Magnesium & sodium d) Hydrogen & calcium
Answer: b) Sodium & hydrogen - Onset of action usually occurs in:
a) 5 minutes b) 1 hour c) 6 hours d) 24 hours
Answer: b) 1 hour - Lokelma is systemically absorbed?
a) Yes b) No Answer: b) No - Common side effect due to sodium exchange:
a) Dehydration b) Edema c) Hypocalcemia d) Hypomagnesemia
Answer: b) Edema - Lokelma is contraindicated in:
a) Severe hyperkalemia emergency b) Mild hyperkalemia c) CKD patients d) RAAS inhibitor use
Answer: a) Severe hyperkalemia emergency - The compound mimics:
a) Sodium channels b) Potassium channels c) Calcium channels d) Claudin junctions
Answer: b) Potassium channels - Lokelma effect on urinary potassium excretion is:
a) Increased b) Unchanged c) Decreased d) Fluctuating
Answer: c) Decreased - Elimination occurs via:
a) Kidneys b) Liver c) Feces d) Sweat
Answer: c) Feces - Administered how?
a) IV b) Oral suspension c) SC injection d) Tablet
Answer: b) Oral suspension - Lokelma starts reducing potassium after:
a) 5 minutes b) 1 hour c) 12 hours d) 48 hours
Answer: b) 1 hour - A key advantage over older resins:
a) Rapid systemic absorption b) Better palatability c) Improved specificity & tolerability d) Lower cost
Answer: c) Improved specificity & tolerability - Lokelma’s binding is ________ in presence of calcium and magnesium.
a) Reduced b) Unchanged c) Enhanced d) Variable
Answer: b) Unchanged - It is best used in:
a) Life-threatening hyperkalemia b) Chronic hyperkalemia c) Hypokalemia d) Acid-base disorders
Answer: b) Chronic hyperkalemia
FAQs
- Can Lokelma be used in emergency hyperkalemia?
No—it works too slowly for emergencies and is best for non-emergent cases. - How quickly does it normalize potassium?
Effects begin in ≈1 hour; most patients normalize within 24–48 hours. - Does Lokelma affect serum calcium or magnesium?
No measurable changes in these electrolytes have been observed. - Should sodium-based Lokelma be used in heart failure?
Caution is advised due to sodium content possibly causing edema. - Can Lokelma alter absorption of other drugs?
It may alter stomach pH transiently—some medications should be spaced by 2 hours.
References
- LOKELMA prescribing information—selective K⁺ binding throughout the GI tract pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+7lokelma-hcp.com+7en.wikipedia.org+7drugs.com+4en.wikipedia.org+4go.drugbank.com+4drugs.com+4myastrazeneca.co.uk+4go.drugbank.com+4ema.europa.eugo.drugbank.com
- DrugBank entry on sodium zirconium cyclosilicate mechanism myastrazeneca.co.uk+6go.drugbank.com+6en.wikipedia.org+6
- Drugs.com summary: Lokelma binds K⁺ in exchange for Na⁺ and H⁺
- EMA Lokelma product info on mechanism and adverse effects
- Pharmacodynamics review by Packham et al. on rapid and irreversible K⁺ trapping pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com