Table of Contents
Introduction
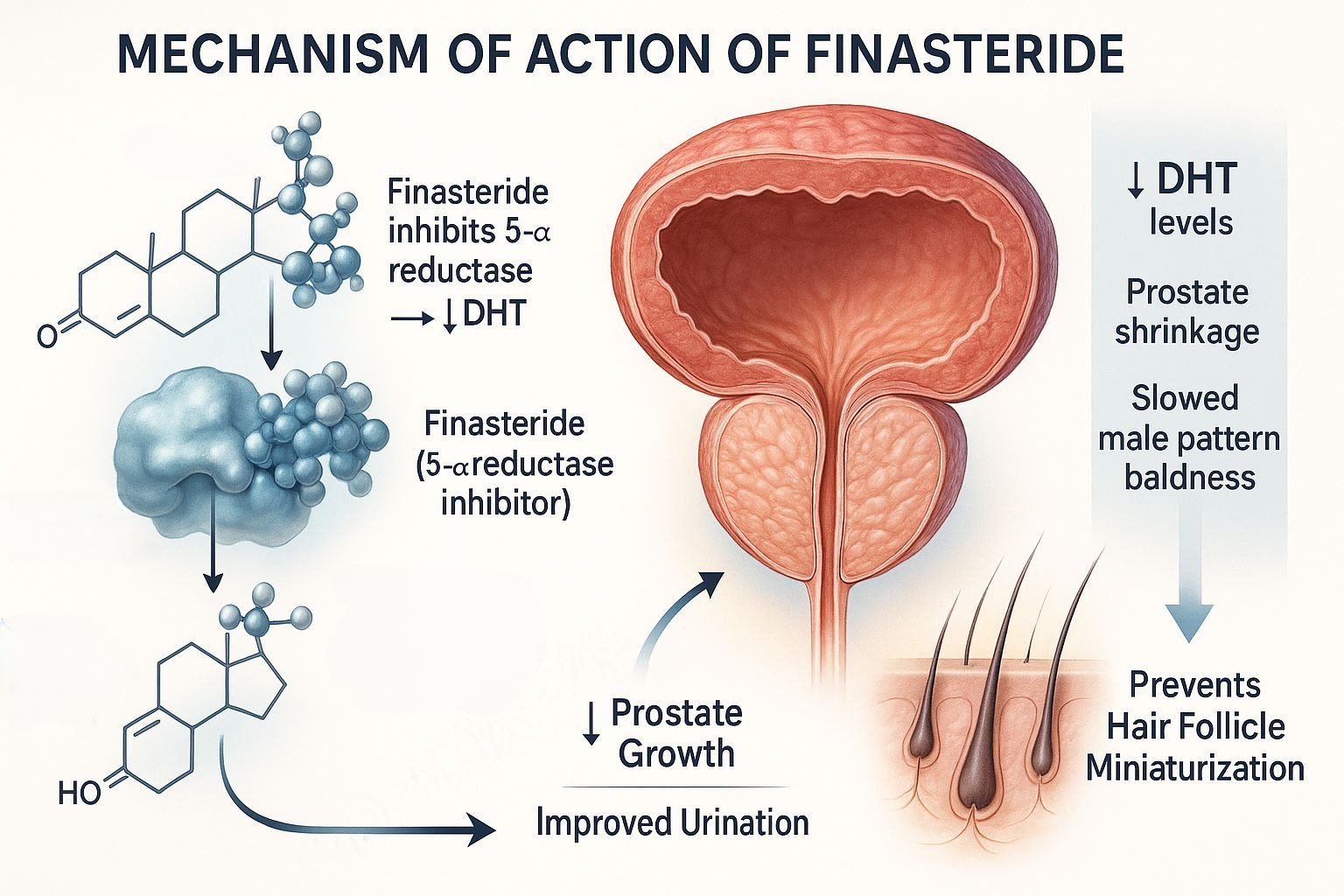
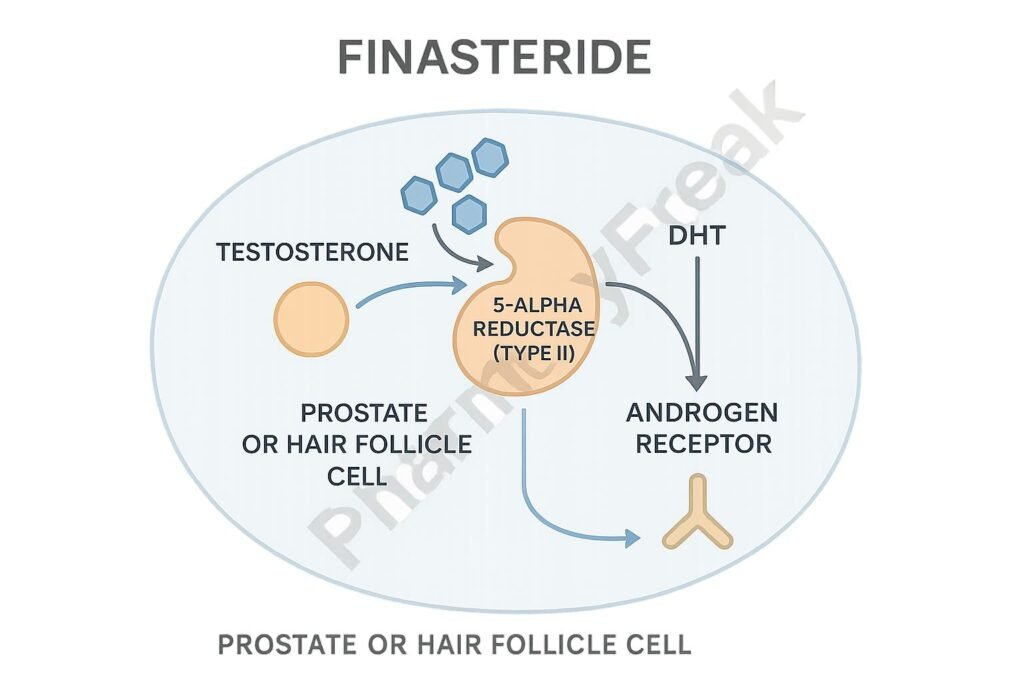
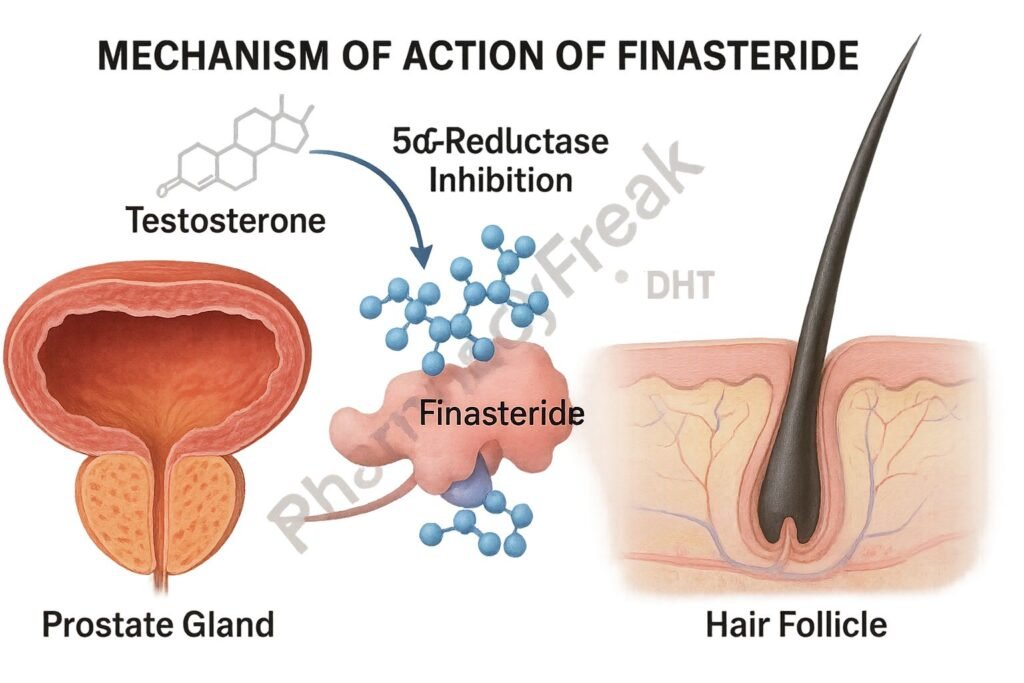
Finasteride is a synthetic 4-azasteroid that functions as a competitive and specific inhibitor of type II 5-alpha-reductase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a potent androgen involved in the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and androgenetic alopecia. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride alleviates symptoms associated with these conditions.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
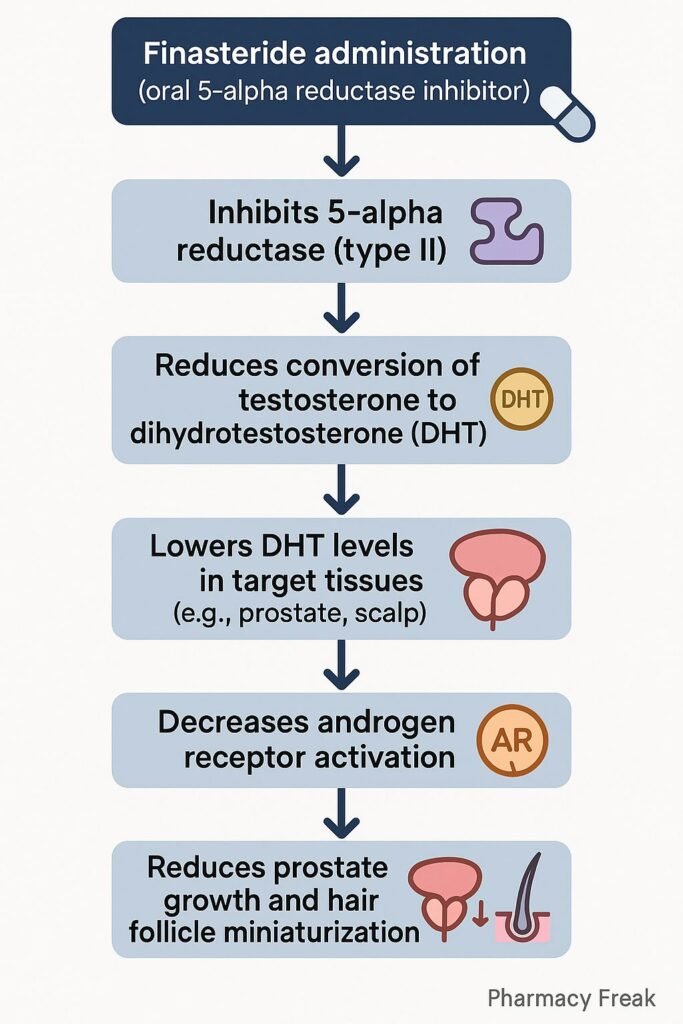
1. Inhibition of Type II 5α-Reductase
Finasteride binds competitively to the type II isoform of the enzyme 5α-reductase.
2. Decreased DHT Synthesis
This inhibition prevents the conversion of testosterone to DHT in tissues like the prostate and scalp.
3. Reduction in DHT Concentration
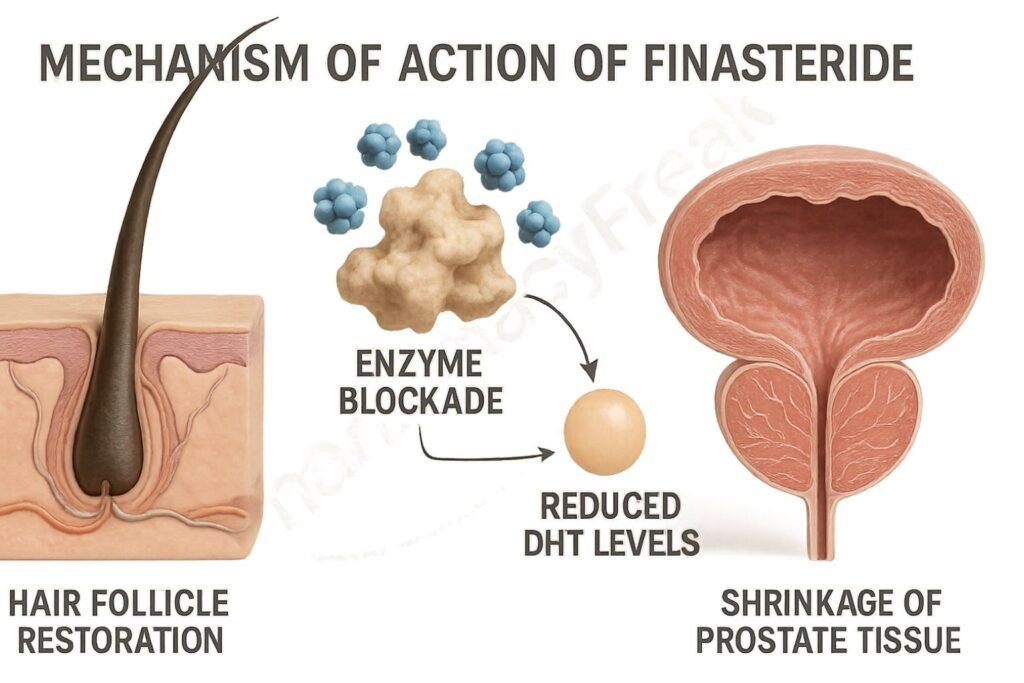
Serum and tissue levels of DHT fall significantly (up to 70%), particularly in the prostate.
4. Suppression of Prostate Growth
Reduced DHT leads to a decrease in prostate volume and improvement in urinary flow symptoms in BPH.
5. Hair Follicle Miniaturization Prevention
In scalp tissue, decreased DHT slows or reverses the miniaturization of hair follicles in androgenetic alopecia.
- Route of Administration: Oral
- Bioavailability: ~65%
- Peak Plasma Concentration: 1–2 hours
- Half-Life: 5–6 hours (young men), up to 8 hours (elderly)
- Metabolism: Hepatic (CYP3A4)
- Excretion: Primarily fecal (via bile), minor renal excretion
Clinical Uses
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- Androgenetic Alopecia (male pattern hair loss)
- Off-label: Hormonal management in transgender women, prostate cancer chemoprevention (controversial)
Adverse Effects
- Sexual dysfunction: Decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, ejaculatory disorders
- Gynecomastia (rare)
- Depression and anxiety (reported, debated)
- Risk of high-grade prostate cancer (controversial)
- Contraindications: Pregnancy (teratogenic), pediatric patients, women of reproductive age
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Finasteride | Dutasteride |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme Inhibition | Type II 5α-reductase | Type I and II 5α-reductase |
| DHT Reduction | ~70% | >90% |
| Onset of Action | Weeks to months | Similar |
| Half-Life | ~6 hours | ~5 weeks |
| Approved Uses | BPH, Alopecia | BPH |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Finasteride primarily inhibits which enzyme?
a) Aromatase
b) 5α-reductase type II
c) 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
d) CYP3A4
Answer: b) 5α-reductase type II
2. What is the clinical effect of reduced DHT levels in BPH?
a) Increased prostate growth
b) Suppression of testosterone
c) Prostate shrinkage
d) Increased libido
Answer: c) Prostate shrinkage
3. Which of the following is NOT an approved use of finasteride?
a) BPH
b) Male pattern baldness
c) Prostate cancer
d) Androgenetic alopecia
Answer: c) Prostate cancer
4. Finasteride should be avoided in:
a) Elderly men
b) Diabetic patients
c) Pregnant women
d) Hypertensive patients
Answer: c) Pregnant women
5. How is finasteride primarily excreted?
a) Renally
b) Through sweat
c) Fecally via bile
d) Through lungs
Answer: c) Fecally via bile
FAQs
Q1. How long does it take for finasteride to show results in BPH?
Usually 3–6 months for significant symptom improvement.
Q2. Can women use finasteride?
No, it is contraindicated in women, especially during pregnancy.
Q3. Does finasteride cause permanent sexual dysfunction?
Sexual side effects are usually reversible, though persistent cases have been reported.
Q4. What should patients avoid while taking finasteride?
Avoid donating blood while on therapy and for 1 month after stopping due to risk to pregnant recipients.
Q5. Is monitoring PSA necessary in patients on finasteride?
Yes, PSA levels decrease with finasteride; adjusted interpretation is needed for prostate cancer screening.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Product monograph for finasteride
- Clinical guidelines for BPH and alopecia management
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com