Table of Contents
Introduction
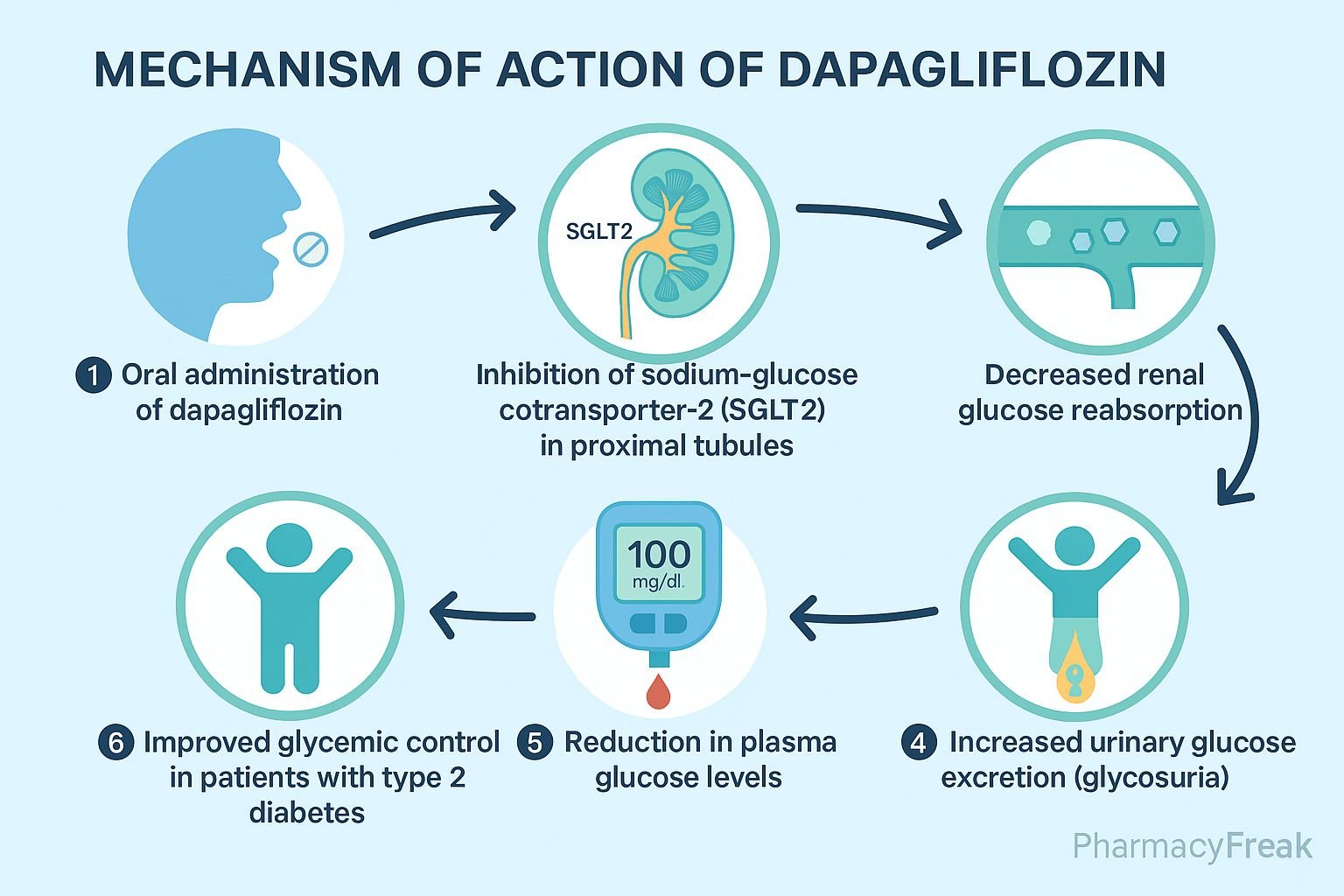
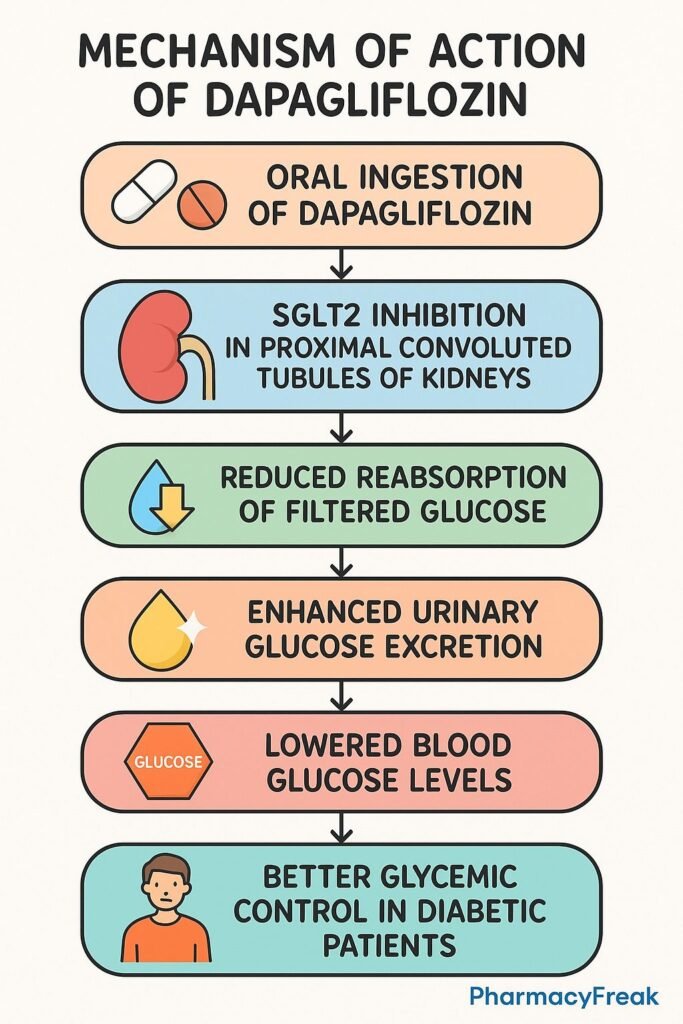
Dapagliflozin is an oral sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Additionally, it offers benefits in heart failure and chronic kidney disease, independent of its glucose-lowering effects.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Selective SGLT2 inhibition in proximal tubules
Dapagliflozin specifically inhibits the SGLT2 transporter in the early proximal convoluted tubule of the kidney. - Reduced renal glucose reabsorption
Normally responsible for about 90% of filtered glucose reabsorption, inhibition leads to elevated urinary glucose excretion (glucosuria). - Osmotic diuresis and natriuresis
Excretion of glucose pulls water and sodium prematurely into the urine, decreasing plasma volume and blood pressure. - Improved glycemic control
By lowering blood glucose via glucosuria, it helps reduce HbA1c without stimulating insulin secretion. - Weight reduction
Caloric loss through urinary glucose excretion leads to modest weight loss. - Cardiorenal protective effects
Volume reduction, decreased intraglomerular pressure, improved vascular function, and metabolic adaptations translate to reduced heart failure hospitalizations and slowed chronic kidney disease progression.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Oral, once daily |
| Bioavailability | ~78% |
| Protein Binding | ~91% |
| Metabolism | Glucuronidation (UGT1A9) |
| Half-life | ~12.9 hours |
| Excretion | Metabolites excreted via urine and feces |
Clinical Uses
- Glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)
- Management of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in diabetics and non-diabetics
Adverse Effects
- Genital mycotic infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Volume depletion (e.g., hypotension, dizziness)
- Rare risk of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis
- Slight increase in LDL cholesterol; rare cases of Fournier’s gangrene
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | SGLT2 Selectivity | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dapagliflozin | High | T2DM, heart failure, CKD, cardiovascular protection |
| Empagliflozin | Very high | Similar benefits; strongest CV data |
| Canagliflozin | Moderate | Adds modest SGLT1 inhibition; amputation risk noted |
MCQs
- Dapagliflozin inhibits transporters in the:
a) Distal tubule b) Loop of Henle c) Proximal tubule d) Collecting duct
Answer: c) Proximal tubule - Primary metabolic effect is:
a) Insulin release b) Glucosuria c) Hepatic gluconeogenesis d) Glucose absorption
Answer: b) Glucosuria - Which effect contributes to blood pressure reduction?
a) Vasodilation b) Natriuresis c) Beta-blockade d) ACE inhibition
Answer: b) Natriuresis - The half-life of dapagliflozin is approximately:
a) 1 hour b) 6 hours c) 12.9 hours d) 24 hours
Answer: c) 12.9 hours - Weight loss with dapagliflozin is due to:
a) Appetite suppression b) Caloric loss in urine c) Fat metabolism d) Increased exercise
Answer: b) Caloric loss in urine - A serious but rare complication is:
a) Euglycemic ketoacidosis b) Hypernatremia c) Hypokalemia d) Hepatic failure
Answer: a) Euglycemic ketoacidosis - Metabolism of dapagliflozin is primarily through:
a) CYP3A4 b) CYP2D6 c) Glucuronidation d) Renal unchanged
Answer: c) Glucuronidation - Cardiorenal protection is due to:
a) Beta-cell preservation b) Intraglomerular pressure reduction c) Increased preload d) Increased HDL
Answer: b) Intraglomerular pressure reduction - Which infections are most common?
a) GI b) Genital mycotic c) Respiratory d) Bloodstream
Answer: b) Genital mycotic - Compared to canagliflozin, dapagliflozin:
a) Inhibits SGLT1 b) Has higher UGT metabolism c) Has less risk of amputations d) Is injectable
Answer: c) Has less risk of amputations
FAQs
1. Is dapagliflozin suitable for non-diabetic patients with kidney disease?
Yes—it’s approved for CKD even in non-diabetics due to its nephroprotective effects.
2. Does it cause hypoglycemia?
Unlikely when used alone, but risk increases with insulin or sulfonylureas.
3. Should renal function be monitored?
Yes—efficacy and safety depend on kidney function; dose adjustments may be required.
4. How long does it take to show cardiovascular benefit?
Benefits on heart failure outcomes may appear within weeks to months of initiation.
5. Are genital infections preventable?
Good hygiene and prompt treatment can reduce the incidence.
References

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com