Table of Contents
Introduction
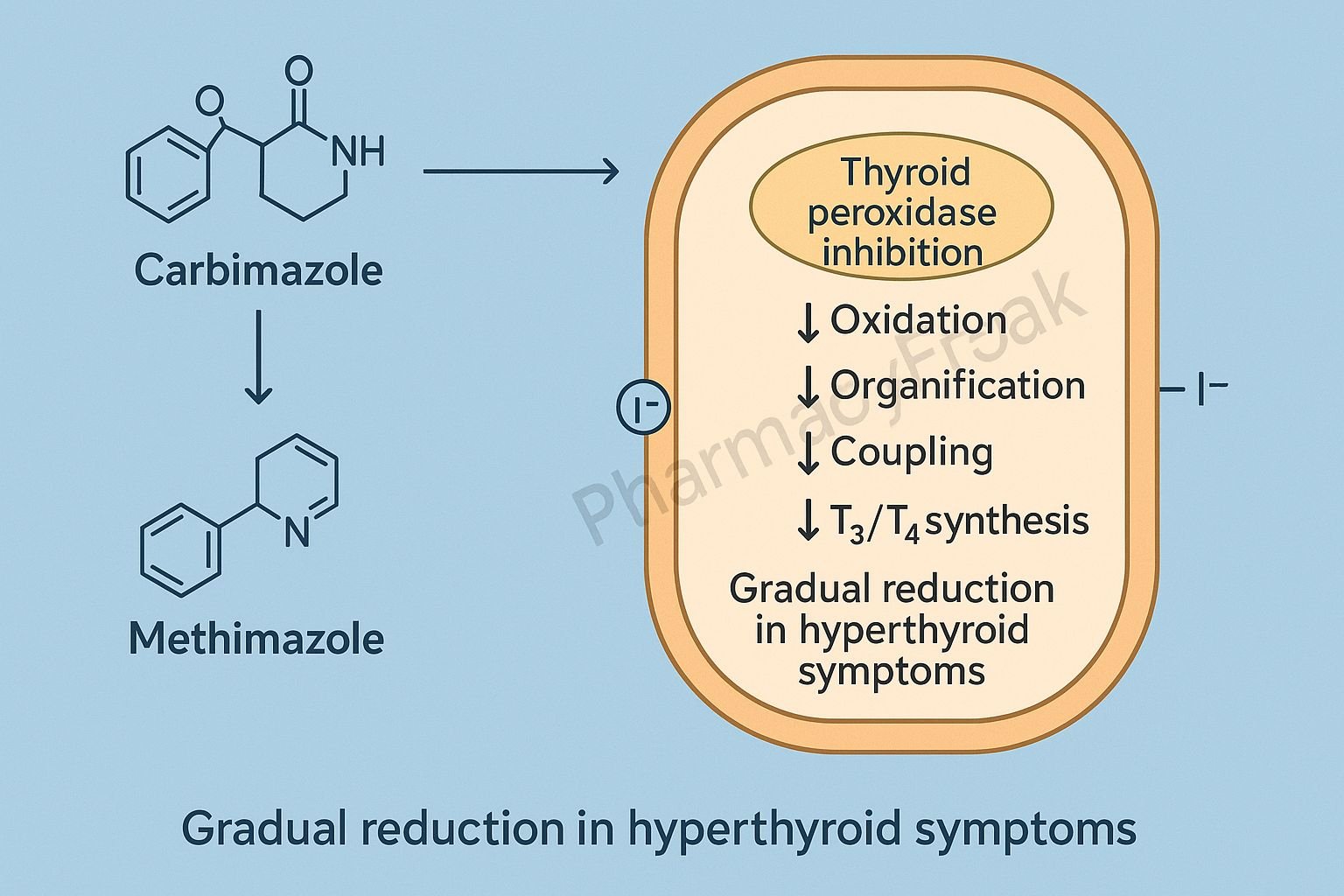
Carbimazole is a thiourea-derived antithyroid drug used primarily in the management of hyperthyroidism, especially Graves’ disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and thyroid storm (as adjunct therapy). After oral administration, carbimazole is rapidly converted to its active metabolite methimazole, which exerts the therapeutic effects.
The Mechanism of Action of Carbimazole involves suppression of thyroid hormone synthesis through inhibition of thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and interference with iodine organification and coupling reactions.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
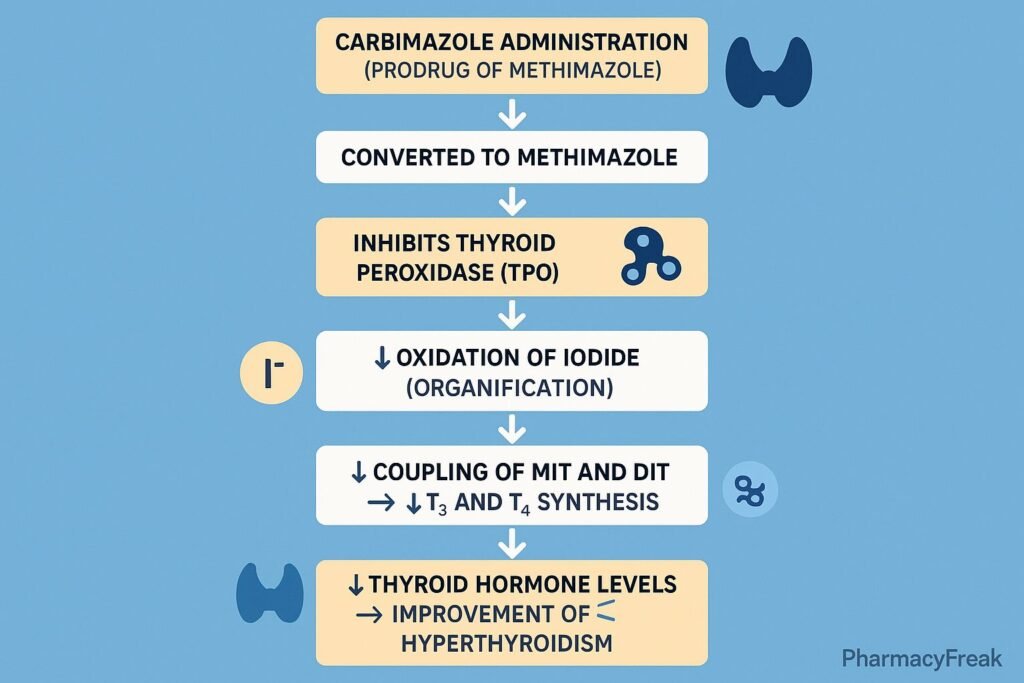
1. Conversion to Active Form: Methimazole
Carbimazole itself is a prodrug.
After absorption:
Carbimazole → Methimazole (active form)
Methimazole mediates all pharmacological effects.
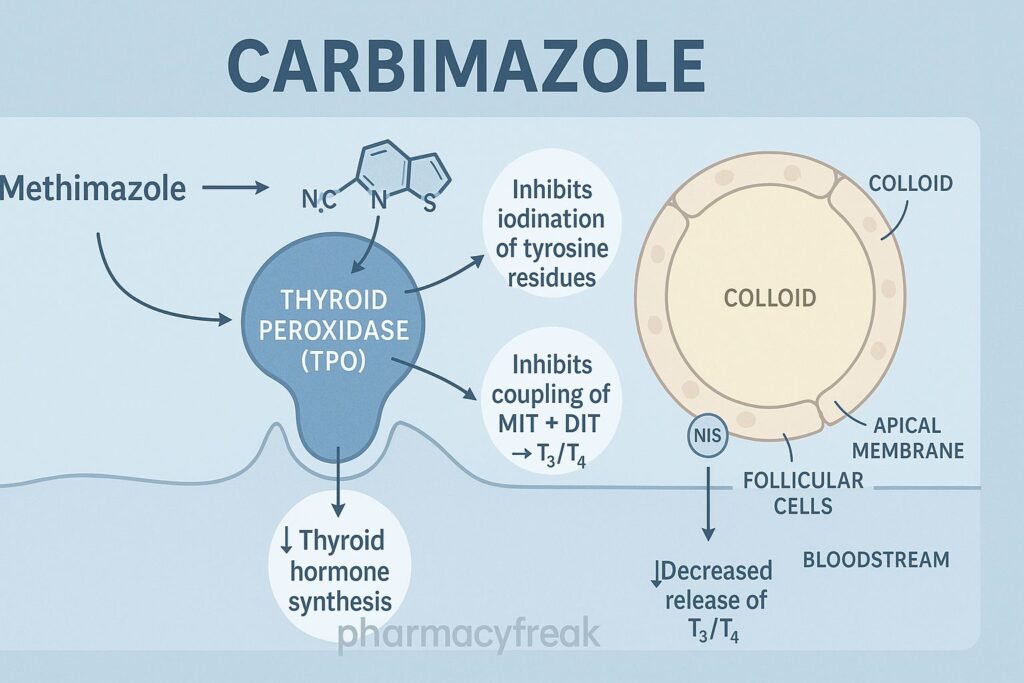
2. Inhibition of Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO) – Primary Mechanism
Methimazole blocks the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, which catalyzes three essential steps in thyroid hormone synthesis:
a) Inhibition of Iodide Oxidation
Iodide (I⁻) → Iodine (I₂)
b) Inhibition of Iodine Organification
Iodine binds to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin to form MIT and DIT.
c) Inhibition of Coupling Reactions
- MIT + DIT → T3
- DIT + DIT → T4
Result: ↓ T3 and T4 synthesis.
3. Does NOT Inhibit Release of Preformed Hormone
Carbimazole does not block the release of stored T3/T4 from the thyroid gland.
Since hormone stores last 2–4 weeks, clinical improvement is gradual.
4. Immunomodulatory Effects (Secondary)
Carbimazole exerts mild immunosuppressive effects:
- ↓ Thyroid-stimulating antibodies (TSI) in Graves’ disease
- ↑ Lymphocyte apoptosis
This contributes to long-term remission.
5. No Effect on Peripheral Conversion
Unlike propylthiouracil (PTU), carbimazole:
- Does not inhibit 5’-deiodinase
- Does not decrease T4 → T3 conversion
Thus, PTU is preferred in thyroid storm.
6. Summary of Mechanism
| Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|
| TPO inhibition | ↓ T3 and T4 synthesis |
| Blocks organification | Prevents iodination of thyroglobulin |
| Blocks coupling | Prevents formation of T3/T4 |
| No effect on release | Slow clinical onset |
| Mild immunosuppression | Remission in Graves’ disease |
Pharmacokinetics
- Prodrug: Carbimazole → methimazole
- Absorption: Rapid oral absorption
- Half-life: 6–8 hours
- Duration: Long due to intrathyroidal accumulation
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Excretion: Renal
Clinical Uses
- Graves’ disease
- Toxic multinodular goiter
- Preoperative preparation for thyroidectomy
- Adjunct in radioactive iodine therapy
- Thyrotoxicosis in pregnancy (if PTU not tolerated after 1st trimester)
Adverse Effects
Common
- Rash
- Pruritus
- Arthralgia
- Nausea
Serious
- Agranulocytosis (life-threatening)
- Hepatotoxicity
- Aplastic anemia
- Vasculitis (ANCA-positive)
Warning: Sudden fever or sore throat → rule out agranulocytosis.
Contraindications
- Pregnancy in first trimester (prefer PTU early in pregnancy)
- Liver disease
- Previous carbimazole-induced agranulocytosis
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Carbimazole | Propylthiouracil (PTU) |
|---|---|---|
| Prodrug | Yes | No |
| TPO inhibition | Yes | Yes |
| Peripheral T4→T3 inhibition | No | Yes |
| Use in pregnancy | Avoid in 1st trimester | Preferred in 1st trimester |
| Potency | Higher | Lower |
| Dosing | Less frequent | More frequent |
MCQs
1. Carbimazole reduces thyroid hormone synthesis by inhibiting:
a) Thyroid peroxidase
b) Sodium-iodide symporter
c) 5’-deiodinase
d) TSH receptors
Answer: a) Thyroid peroxidase
2. Carbimazole does NOT affect:
a) Organification of iodine
b) Coupling reactions
c) Release of stored T3/T4
d) TPO activity
Answer: c) Release of stored T3/T4
3. Methimazole is formed from:
a) PTU
b) Carbimazole
c) T3
d) Tyrosine
Answer: b) Carbimazole
4. Agranulocytosis due to carbimazole usually presents with:
a) Hypothermia
b) Fever and sore throat
c) Polyuria
d) Bradycardia
Answer: b) Fever and sore throat
5. Carbimazole does not inhibit peripheral conversion of:
a) T4 to T3
b) T3 to T4
c) Tyrosine iodination
d) MIT/DIT coupling
Answer: a) T4 to T3
FAQs
Q1. How long does carbimazole take to work?
2–4 weeks due to presence of preformed hormone.
Q2. Can carbimazole be used in pregnancy?
Avoid in first trimester; PTU is preferred early, carbimazole later.
Q3. What is the most serious side effect?
Agranulocytosis.
Q4. Is carbimazole better than PTU?
Yes, except in thyroid storm and first-trimester pregnancy.
Q5. How should patients monitor for toxicity?
Watch for fever or sore throat; get urgent CBC.
References
Goodman & Gilman’s Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2189
Katzung: Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2464
Tripathi: Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://jaypeebrothers.com/
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2129

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com