Table of Contents
Introduction
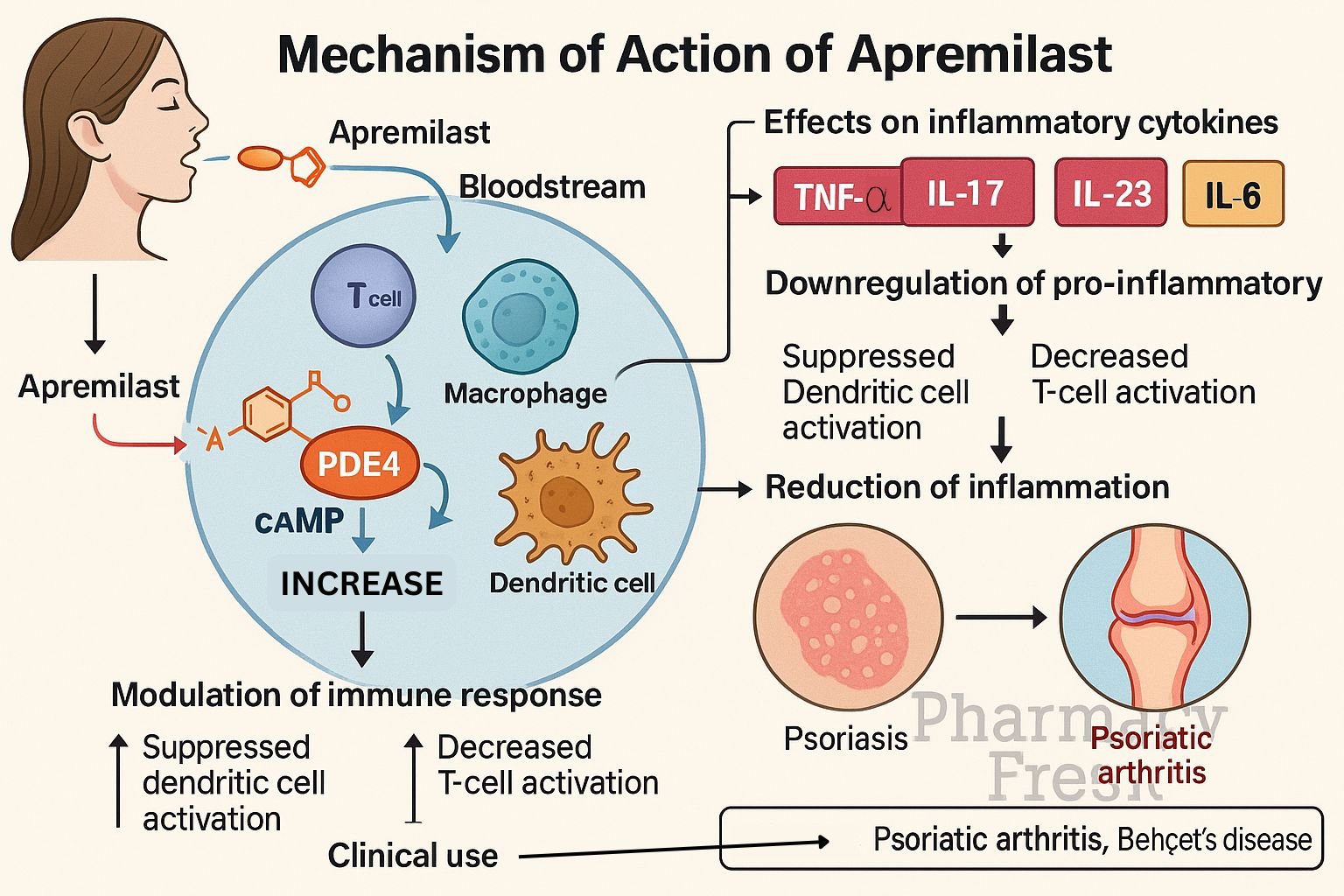
Apremilast (Otezla) is an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor approved for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Behçet’s disease‑associated oral ulcers. By modulating intracellular signaling, it reduces inflammation and disease symptoms through balanced cytokine regulation.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Inhibition of PDE4 enzyme
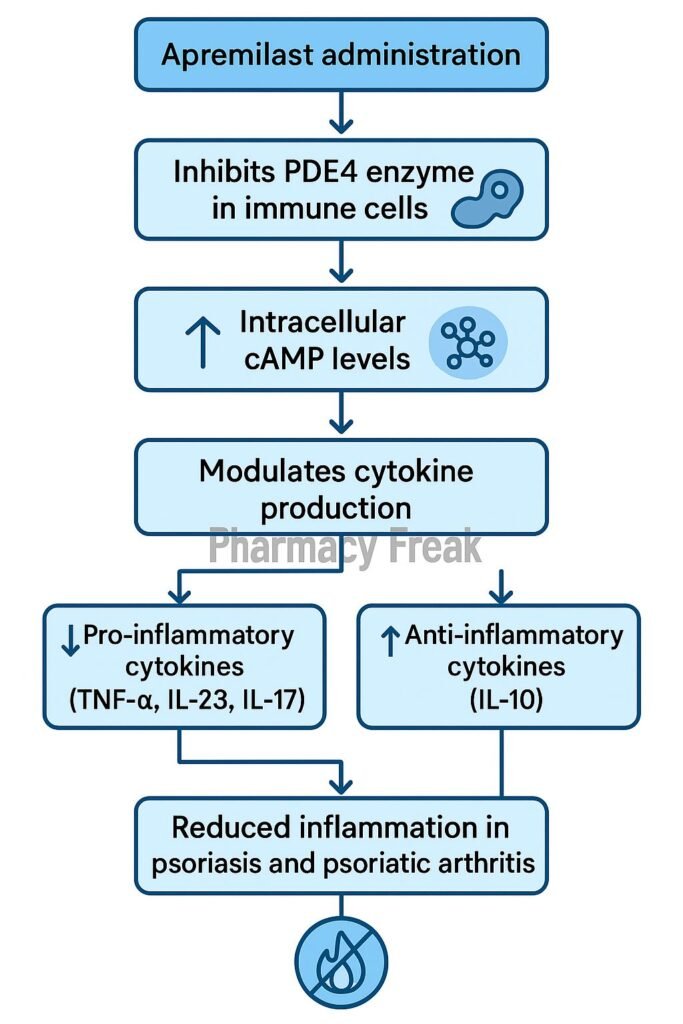
Apremilast selectively inhibits PDE4 in immune cells, preventing breakdown of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). - cAMP accumulation
Elevated intracellular cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA) and the transcription factor CREB to alter gene expression. - Pro-inflammatory cytokine suppression
It decreases synthesis of TNF‑α, IL‑23, IL‑17, and IFN‑γ—key mediators in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. - Anti-inflammatory cytokine induction
Levels of IL‑10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, are increased. - Reduced inflammatory cell recruitment
The net result is diminished migration and activation of inflammatory cells, reducing tissue damage and clinical symptoms.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Oral (delayed-release tablet) |
| Bioavailability | ~73% |
| Time to Peak (Tmax) | ~2–4 hours |
| Protein Binding | ~68% |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic via CYP3A4, CYP1A2, CYP2A6 |
| Half-life | ~6–9 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (~58%), feces (~39%) |
Clinical Uses
- Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis
- Active psoriatic arthritis
- Oral ulcers in Behçet’s disease
Adverse Effects
- Common: diarrhea, nausea, headache, upper respiratory infections, weight loss
- Rare: depression, mood changes
- Low risk: serious infections, malignancy
Comparative Analysis
| Drug | Target | Administration | Primary Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apremilast | PDE4 | Oral daily | Psoriasis, PsA, Behçet’s |
| Methotrexate | DHFR inhibitor | Oral/IM weekly | Psoriasis, PsA, RA |
| Biologics | TNF, IL‑17 | Injectable | Moderate-to-severe disease |
MCQs
- Apremilast inhibits which enzyme?
a) PDE3 b) PDE4 c) PDE5 d) PDE6
Answer: b) PDE4 - What is the result of PDE4 inhibition?
a) ↓ cAMP b) ↑ cAMP c) ↓ cGMP d) ↑ cGMP
Answer: b) ↑ cAMP - Pro-inflammatory cytokine reduced by apremilast includes:
a) IL‑2 b) TNF‑α c) IL‑4 d) IL‑1β
Answer: b) TNF‑α - Which cytokine is increased?
a) IL‑17 b) IFN‑γ c) IL‑23 d) IL‑10
Answer: d) IL‑10 - Common GI side effects are:
a) Constipation b) Diarrhea, nausea c) Pancreatitis d) Gallstones
Answer: b) Diarrhea, nausea - Route of elimination includes:
a) Renal and fecal b) Pulmonary c) Biliary only d) Sweat
Answer: a) Renal and fecal - Half-life of apremilast is:
a) 2–3 hrs b) 6–9 hrs c) 12–16 hrs d) 24 hrs
Answer: b) 6–9 hrs - Primary therapeutic uses include:
a) Hypertension b) Psoriasis, PsA, Behçet’s c) Diabetes d) Asthma
Answer: b) Psoriasis, PsA, Behçet’s - Apremilast affects CREB via:
a) ↓ cAMP b) ↑ cAMP c) ↓ cGMP d) ↑ cGMP
Answer: b) ↑ cAMP - Compared to biologics, apremilast advantage is:
a) Injectable administration b) Oral dosing c) Higher cost d) More side effects
Answer: b) Oral dosing
FAQs
1. Can apremilast be used with methotrexate?
Yes—combination therapy is common in psoriatic arthritis for better disease control.
2. How fast do symptoms improve?
Most patients see improvement within 2–4 weeks, with continued benefit over months.
3. Does it require lab monitoring?
No regular lab tests needed, unlike methotrexate or biologics.
4. Is weight loss permanent?
Usually mild and stabilizes over time; monitor if significant.
5. Can it worsen mood disorders?
Rarely—patients with depression history should be monitored for mood changes.
References
- Apremilast prescribing information (FDA)
- DrugBank: Apremilast mechanisms
- StatPearls: Apremilast in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis
- PubMed review: PDE4 inhibition and inflammatory disease

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com