Table of Contents
Introduction
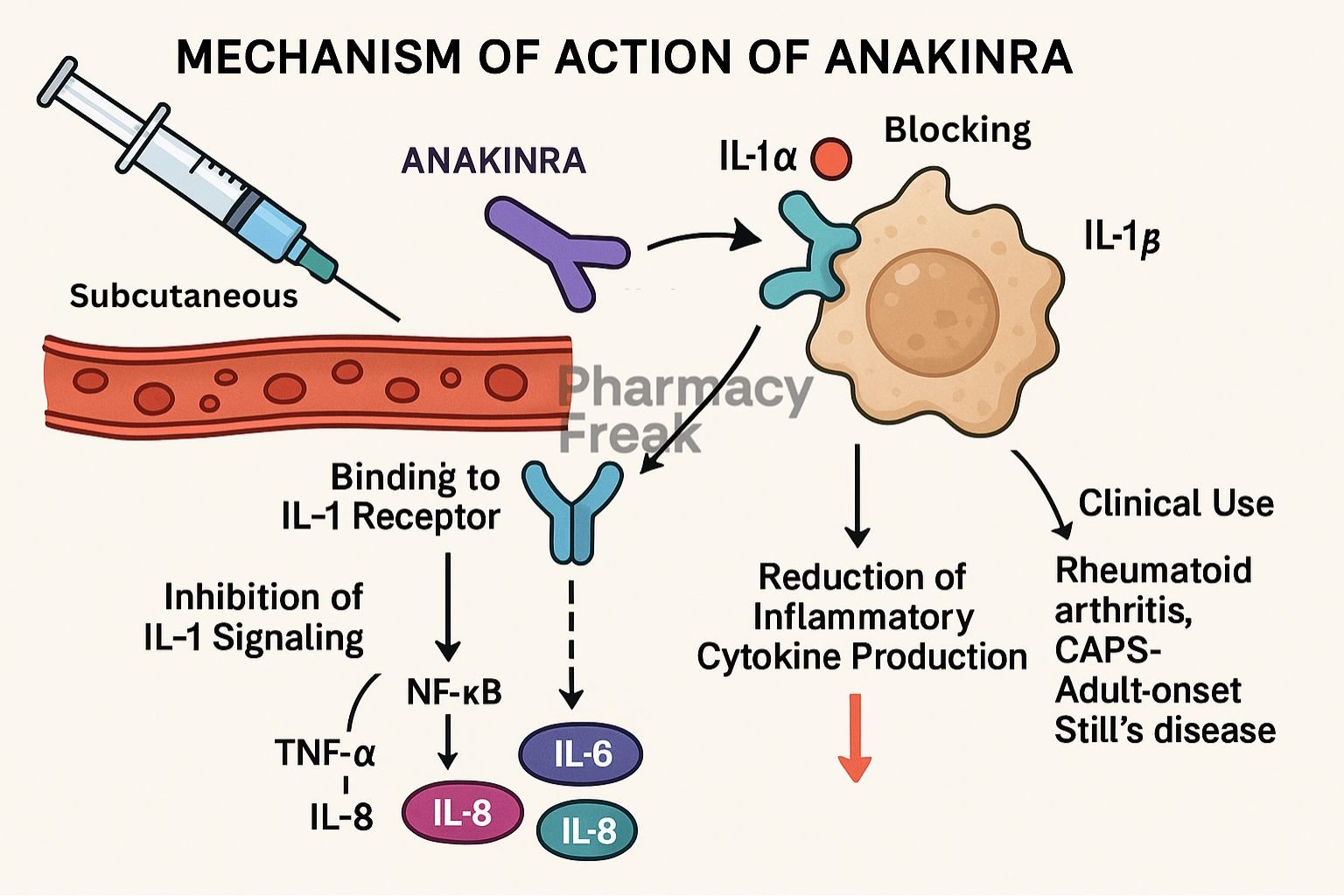
Anakinra is a recombinant human interleukin‑1 receptor antagonist (IL‑1Ra) used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID), and other autoinflammatory conditions. It competitively inhibits IL‑1α and IL‑1β binding to IL‑1 receptors, effectively reducing inflammation.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Competitive blockade of IL‑1 receptor
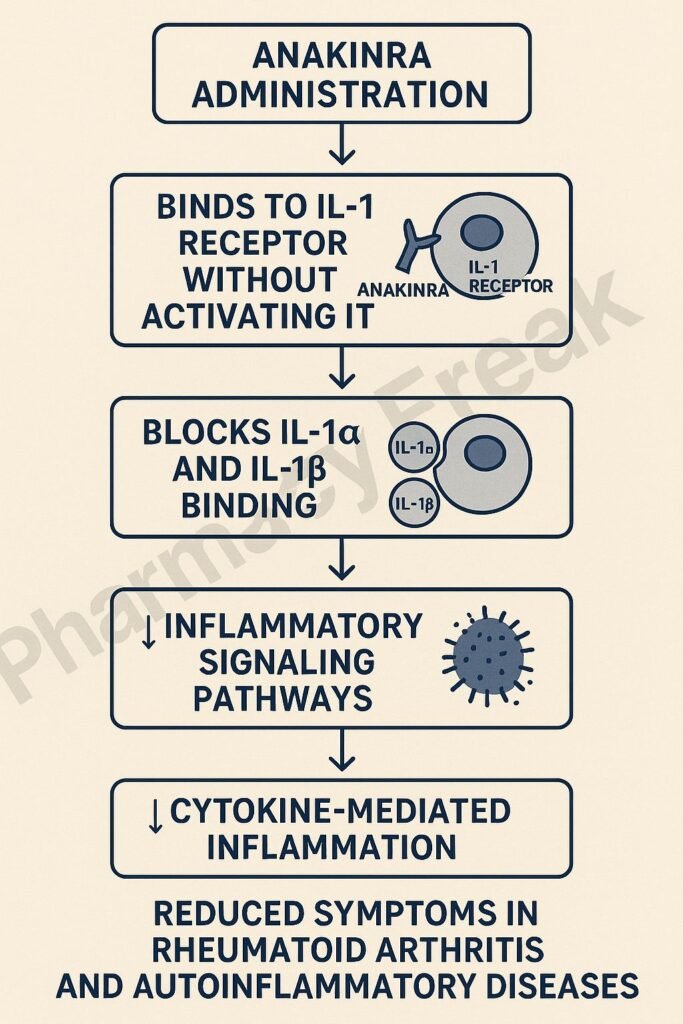
Anakinra binds to IL‑1 receptor type I (IL‑1RI) without activating it, preventing IL‑1α and IL‑1β from triggering signaling. - Inhibition of pro-inflammatory signaling
By blocking IL‑1RI, it prevents activation of NF‑κB and MAPK pathways that mediate inflammatory gene expression. - Reduced production of cytokines and enzymes
This blockade reduces downstream inflammatory mediators such as TNF‑α, IL‑6, COX‑2, and MMPs. - Decreased leukocyte recruitment
Lower cytokine levels result in reduced migration of neutrophils and monocytes to inflamed tissues. - Improved tissue stability and symptom relief
Overall, anakinra decreases joint swelling, pain, and acute-phase reactants in inflammatory diseases.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Subcutaneous injection (daily) |
| Bioavailability | ~95% |
| Time to Peak (Tmax) | ~3 to 7 hours |
| Half-life | ~4 to 6 hours |
| Metabolism/Excretion | Renal (no metabolism); dose adjustment in renal impairment |
Clinical Uses
- Rheumatoid arthritis (as monotherapy or combined with DMARDs)
- Neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID)
- Off-label use: gout, adult-onset Still’s disease, pericarditis
Adverse Effects
- Injection site reactions (common)
- Increased risk of serious infections
- Transient neutropenia
- Mild elevation of liver enzymes
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Target | Dosing Frequency | Primary Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anakinra | IL‑1 receptor | Daily SC | RA, NOMID, autoinflammatory diseases |
| Canakinumab | IL‑1β cytokine | Every 8 weeks | CAPS, periodic fever syndromes |
| Tocilizumab | IL‑6 receptor | Every 2–4 weeks | RA, giant cell arteritis |
MCQs
- Anakinra blocks which receptor?
a) TNF‑α receptor
b) IL‑1 receptor type I
c) IL‑6 receptor
d) IL‑17 receptor
Answer: b) IL‑1 receptor type I - What is the dosing frequency?
a) Daily
b) Weekly
c) Monthly
d) Every 8 weeks
Answer: a) Daily - Primary metabolism and excretion are via:
a) Hepatic CYP enzymes
b) Renal excretion
c) Fecal excretion
d) Biliary excretion
Answer: b) Renal excretion - Common adverse effect is:
a) Injection site reaction
b) Hair loss
c) Cardiac arrhythmias
d) Hypoglycemia
Answer: a) Injection site reaction - Anakinra is used for:
a) Asthma
b) NOMID
c) Type 1 diabetes
d) Hypertension
Answer: b) NOMID - Which pathway is inhibited?
a) NF‑κB and MAPK
b) JAK‑STAT
c) PI3K‑AKT
d) mTOR
Answer: a) NF‑κB and MAPK - It reduces production of:
a) IL‑10
b) COX‑2 and MMPs
c) Anti-inflammatory cytokines
d) Beta‑endorphin
Answer: b) COX‑2 and MMPs - Neutropenia occurs due to:
a) Bone marrow suppression
b) Fluid shift
c) Renal failure
d) Hepatic clearance
Answer: a) Bone marrow suppression - Advantages over canakinumab include:
a) Lower infection risk
b) Less frequent dosing
c) Daily control of IL‑1
d) Oral administration
Answer: c) Daily control of IL‑1 - Onset of action occurs within:
a) Minutes
b) Hours to days
c) Weeks
d) Months
Answer: b) Hours to days - Which mediator is not reduced?
a) IL‑6
b) TNF‑α
c) CRP
d) Insulin
Answer: d) Insulin - Primary route is:
a) Oral
b) IV
c) Subcutaneous
d) Inhaled
Answer: c) Subcutaneous - Half-life is approximately:
a) 4–6 hours
b) 24 hours
c) 7 days
d) 28 days
Answer: a) 4–6 hours - Anakinra is contraindicated in:
a) Severe renal impairment
b) Mild hypertension
c) Osteoarthritis
d) Childhood obesity
Answer: a) Severe renal impairment - Injection site reactions are usually:
a) Severe and lasting
b) Mild and transient
c) Associated with fever
d) Dose-limiting
Answer: b) Mild and transient
FAQs
- Can anakinra be used in gout flares?
Yes, as off-label therapy in resistant cases. - Is routine blood count monitoring needed?
Yes—especially neutrophil counts due to risk of neutropenia. - How long does it take to work in RA?
Symptomatic improvement may appear within days to 1 week. - Can it be used with methotrexate?
Yes, combination therapy is common in refractory cases. - What about vaccination during therapy?
Live vaccines should be avoided during treatment.
References
- Anakinra (IL-1 receptor antagonist)
- StatPearls: Anakinra therapy in rheumatic disease
- PubMed review: IL‑1 blockade with anakinra

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com