Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
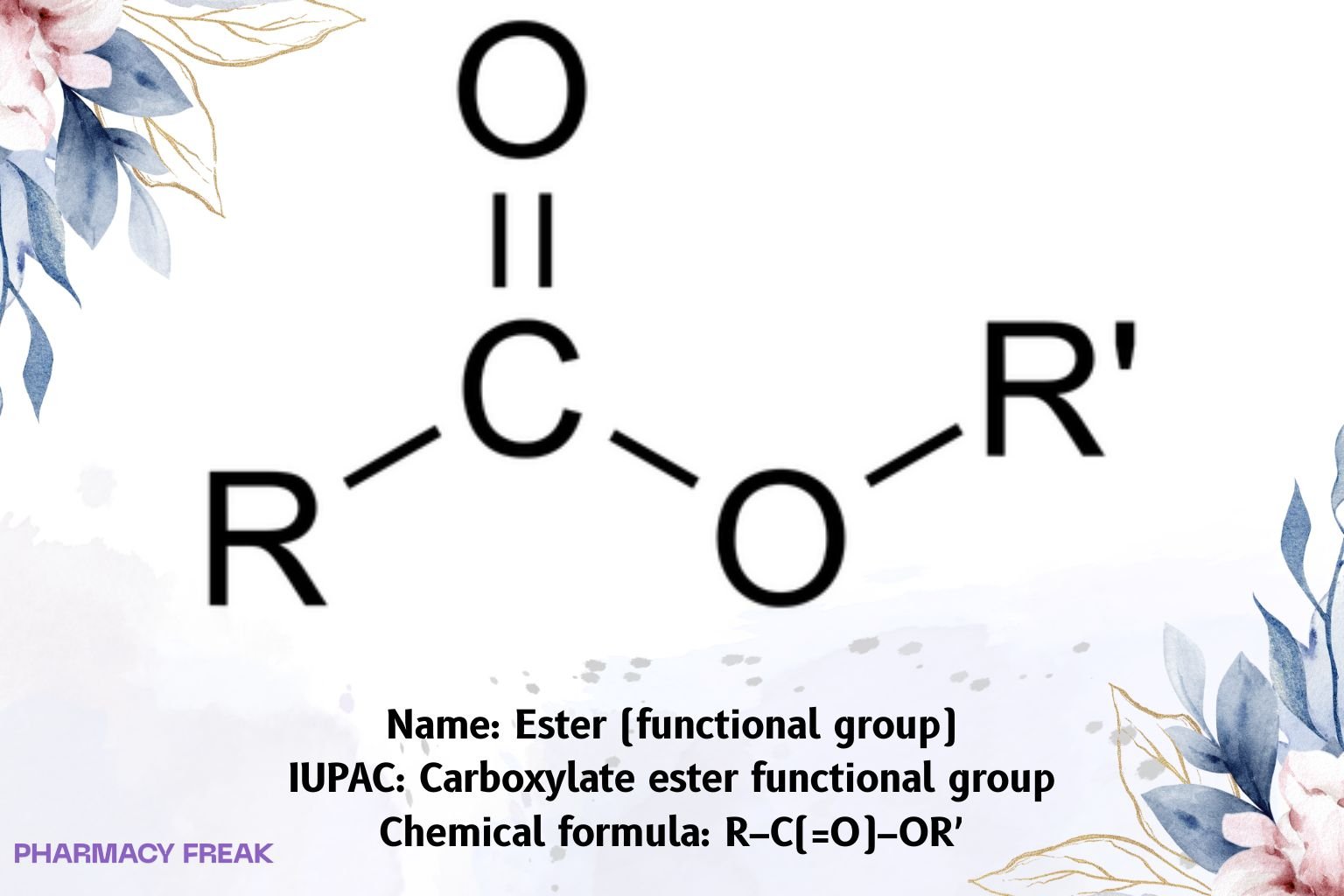
Ester denotes the carboxylate ester functional group with general formula R–C(=O)–OR′ (R, R′ = carbon substituents). Esters are polar, aprotic, H-bond acceptors (C=O, C–O) but not donors, display a characteristic IR C=O band ~1735 cm⁻¹ for saturated aliphatic esters (lower with conjugation or ring strain), and strong C–O stretches ~1050–1300 cm⁻¹. ¹³C NMR carbonyl resonates ~160–175 ppm; ¹H NMR O-alkyl protons commonly ~3.7–4.3 ppm. IUPAC naming: alkyl alkanoate (e.g., ethyl ethanoate).
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
Ester (carboxylate ester)
Background
Ubiquitous in natural products (fats as triacylglycerols, lactones) and pharmaceuticals (prodrugs). Common preparations:
• Fischer esterification (carboxylic acid + alcohol, acid catalysis, water removal)
• Steglich/Yamaguchi variants (DCC/EDC + DMAP; mixed anhydrides)
• Acid chloride/anhydride + alcohol (base capture of HX)
• Transesterification (alcoholate/base or acid catalysis)
• Lactonization (intramolecular, hydroxy acids → cyclic esters)
Modality
Functional group (small-molecule chemistry)
Groups
Endogenous biomolecules; industrial and medicinal chemistry motif
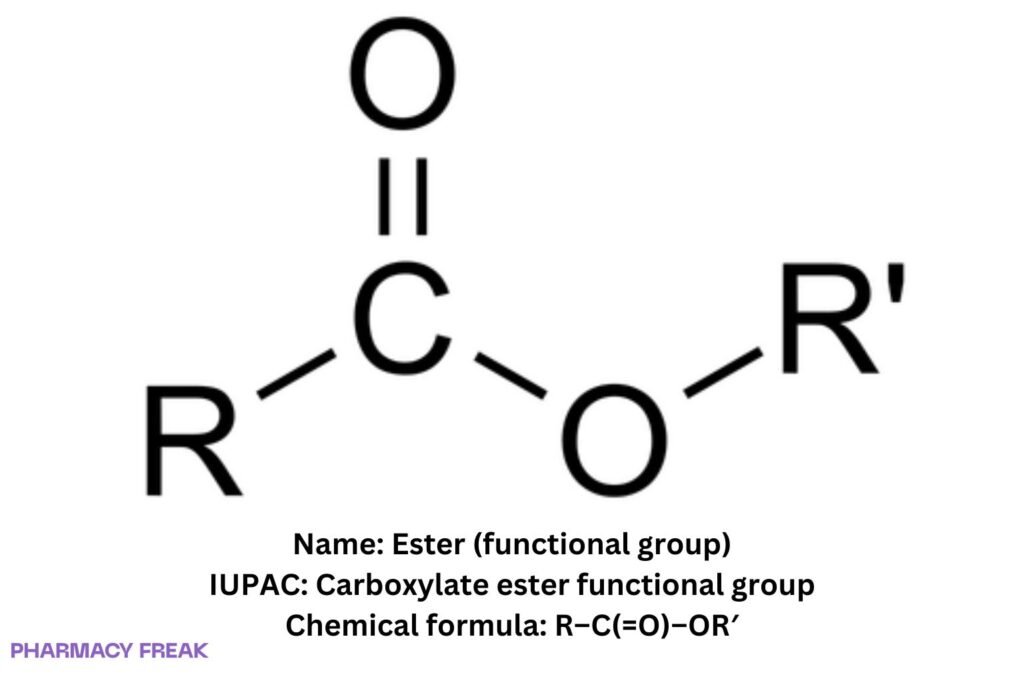
Structure
Weight
Not applicable (class)
Chemical Formula
R–C(=O)–OR′
Synonyms
Carboxylate ester; Alkyl alkanoate; –COOR
External IDs
Not applicable (generic functional group)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not a drug (group descriptor).
Associated Conditions
Occurs in lipids, fragrances/flavors, and many APIs; frequently used in prodrug design to mask acidic/alcoholic groups and improve permeability.
Associated Therapies
Ester prodrugs hydrolyzed by carboxylesterases/paraoxonases to release the active acid/alcohol.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable at group level.
Pharmacodynamics
Chemical—no pharmacologic action as a class. In drug molecules, esters modulate lipophilicity, permeability, and clearance via esterase hydrolysis.
Mechanism of action
Reactivity proceeds via nucleophilic acyl substitution through a tetrahedral intermediate at the carbonyl carbon.
Absorption
Class effect in ADME: esterification typically increases lipophilicity; in vivo hydrolysis regenerates polar parents.
Volume of distribution / Protein binding / Metabolism / Elimination / Half-life / Clearance
Scaffold-dependent; hydrolytic metabolism (enzymatic/chemical) dominates.
Adverse Effects / Toxicity
Not intrinsic to the group; byproducts (released alcohol/acid) and rate of hydrolysis are scaffold-specific.
Pathways
High-yield transformations:
- Hydrolysis: acid-catalyzed (reversible) or base-promoted saponification (irreversible to carboxylate)
- Transesterification (acid or base)
- Reduction: LiAlH₄ → primary alcohols; DIBAL-H (−78 °C) → aldehydes (from methyl/primary esters)
- Grignard/organolithium addition: two equivalents → tertiary alcohols (via ketone stage)
- Claisen condensation/Dieckmann (enolates of esters)
- Aminolysis → amides (activation often helpful)
- Acetalization of embedded carbonyls not typical; protection uses acyl derivatives instead
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Not applicable to the group.
3. Interactions
Chemical Interactions
H-bond acceptor interactions with donors (proteins/solvents); Lewis base coordination at carbonyl oxygen; salt formation not typical unless hydrolyzed to acid.
Food Interactions
Not applicable (functional group).
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None (functional group)
Drug Categories
Functional group; Carboxylic acid derivative; Prodrug handle
Chemical Taxonomy
sp² carbonyl with alkoxy leaving group; resonance-stabilized acyl–oxygen framework; hydrolytic lability shaped by electronics/sterics and medium (acid/base/enzymes).
Affected organisms
Not applicable
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII / CAS / InChI / InChIKey
Not applicable for the class.
Generic SMILES: R–C(=O)–OR′
IUPAC Name
Carboxylate ester functional group
6. References
IUPAC Gold Book — definitions and nomenclature of carboxylic esters.
Clayden, Greeves, Warren. Organic Chemistry — ester formation/hydrolysis, mechanisms (tetrahedral intermediate), Claisen condensation.
March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry — kinetics/thermodynamics of esterification and saponification; reduction chemistry (LiAlH₄, DIBAL-H).
Silverstein et al., Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds — IR (C=O ~1735 cm⁻¹; C–O 1050–1300 cm⁻¹), NMR assignments.
Carey & Sundberg. Advanced Organic Chemistry — acyl substitution, transesterification, and aminolysis strategies.

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com