Essential drug concept define the priority drug that must be available in a country to ensure the health and safety of the public.
Table of Contents
DEFINITION
According to World Health Organization (WHO)
“Those drugs that satisfy the priority of healthcare needs of the population”.
They should be available in adequate amounts & an appropriate dosage form. The list must be updated from time to time. Direct responsibility of each country to evaluate & adopt a list of essential drugs according to its policy in the field of health.
CONCEPTS
- The principle of the concept is that a Limited number of drugs lead to:
- A better supply of drugs.
- More rational prescribing.
- Procurement of good quality at lower Costs.
- Easier storage, distribution, and Dispensing.
- Focused training and drug information.
- More experience with fewer drugs, Better recognition of adverse drug Reactions (ADR).
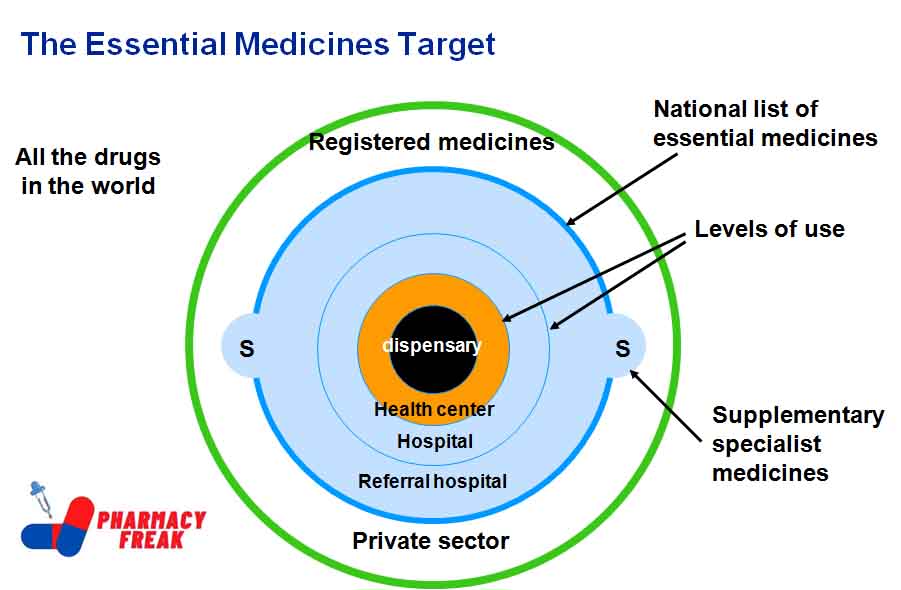
SELECTION CRITERIA
- Based on morbidity pattern – incidence & prevalence of diseases in the country.
- Adequate data on the safety & efficacy of the drug.
- Availability in a dosage form of suitable Strength, for which adequate quality In terms of – bioavailability can be assured.
- Stability under climate conditions.
- Pharmaceutical form- based on cost, p/k, bioavailability, stability, and local preference.
- Compare 2 drugs in respect of efficacy, safety, quality, availability & cost.
- Preferably as a single active ingredient.
- Fixed dose combination-only when proven advantage over single
HISTORY OF THE WHO MODEL LIST OF ESSENTIAL DRUGS
- 1977 First Model list published + 200 active substances.
- The list is revised every two years by WHO Expert Committee.
- April 2003 revised Model list contains 315 active substances.
- 2007, a separate list for children up to 12 years was included.
- Latest, The 18th edition for adults and the 4th edition for children were released in April 2013.
Advantage
- Ensures availability of most required drugs at all times, in sufficient amounts, and appropriate dosage forms.
- Keeps a check on the prices of generically listed drugs.
- Substantial savings (50-60 %) including foreign exchange is possible without compromising the quality of health care.
- Curtailing the no. of drugs improves drug dispensing & patient compliance.
- Procurement & distribution can be uniform & systemic.
THE WHO MODEL LIST OF ESSENTIAL MEDICINES IS A MODEL PRODUCT, MODEL PROCESS, AND PUBLIC HEALTH TOOL
Model product: List of essential drugs with information.
Core list: Minimum drug needs for a basic health care system, listing the most cost-effective drugs for priority conditions (selected based on the burden of disease and potential for safe and cost-effective treatment).
Complementary list: Essential drugs for priority diseases that are cost-effective but not necessarily affordable or for which specialized health care facilities may be needed and essential drugs for less frequent diseases.
SEVEN STEPS TO GET A NEW MEDICINE ON THE WHO MODEL LIST OF ESSENTIAL DRUGS
- Identification of the public-health need for medicine.
- Development of the medicine; phase I – II – III trials.
- Regulatory approval in several countries. Effective and safe medicine on the market
- More experience under different field circumstances; post-marketing surveillance.
- Price indication for public sector use.
- Review by WHO disease program; define comparative effectiveness and safety in real-life situations, comparative cost-effectiveness, and public health relevance. Medicine included in WHO treatment guideline
- Submission to WHO Expert Committee on Essential Drugs.
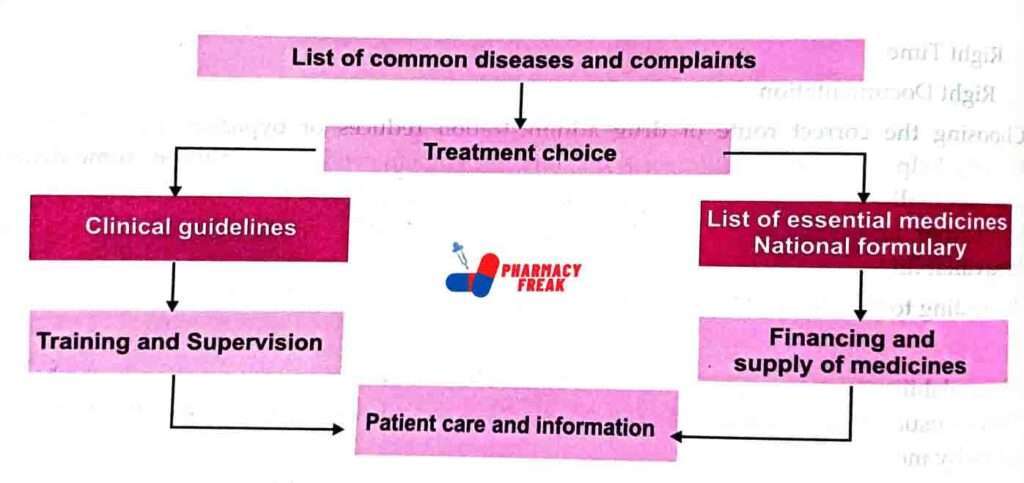
HOW TO DEVELOP A NATIONAL LIST OF ESSENTIAL MEDICINES
The selection criteria of essential medicine should be evidence-based and linked with standard clinical trial guidelines. A review of the clinical guidelines and the list should be carried out at least every second year, and their use and impact should be monitored.
A standing committee should be appointed to give technical advice. This committee may include people from different fields, such as medicine, nursing, pharmacology, pharmacy, public health, consumer affairs, and health workers at the grass-roots level.
Formal and informal consultations may be organized with interested parties, including representatives of professional bodies, pharmaceutical manufacturers, consumer organizations, and the government budget and finance group.
However, the final medicines selection by the committee members should be carried out independently. An important principle that needs to be accepted by the committee is that not all evidence is equally strong. For example, the result of a systematic review of clinical trials carries more weight than the result of an observational study without controls and much more than the personal experience of individual experts.
The strength of the evidence defines the strength of the recommendation.
National list of essential medicine of Different Countries.
- National list of essential medicine of India – Click Here to Read
- National list of essential medicine of UK – Click Here to Read
- National list of essential medicine of USA- Click Here to Read
- National list of essential medicine of Canada- Click Here to Read
- National list of essential medicine of Australia- Click Here to Read
- National list of essential medicine of Germany- Click Here to Read
- National list of essential medicine of France- Click Here to Read
Reference
- Dr. Kiran D Patil, Dr. Pralhad K. Kanke, Dr. Md. Rageeb, Dr. Md Usman, Dr. Atul Kabra, A textbook of pharmacology-1 , pv publications. Page no 24-28.
- https://www.who.int/
Read other articles relate to Pharmacology.

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com

