Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Diclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for relief of pain, fever, and inflammation across oral, injectable, topical, ophthalmic, and rectal routes; like other NSAIDs, labeling warns about serious cardiovascular and gastrointestinal risks with systemic use.
Brand Names
Voltaren, Cataflam, Cambia, Zipsor, Zorvolex (regional/generic variants common)
Name
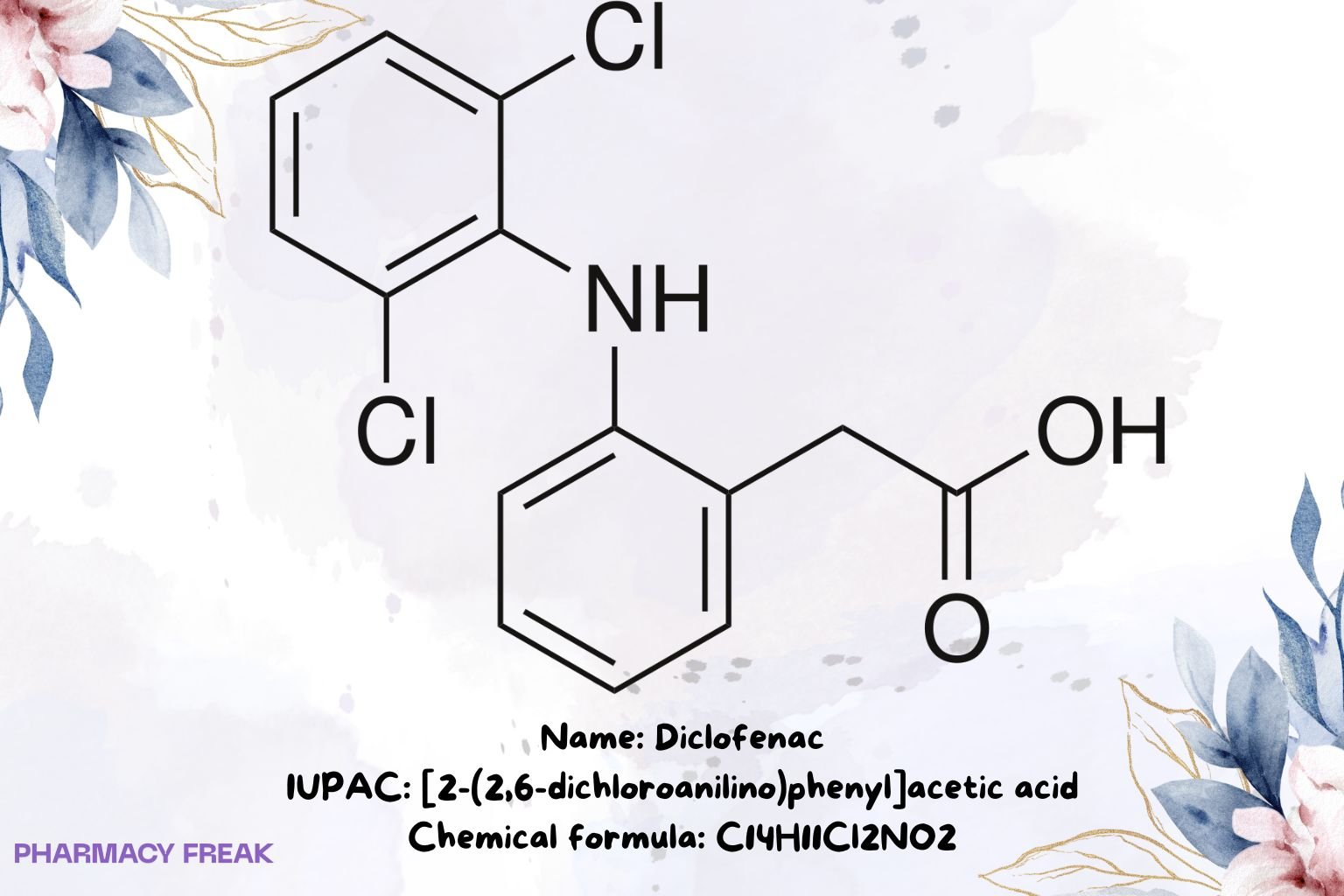
Diclofenac
Background
A benzeneacetic acid–class NSAID introduced in the 1970s; supplied as free acid and multiple salts (e.g., sodium, potassium, diethylamine, epolamine) formulated for systemic or topical delivery.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; OTC/Rx (region-dependent)
Structure
![Diclofenac 2D chemical structure (benzeneacetic acid derivative). Formula C14H11Cl2NO2; IUPAC [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid; CAS 15307-86-5.](https://pharmacyfreak.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/DICLO2-1024x683.jpg)
Weight
~296.15 g/mol (free acid)
Chemical Formula
C₁₄H₁₁Cl₂NO₂ (free acid)
Synonyms
2-[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid; diclofenac free acid
External IDs
CAS (free acid): 15307-86-5; PubChem CID: 3033
UNII (active moiety): 144O8QL0L1; ATC (oral/parenteral/rectal): M01AB05
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Short-term treatment of mild–moderate pain; symptomatic relief in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, primary dysmenorrhoea; acute migraine (certain oral products); postoperative/ocular inflammation (ophthalmic/topical forms).
Associated Conditions
Musculoskeletal pain, tendonitis/bursitis, dental/post-traumatic pain; actinic keratosis or localized OA (topical forms per label).
Associated Therapies
Co-use with gastroprotection (e.g., PPI) in high GI-risk patients; fixed-dose diclofenac/misoprostol in some markets.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
NSAID boxed warnings for CV thrombotic events and GI bleeding/ulcer/perforation; contraindicated for CABG peri-operative pain, in NSAID/aspirin hypersensitivity, and from 30 weeks’ gestation due to fetal ductus arteriosus risk.
Pharmacodynamics
Reversible COX-1/COX-2 inhibition reduces prostaglandins → analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory effects; high protein binding and tissue distribution contribute to effect persistence beyond plasma half-life.
Mechanism of action
Competitive inhibition of prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthases (COX-1/COX-2), lowering PGE₂/TXA₂ synthesis; some COX-2 preference reported in vitro; clinical selectivity remains dose-/context-dependent.
Absorption
Oral bioavailability is limited by first-pass metabolism; salts/formulations (e.g., potassium, enteric-coated sodium, soft-gel) alter tₘₐₓ and tolerability; topical forms produce lower systemic exposure.
Volume of distribution
Typically ~0.1–0.2 L/kg (low to moderate), with penetration into synovial fluid reported.
Protein binding
>99% (primarily albumin)
Metabolism
Extensive hepatic metabolism: oxidative CYP2C9 (and others) to hydroxylated metabolites plus UGT2B7 glucuronidation; metabolites generally inactive.
Route of elimination
Predominantly as metabolites via urine (major) and bile/feces (minor to moderate); little unchanged drug renally excreted.
Half-life
Unchanged diclofenac ~1–2 h (longer for total metabolites/apparent effect).
Clearance
Apparent oral clearance influenced by formulation, hepatic function, and drug interactions (e.g., CYP2C9 modulators).
Adverse Effects
Dyspepsia, nausea, abdominal pain, edema, dizziness, rash; serious events include GI bleeding, CV thrombotic events, hepatic injury, renal events, anaphylaxis, and severe cutaneous reactions.
Toxicity
Overdose typically managed supportively; chronic/high-dose risks align with class warnings; topical misuse still carries systemic risk.
Pathways
COX inhibition → ↓prostaglandins; distribution into inflamed tissues; enterohepatic handling varies by product.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
CYP2C9 genotype and inhibitors can alter exposure; routine PGx testing not standard—monitor when interacting drugs/diseases present.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
- Anticoagulants/antiplatelets/SSRIs/SNRIs: ↑ bleeding risk.
- ACEI/ARB/diuretics (“triple whammy”): additive renal risk.
- CYP2C9 inhibitors/inducers (e.g., fluconazole / rifampin): ↑/↓ diclofenac exposure.
- Other NSAIDs/salicylates: avoid co-use (↑ toxicity, little added benefit).
- Lithium/methotrexate: potential ↑ levels—monitor.
Food Interactions
Food/enteric coating can delay tₘₐₓ and improve GI tolerability; alcohol co-use increases GI risk.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
M01AB05 (systemic); topical and ophthalmic subclasses exist (e.g., M02AA15, S01BC03 per product).
Drug Categories
NSAID; Analgesic; Antipyretic; Anti-inflammatory; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Aromatic benzeneacetic acid derivative; diphenylamine motif with 2,6-dichloro substitution
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
144O8QL0L1 (diclofenac, active moiety)
CAS number
15307-86-5 (diclofenac free acid)
InChI Key
DCOPUUMXTXDBNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C14H11Cl2NO2/c15-10-5-3-6-11(16)14(10)17-12-7-2-1-4-9(12)8-13(18)19/h1-7,17H,8H2,(H,18,19)
IUPAC Name
[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid
SMILES
O=C(O)Cc1ccccc1Nc2c(Cl)cccc2Cl
6. References
- PubChem Compound Summary: Diclofenac (CID 3033) — formula C₁₄H₁₁Cl₂NO₂, identifiers, structure. PubChem
- FDA GSRS / UNII — Diclofenac active moiety UNII 144O8QL0L1, InChIKey DCOPUUMXTXDBNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N. precisionFDA
- ATC/DDD Index (FHI) — systemic M01AB05 diclofenac; route/DDDs. atcddd.fhi.no
- NIST WebBook — InChI / molecular formula / MW confirmation for diclofenac free acid. NIST WebBook
- DailyMed / FDA labels — NSAID boxed warnings; GI/CV risks; pregnancy (≥30 wks) ductus risk. DailyMed
- Drugs.com Pro (label compendium) — PK summary (half-life ~2 h), elimination primarily via metabolism. Drugs.com
- DrugBank — Vd/clearance ranges; metabolizing enzymes (CYP2C9; UGT2B7). DrugBank
- Peer-reviewed PK sources — High protein binding (>99%), Vd ~0.12–0.17 L/kg, first-pass effect. PTFarm+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com