Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Ceftriaxone is a parenteral third-generation cephalosporin for susceptible systemic infections, including meningitis and gonorrhea; long elimination half-life enables once-daily dosing in many indications.
Brand Names
Rocephin; multiple generics
Name
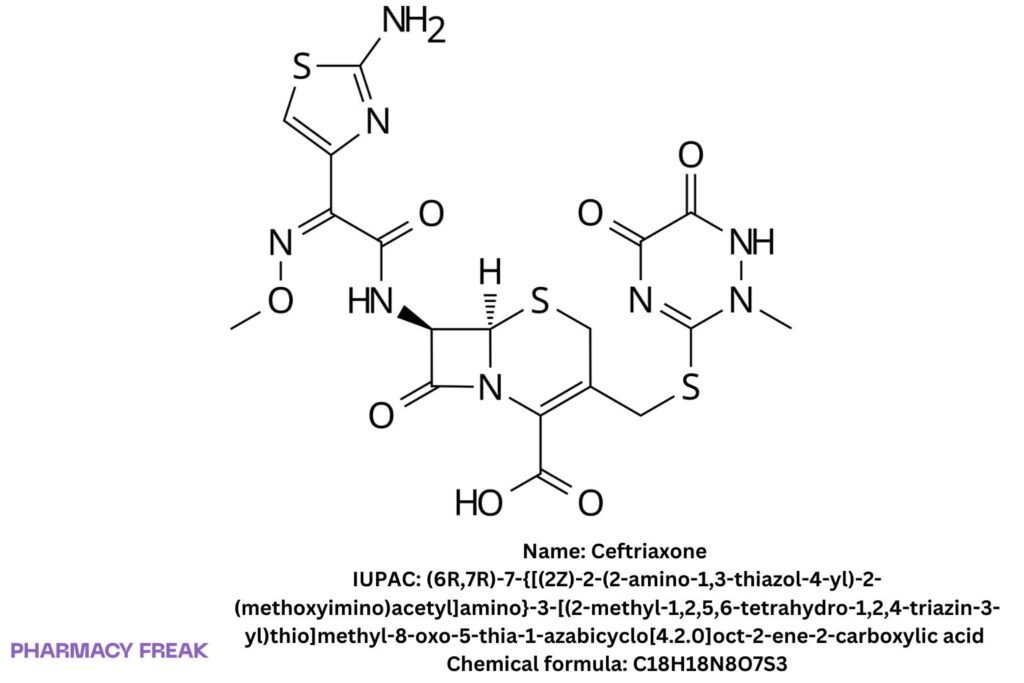
Ceftriaxone
Background
IV/IM only; high protein binding with concentration dependence; dual renal–biliary elimination; avoid IV calcium co-administration in neonates; risk of biliary “sludge.”
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
Weight
~554.57 g/mol (free acid/base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₈H₁₈N₈O₇S₃
Synonyms
(6R,7R)-7-[(Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamido]-3-[(2-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)thio]methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
External IDs
CAS (base): 73384-59-5; PubChem CID: 5479530; UNII (base): 75J73V1629; ATC: J01DD04
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Susceptible infections: community-acquired and nosocomial pneumonia, meningitis, acute otitis media, skin/soft-tissue, intra-abdominal, bone/joint, urinary tract, septicemia, pelvic inflammatory disease, and uncomplicated gonorrhea; surgical prophylaxis per label.
Associated Conditions
Bacterial meningitis (including S. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, H. influenzae), disseminated gonococcal infection, typhoid fever (regional guidance), Lyme neuroborreliosis (guideline-dependent).
Associated Therapies
With other agents per site/severity (e.g., vancomycin for empirical meningitis; metronidazole for intra-abdominal sepsis).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
No boxed warning. Contraindicated in neonates ≤28 days requiring IV calcium-containing solutions (risk of precipitation) and in hyperbilirubinemic neonates (bilirubin displacement). Severe hypersensitivity to cephalosporins or serious β-lactam allergy.
Pharmacodynamics
β-lactam PBP inhibition → blocked peptidoglycan crosslinking → bactericidal cell-wall action; time-dependent killing.
Mechanism of action
Covalent acylation of PBPs; activity against many Enterobacterales, Neisseria, H. influenzae, streptococci; limited activity vs Pseudomonas (not a antipseudomonal cephalosporin).
Absorption
Not orally available; complete systemic availability after IV/IM administration.
Volume of distribution
~5.8–13.5 L in healthy adults; penetrates CSF with inflamed meninges.
Protein binding
~95% → 85% over rising plasma concentrations (concentration-dependent, reversible).
Metabolism
Minimal.
Route of elimination
~33–67% renal unchanged; remainder biliary/fecal (enterohepatic cycling).
Half-life
~5.8–8.7 h in healthy adults (longer in neonates/elderly).
Clearance
Plasma clearance ~0.58–1.45 L/h; renal clearance ~0.32–0.73 L/h across 0.15–3 g dosing range.
Adverse Effects
Injection-site reactions, diarrhea, rash, eosinophilia/thrombocytosis; C. difficile–associated diarrhea; biliary pseudolithiasis/sludge; rare hemolytic anemia, severe cutaneous reactions.
Toxicity
Precipitation with IV calcium in neonates (lung/kidney deposition); manage exposures supportively.
Pathways
PBP binding; dual elimination (renal/biliary).
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
None established for patient selection.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
IV calcium products in neonates ≤28 days: contraindicated (precipitation).
Vitamin K antagonists: possible ↑ INR; monitor.
Aminoglycosides: potential synergy (do not co-mix in same IV line).
Bacteriostatic antibiotics: possible antagonism in severe infections (clinical context dependent).
Food Interactions
Not applicable (parenteral use).
4. Categories
ATC Codes
J01DD04 (third-generation cephalosporins)
Drug Categories
Third-generation cephalosporin; β-lactam; Antibacterial; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Cephem core with methoxyimino and aminothiazole moieties; thiotriazinone-thio side chain.
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use); target bacteria susceptible to β-lactams
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
75J73V1629 (ceftriaxone, base)
CAS number
73384-59-5 (base)
InChI Key
VAAUVRVFOQPIGI-SPQHTLEESA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C18H18N8O7S3/c1-25-18(22-12(28)13(29)23-25)36-4-6-3-34-15-9(14(30)26(15)10(6)16(31)32)21-11(27)8(24-33-2)7-5-35-17(19)20-7/h5,9,15H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H2,19,20)(H,21,27)(H,23,29)(H,31,32)/b24-8-/t9-,15-/m1/s1
IUPAC Name
(6R,7R)-7-{[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino}-3-[(2-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)thio]methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
SMILES
O=C2N1/C(=C(\CS[C@@H]1[C@@H]2NC(=O)C(=N\OC)/c3nc(sc3)N)CS\C4=N\C(=O)C(=O)NN4C)C(=O)O
6. References
DailyMed/FDA labels—adult PK (t½ 5.8–8.7 h, Vd 5.78–13.5 L, plasma/renal clearance; protein binding 95%→85%), distribution, pregnancy passage. DailyMed+2DailyMed+2
FDA/label safety—neonatal calcium–ceftriaxone precipitation and updated contraindication scope; warning context. FDA Access Data+2AAP Publications+2
WHOCC ATC/DDD Index—classification J01DD04 (ceftriaxone). FHI+1
PubChem—ceftriaxone base record (formula C₁₈H₁₈N₈O₇S₃, identifiers). PubChem
precisionFDA/GSRS—UNII 75J73V1629 and InChIKey VAAUVRVFOQPIGI-SPQHTLEESA-N. precisionFDA+1
Wikipedia (cross-checked identifiers; SMILES/InChI string; molar mass 554.57 g/mol). Wikipedia
Pfizer labeling—indications list for Ceftriaxone for Injection, USP. Pfizer Labeling

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
