Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
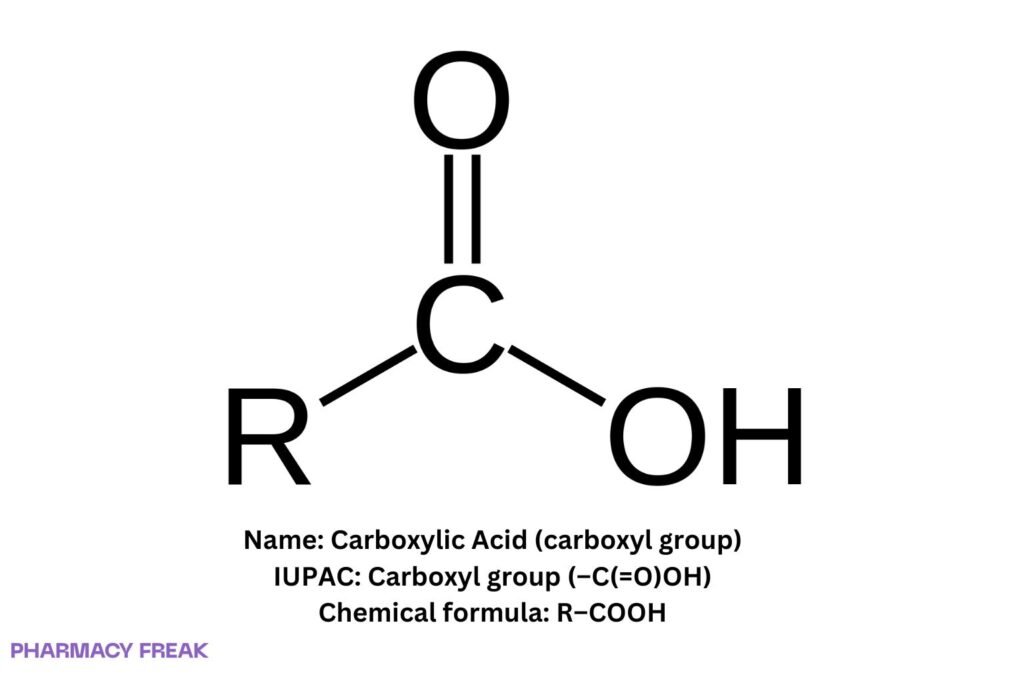
Carboxylic acid denotes the carboxyl (–C(=O)OH) functional group; general formula R–COOH. Core features: acidic proton on the hydroxyl, resonance-stabilized carboxylate conjugate base, strong hydrogen bonding, and broad derivatization (esters, amides, anhydrides, acid chlorides).
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
Carboxylic acid (carboxyl group)
Background
Ubiquitous in organic, medicinal, and biochemistry contexts (fatty acids, amino acids, many APIs). Electron-withdrawing substituents lower pKₐ; electron-donating substituents raise pKₐ. Common laboratory/industrial transformations: Fischer esterification, amide coupling, anhydride formation, acyl chloride formation, reduction to alcohols/aldehydes.
Modality
Functional group (class of small molecules)
Groups
Endogenous biomolecules; industrial chemicals
Structure
Weight
Not applicable (class; depends on R)
Chemical Formula
R–COOH
Synonyms
Carboxyl group; Carboxy group; –CO₂H
External IDs
Not applicable (generic functional group)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not a therapeutic active (class descriptor).
Associated Conditions
Occurs in endogenous metabolites (e.g., fatty acids, bile acids); present in numerous approved drugs as a free acid or masked as esters/amides.
Associated Therapies
Medicinal chemistry prodrug strategies (e.g., ester prodrugs) to modulate permeability and absorption.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable (class).
Pharmacodynamics
Weak Brønsted acid; typical simple aliphatic/benzoic acids show pKₐ ~4–5 (substituent and environment dependent). Ionization to R–COO⁻ drives aqueous solubility and salt formation.
Mechanism of action
Chemical, not pharmacologic: proton donation; resonance delocalization over C=O/O⁻ stabilizes the conjugate base.
Absorption
Ionization state controls membrane permeability; unionized acids cross membranes more readily than carboxylates.
Volume of distribution
Not applicable (class property varies by scaffold).
Protein binding
Carboxylates bind albumin and interact with cationic sites; magnitude is scaffold-dependent.
Metabolism
Biotransformations include conjugation (e.g., glucuronidation), β-oxidation for long-chain acids, and amidation/ester hydrolysis pathways.
Route of elimination
Often renal as carboxylate or conjugates; biliary for lipophilic acids.
Half-life
Not applicable (scaffold-dependent).
Clearance
Not applicable (scaffold-dependent).
Adverse Effects
Not applicable to the functional group per se; scaffold-specific.
Toxicity
Not applicable (class).
Pathways
Acid–base ionization; conjugation; interconversion with derivatives (esters/amides/anhydrides/acyl chlorides).
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Not applicable at the group level.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Forms salts with bases (e.g., Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺); ion-pairing with cations; H-bonding and ionic interactions in proteins, transporters, and excipients.
Food Interactions
pH-dependent ionization influences dissolution and absorption of acid-bearing APIs.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None (functional group).
Drug Categories
Functional group; Acidic moiety
Chemical Taxonomy
Carboxyl group: trigonal carbonyl carbon bonded to hydroxyl and substituent R; conjugate base carboxylate (R–COO⁻) with two equivalent C–O bonds by resonance.
Affected organisms
Not applicable (chemical class)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
Not applicable.
CAS number
Not applicable (class). Example references for context: acetic acid 64-19-7; benzoic acid 65-85-0.
InChI Key
Not applicable (class).
InChI
Not applicable (class).
IUPAC Name
Carboxylic acid functional group (carboxyl group)
SMILES
Generic: R C(=O)O
6. References
IUPAC Gold Book: definitions of carboxylic acid and carboxylate; resonance and nomenclature.
Clayden, Greeves, Warren. Organic Chemistry: acidity trends, substituent effects, and derivatization.
March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry: physical properties (H-bonding, dimerization), reactivity, and transformations.
Carey & Sundberg. Advanced Organic Chemistry: mechanisms of acyl substitution and ester/amide formation.

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
