Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Azithromycin is a 15-membered azalide macrolide antibiotic indicated for susceptible infections across respiratory, skin/soft-tissue, sexually transmitted, and atypical pathogen settings; class cautions include QT prolongation/arrhythmia risk, hepatotoxicity, C. difficile–associated diarrhea, and myasthenia gravis exacerbation.
Brand Names
Zithromax, Sumamed; multiple generics (region-dependent)
Name
Azithromycin
Background
Semisynthetic azalide derived from erythromycin A; oral, IV, and ophthalmic forms; prolonged tissue persistence enables short-course regimens.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
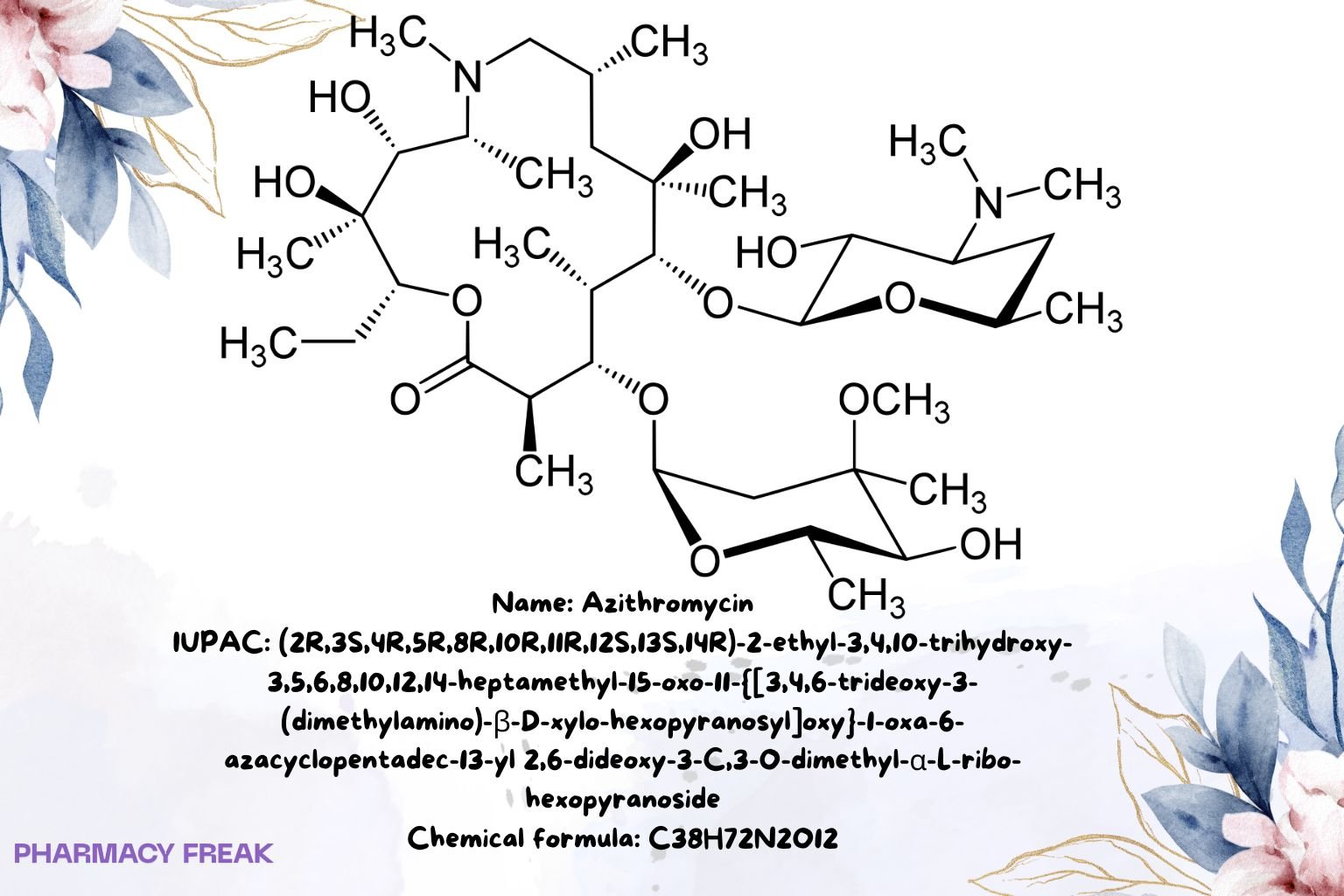
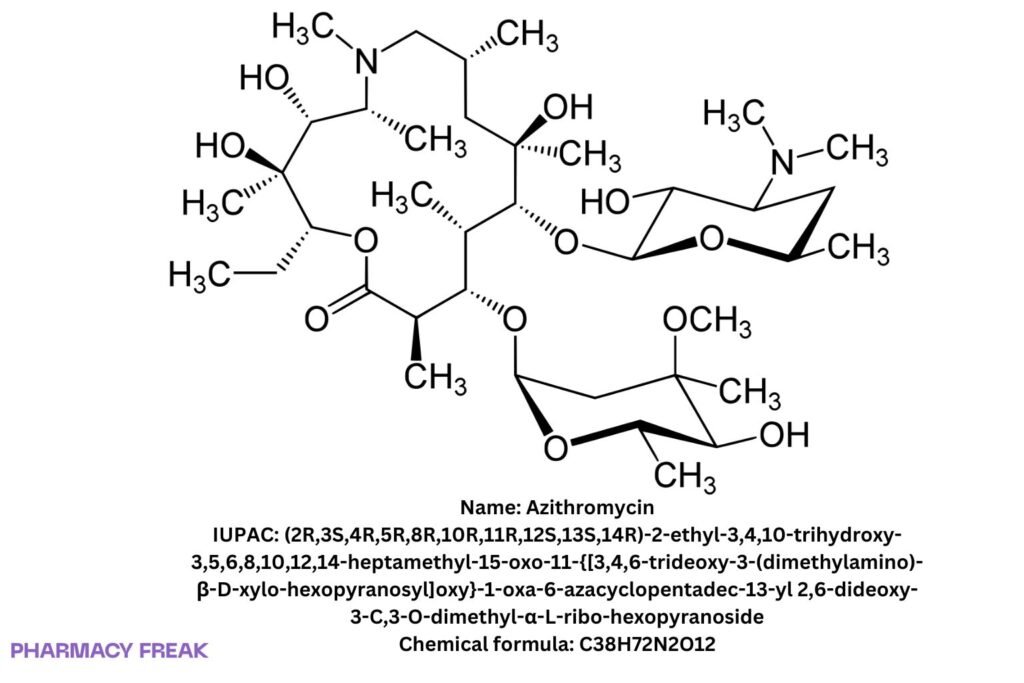
Structure
Weight
~748.98–749 g/mol (anhydrous base)
Chemical Formula
C₃₈H₇₂N₂O₁₂
Synonyms
9-deoxy-9a-aza-9a-methyl-9a-homoerythromycin A; azithromycin anhydrous; azithromycin dihydrate (hydrate form)
External IDs
CAS (base): 83905-01-5; PubChem CID: 447043 / 55185; UNII (anhydrous): J2KLZ20U1M; UNII (unspecified): F94OW58Y8V; ATC: J01FA10
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Treatment of mild–moderate infections due to susceptible organisms (e.g., community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial sinusitis, acute otitis media, pharyngitis/tonsillitis when appropriate, uncomplicated genital chlamydia, skin/soft-tissue); ophthalmic forms for bacterial conjunctivitis; part of MAC prophylaxis/therapy per guidelines.
Associated Conditions
Atypical respiratory pathogens (Mycoplasma, Chlamydophila, Legionella), travel/enteric pathogens where indicated, STI protocols.
Associated Therapies
With ceftriaxone for gonorrhea regimens (jurisdiction-specific), with ethambutol/others for MAC; avoid routine macrolide combination with other QT-prolonging agents.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
No boxed warning. Contraindicated with known azithromycin/macrolide hypersensitivity. Major warnings: QT prolongation/torsades, hepatotoxicity, infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, C. difficile–associated diarrhea, myasthenia gravis exacerbation.
Pharmacodynamics
Bacteriostatic at typical exposures; concentration-dependent killing for some pathogens; extensive intracellular/tissue accumulation drives prolonged post-antibiotic effect.
Mechanism of action
Binds the 50S ribosomal subunit → inhibits translocation and protein synthesis.
Absorption
Oral absolute bioavailability ~34–38% (product/strength dependent). Food may increase Cmax without changing AUC for some tablets. Al/Mg antacids markedly reduce absorption—separate doses.
Volume of distribution
Very large (~25–35 L/kg) with high tissue levels and intracellular accumulation.
Protein binding
Concentration-dependent: ~51% at 0.02 µg/mL decreasing to ~7% at 2 µg/mL.
Metabolism
Limited hepatic metabolism; parent drug predominates.
Route of elimination
Primarily biliary/fecal as unchanged drug; minor urinary excretion.
Half-life
Terminal ~68 h (reflects tissue release; supports once-daily/short-course dosing).
Clearance
Hepatobiliary clearance predominates; renal function has limited effect on total exposure.
Adverse Effects
GI upset, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea; less frequent: headache, taste disturbance; serious: QT prolongation/arrhythmia, hepatotoxicity, hypersensitivity, CDAD.
Toxicity
Overdose: supportive care; monitor ECG/electrolytes in at-risk patients.
Pathways
Ribosomal protein synthesis inhibition; hepatobiliary excretion; tissue sequestration.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No required PGx. Clinical risk varies with cardiac comorbidity, electrolytes, and co-administered QT-prolonging drugs.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
QT-prolonging agents (e.g., class IA/III antiarrhythmics, certain antipsychotics, fluoroquinolones): additive arrhythmia risk.
Al/Mg antacids, sucralfate, iron, zinc: chelation/adsorption → ↓ absorption; separate dosing.
Warfarin: monitor INR (case variability).
Digoxin: possible ↑ levels via microbiome/P-gp effects; monitor.
Ergot derivatives: avoid (class precaution across macrolides).
Food Interactions
Food can raise Cmax for some tablets without changing AUC; follow product labeling for meal timing.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
J01FA10 (macrolides, systemic use)
Drug Categories
Macrolide/azalide antibiotic; Protein-synthesis inhibitor; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
15-membered azalide macrolide with desosamine and cladinose sugars; tertiary dimethylamino substituent.
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use); target bacteria susceptible to macrolides
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
J2KLZ20U1M (azithromycin anhydrous); F94OW58Y8V (unspecified form)
CAS number
83905-01-5 (base)
InChI Key
MQTOSJVFKKJCRP-BICOPXKESA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C38H72N2O12/c1-15-27-38(10,46)31(42)24(6)40(13)19-20(2)17-36(8,45)33(52-35-29(41)26(39(11)12)16-21(3)48-35)22(4)30(23(5)34(44)50-27)51-28-18-37(9,47-14)32(43)25(7)49-28/h20-33,35,41-43,45-46H,15-19H2,1-14H3/t20-,21-,22+,23-,24-,25+,26+,27-,28+,29-,30+,31-,32+,33-,35+,36-,37-,38-/m1/s1
IUPAC Name
(2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-15-oxo-11-{[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadec-13-yl 2,6-dideoxy-3-C,3-O-dimethyl-α-L-ribo-hexopyranoside
SMILES
6. References
PubChem Compound Summary — azithromycin: formula C38H72N2O12; MW ~749 g/mol; CAS 83905-01-5; identifiers. PubChem+1
FDA GSRS/UNII — J2KLZ20U1M (anhydrous) with InChIKey MQTOSJVFKKJCRP-BICOPXKESA-N; F94OW58Y8V (unspecified). precision.fda.gov+1
DailyMed labeling — bioavailability ~34%, food ↑Cmax without AUC change (600-mg tablets), protein binding 51%→7% (conc-dependent), and major warnings (QT, hepatotoxicity, CDAD, MG). DailyMed+1
ATC/DDD Index — J01FA10 azithromycin classification and DDDs. ATCDDD
StatPearls — tissue penetration/intracellular accumulation, protein-binding profile. NCBI
Clinical PK literature — Vd ~25–35 L/kg, biliary/fecal excretion of unchanged drug. PubMed
Sigma-Aldrich/Merck Index/Tocris — InChI/InChIKey confirmation, MW ~748.98–749 g/mol. MilliporeSigma+2Merck Index+2

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com