Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
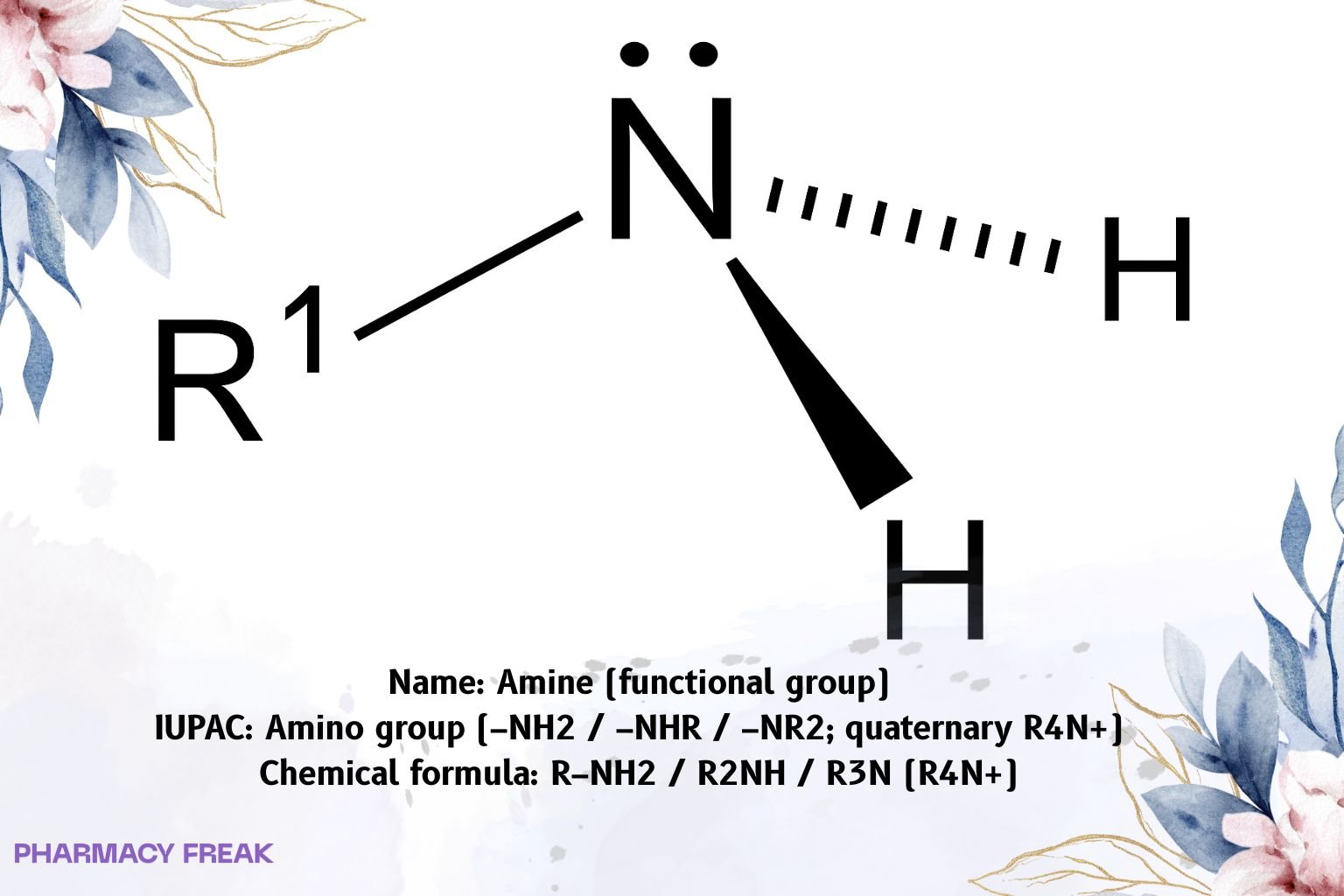
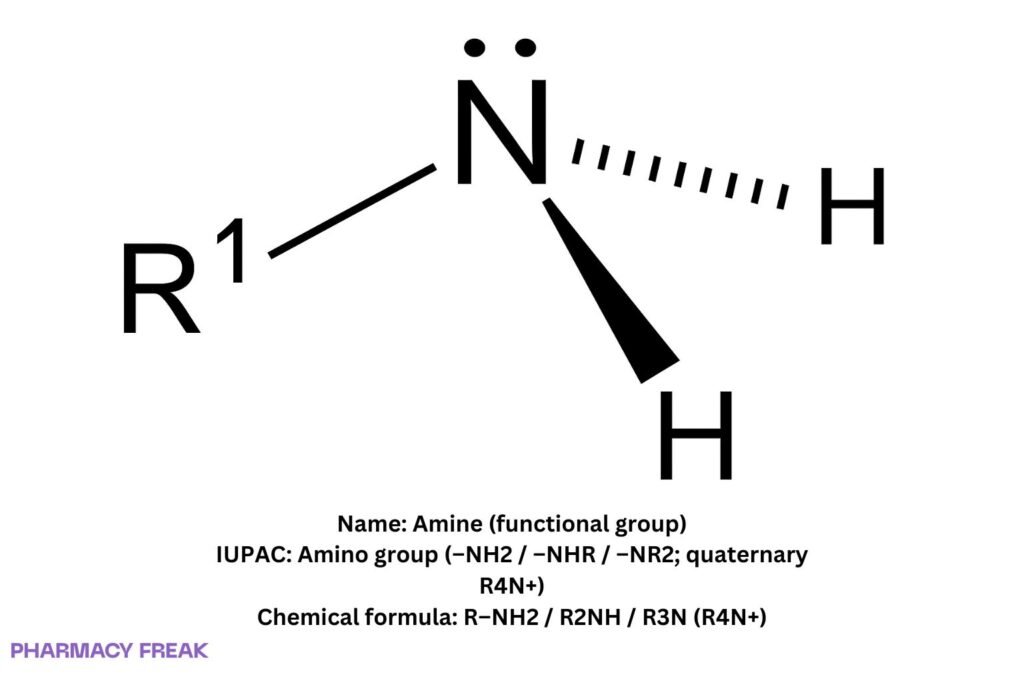
Amine denotes the amino functional group in which nitrogen bears one to three carbon substituents: primary (R–NH₂), secondary (R₂NH), tertiary (R₃N); quaternary ammonium (R₄N⁺) is permanently charged. Typical basicity (pKₐH): aliphatic amines ~9–11; anilines ~4–6 (weaker). Strong hydrogen bonding elevates boiling points vs hydrocarbons; amines are H-bond donors (1°/2°) and acceptors (all).
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
Amine (amino functional group)
Background
Subclasses: aliphatic, aromatic (anilines), heterocyclic; salts with mineral/organic acids improve aqueous solubility (e.g., HCl, sulfate, tartrate salts). Spectroscopy: IR N–H stretch 3300–3500 cm⁻¹ (1°: two bands; 2°: one; 3°: none), C–N stretch ~1020–1250 cm⁻¹; ¹H NMR N–H often broad/solvent-exchangeable.
Modality
Functional group (class of small molecules)
Groups
Endogenous metabolites and exogenous chemicals; core pharmacophore in many APIs
Structure
Weight
Not applicable (class)
Chemical Formula
R–NH₂ / R₂NH / R₃N (quaternary: R₄N⁺)
Synonyms
Amino group; Alkanamine/Aniline (subclasses); Trialkylamine; Quaternary ammonium (salt)
External IDs
Not applicable (class)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not a drug; functional group used across medicines.
Associated Conditions
Widespread in neurotransmitters, amino acids, alkaloids, and pharmaceuticals.
Associated Therapies
Medicinal chemistry: protonatable amine → water-soluble salt, tertiary amine for receptor ionic contacts, quaternary ammonium for peripheral restriction.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable at group level.
Pharmacodynamics
Chemical basicity: protonation ↔ deprotonation equilibrium governs ionization, permeability, target binding, and salt formation.
Mechanism of action
Chemical, not pharmacologic: Lewis base; nucleophilic at N; forms amides (acylation), imines/enamines (with carbonyls), quaternary salts (alkylation).
Absorption
Ionization (pH-dependent) controls membrane crossing: unionized base permeates membranes; ammonium salts enhance dissolution and may reduce permeability.
Volume of distribution / Protein binding / Metabolism / Elimination / Half-life / Clearance
Scaffold-dependent (not defined at group level).
Adverse Effects / Toxicity
Not applicable to the group per se.
Pathways
High-yield transformations: reductive amination, acylation → amide, alkylation → 4° ammonium, Gabriel synthesis (1° amines), Hofmann elimination (from 4° ammonium hydroxides), diazotization/Sandmeyer (anilines), carbamate/urea formation.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Not applicable.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Chemical level: salt formation with acids, metal coordination, H-bonding/ionic contacts in proteins and receptors. Quaternary ammonium groups interact with anion exchangers and ACh receptors (scaffold dependent).
Food Interactions
pH and co-solutes modulate ionization and dissolution (formulation dependent).
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None (functional group)
Drug Categories
Functional group; Basic heteroatom motif; Pharmacophore
Chemical Taxonomy
sp³ nitrogen (pyramidal; inverts via umbrella motion unless quaternary); basic Lewis site; 1°/2° N–H donors, all are H-bond acceptors; quaternary ammonium is permanently cationic.
Affected organisms
Not applicable
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII / CAS / InChI / InChIKey
Not applicable for the class.
Generic SMILES: RNH2 / RN(R)R / N+(R)R
IUPAC Name
Amine functional group (amino group)
6. References
IUPAC Gold Book — definitions of amine, ammonium, and basicity; nomenclature conventions.
Clayden, Greeves, Warren. Organic Chemistry — amine structure/basicity, spectroscopy, and reactivity (acylation, alkylation, reductive amination).
March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry — mechanistic detail (Gabriel synthesis, Hofmann elimination, diazotization/Sandmeyer for anilines).
Silverstein et al., Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds — IR/NMR signatures of amines.

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com