Table of Contents
Introduction
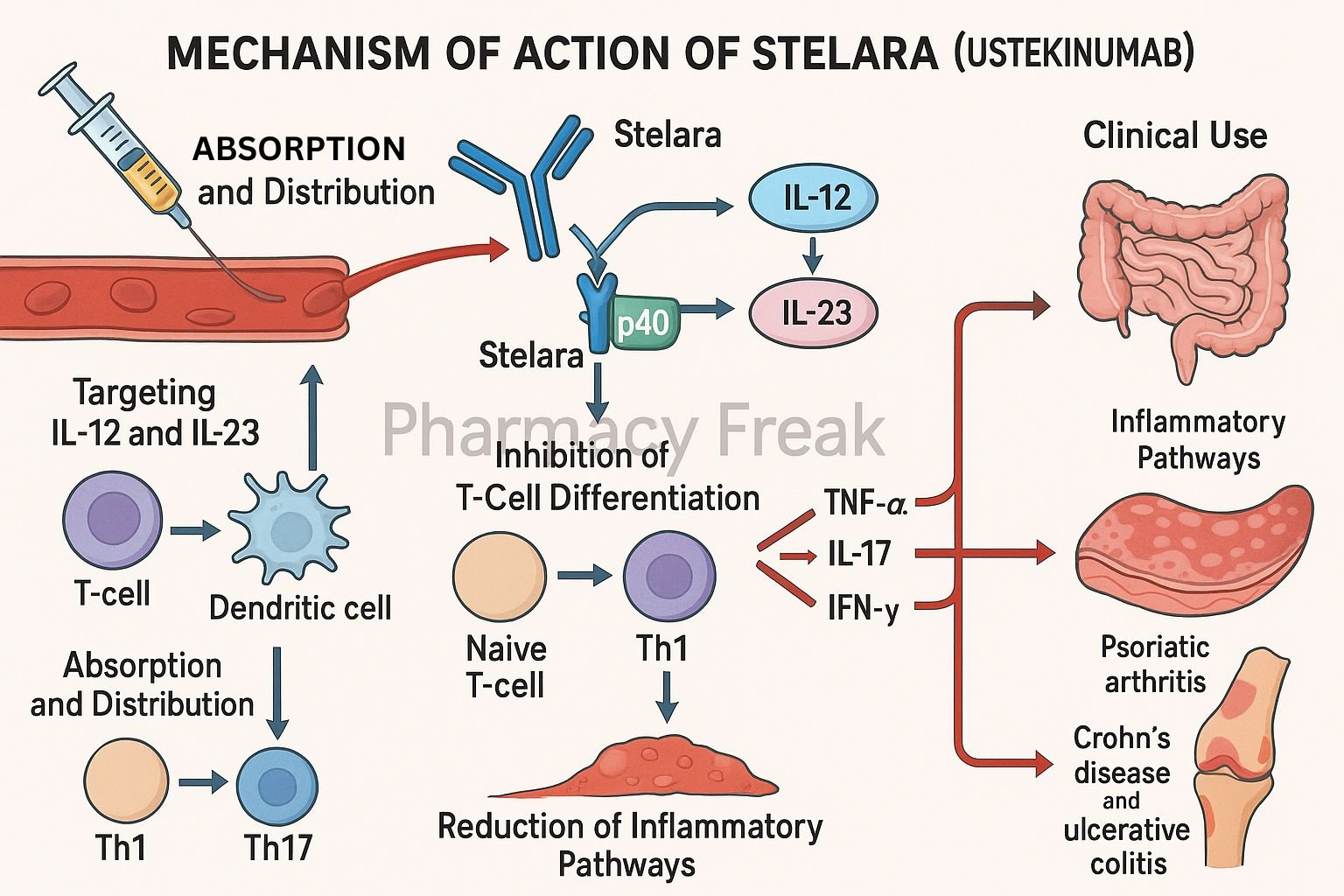
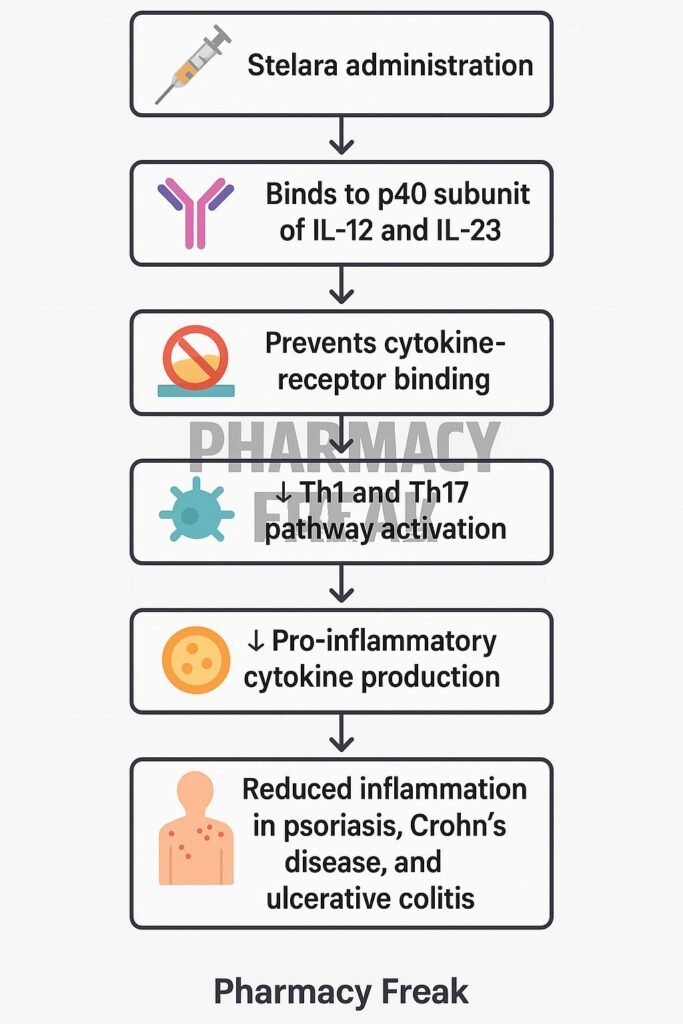
Stelara (ustekinumab) is a fully human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody designed to target key cytokines involved in immune-mediated diseases. It selectively binds to the p40 subunit common to interleukin-12 (IL-12) and interleukin-23 (IL-23), blocking their interaction with cell surface receptors. Stelara is approved for several chronic inflammatory conditions including plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Binding to p40 Subunit
Ustekinumab binds with high affinity to the p40 protein subunit that is shared by IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines. - Prevention of Receptor Binding
This binding inhibits the interaction of IL-12 and IL-23 with their receptor (IL-12Rβ1) on the surface of immune cells. - Inhibition of Th1 and Th17 Pathways
IL-12 is essential for Th1 differentiation, while IL-23 is crucial for the maintenance and activation of Th17 cells. Blocking these pathways reduces downstream inflammatory cytokines like IFN-γ, IL-17, and TNF-α. - Suppression of Inflammatory Response
By inhibiting Th1 and Th17 mediated pathways, ustekinumab reduces chronic inflammation in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. - No Fc-Mediated Cytotoxicity
As an IgG1κ antibody, ustekinumab does not mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), contributing to its safety profile.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Subcutaneous or Intravenous |
| Bioavailability | ~57% (subcutaneous) |
| Time to Peak | 7 to 14 days |
| Half-life | ~20 days (range: 15–32 days) |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic degradation |
| Excretion | Non-renal, non-biliary |
Clinical Uses
- Moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (≥6 years old)
- Active psoriatic arthritis
- Moderate to severe Crohn’s disease
- Moderate to severe ulcerative colitis
Adverse Effects
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Headache and fatigue
- Injection site reactions
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Rare risk of serious infections and malignancies
Comparative Analysis
| Biologic | Target | Dosing Interval | Approved Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ustekinumab | IL-12/IL-23 p40 | Every 8–12 weeks | Psoriasis, PsA, Crohn’s, UC |
| Secukinumab | IL-17A | Monthly | Psoriasis, PsA |
| Adalimumab | TNF-α | Every 2 weeks | Psoriasis, PsA, RA, Crohn’s, UC |
MCQs
1. Ustekinumab inhibits which cytokines?
a) IL-6 and IL-1β
b) IL-12 and IL-23
c) IL-17A and IL-4
d) TNF-α and IL-10
Answer: b) IL-12 and IL-23
2. The shared subunit targeted by Stelara is:
a) p28
b) p19
c) p40
d) p65
Answer: c) p40
3. Which T-cell pathways are downregulated by ustekinumab?
a) Th2 and Treg
b) Th1 and Th17
c) Th9 and Th2
d) Treg and Th22
Answer: b) Th1 and Th17
4. Ustekinumab is classified as:
a) Chimeric monoclonal antibody
b) Fully human monoclonal antibody
c) Humanized monoclonal antibody
d) Murine monoclonal antibody
Answer: b) Fully human monoclonal antibody
5. One of the serious adverse effects is:
a) Pancreatitis
b) Cardiac arrhythmia
c) Serious infection
d) Cataracts
Answer: c) Serious infection
6. Which condition is NOT an approved indication?
a) Psoriasis
b) Rheumatoid arthritis
c) Crohn’s disease
d) Ulcerative colitis
Answer: b) Rheumatoid arthritis
7. Time to reach peak concentration after SC injection is:
a) 24 hours
b) 3 days
c) 7–14 days
d) 30 minutes
Answer: c) 7–14 days
8. Primary mode of elimination of ustekinumab is:
a) Renal excretion
b) Hepatic metabolism
c) Proteolytic degradation
d) Fecal elimination
Answer: c) Proteolytic degradation
9. Th17 cells primarily secrete:
a) IL-4
b) IL-5
c) IL-17
d) IL-10
Answer: c) IL-17
10. Mechanism of action includes inhibition of:
a) B-cell activity
b) T-cell proliferation
c) IL-12/IL-23 signaling
d) TNF-α production directly
Answer: c) IL-12/IL-23 signaling
11. The antibody isotype of ustekinumab is:
a) IgA
b) IgG1κ
c) IgM
d) IgE
Answer: b) IgG1κ
12. Ustekinumab dosing frequency is typically:
a) Weekly
b) Every 4 weeks
c) Every 8–12 weeks
d) Daily
Answer: c) Every 8–12 weeks
13. Major cytokine involved in Th1 activation is:
a) IL-17
b) IL-10
c) IL-12
d) IL-5
Answer: c) IL-12
14. Fc-mediated cytotoxicity with Stelara is:
a) Common
b) Absent
c) Dose-dependent
d) Inhibitory only
Answer: b) Absent
15. The receptor involved in IL-12/IL-23 signaling is:
a) IL-17R
b) IL-2R
c) IL-12Rβ1
d) TNFR1
Answer: c) IL-12Rβ1
FAQs
1. What is Stelara used for?
It is used to treat psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
2. How does Stelara differ from anti-TNF drugs?
It targets upstream cytokines (IL-12 and IL-23), while anti-TNF drugs neutralize TNF-α directly.
3. Is Stelara safe in children?
It is approved for children ≥6 years with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
4. Can Stelara be self-injected?
Yes, the subcutaneous formulation allows for self-administration.
5. Is routine lab monitoring required?
Routine monitoring is not mandatory but assess for infections and TB before initiation.
References
- Stelara Prescribing Information – Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- DrugBank: Ustekinumab
- StatPearls: Ustekinumab
- FDA Stelara Label – DailyMed
- PubMed Review on IL-12/23 Inhibition

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com