Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Morphine is a natural phenanthrene (morphinan) opioid indicated for moderate–severe pain when alternative treatments are inadequate. Analgesia, respiratory/CNS depression, miosis, constipation, histamine-mediated pruritus, tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal are characteristic class effects.
Brand Names
MS Contin, Kadian, Oramorph, Statex; numerous generics (region-dependent)
Name
Morphine
Background
Primary alkaloid of Papaver somniferum (opium poppy); supplied mainly as sulfate or hydrochloride salts in immediate- and extended-release oral, parenteral, epidural, and intrathecal formulations.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription/controlled substance (jurisdiction-specific scheduling)
Structure
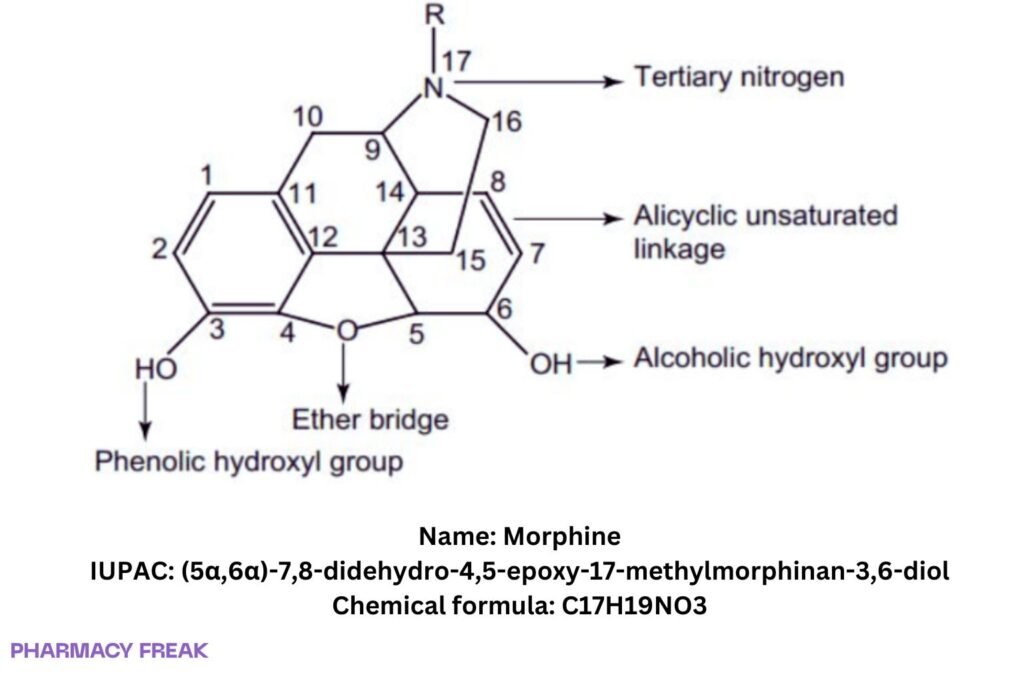
Weight
~285.34 g/mol (free base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₇H₁₉NO₃
Synonyms
3,6-dihydroxy-N-methylmorphinan; (5α,6α)-7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3,6-diol; (−)-morphine
External IDs
CAS (base): 57-27-2; PubChem CID: 5288826; UNII: 76I7G6D29C; ATC: N02AA01; KEGG: D08233; ChEBI: 17303
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Management of moderate to severe acute or chronic pain where opioid analgesia is appropriate and alternatives are insufficient.
Associated Conditions
Cancer pain, palliative care, postoperative pain, vaso-occlusive crises (sickle cell), trauma; neuraxial use for obstetric/operative analgesia.
Associated Therapies
Monotherapy or combined in multimodal regimens (acetaminophen/NSAIDs, adjuvants). Neuraxial single-dose or infusion per protocol.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Boxed warnings (class): addiction, abuse, misuse; life-threatening respiratory depression; accidental ingestion; neonatal opioid withdrawal; risks with benzodiazepines/CNS depressants. Contraindications include significant respiratory depression, acute/severe bronchial asthma without monitoring, GI obstruction, and known hypersensitivity.
Pharmacodynamics
μ-opioid receptor agonist → inhibition of ascending nociceptive transmission and modulation in brain/spinal cord; κ/δ agonism contributes. Histamine release may cause vasodilation/pruritus.
Mechanism of action
G-protein–coupled μ-receptor activation ↓ cAMP, opens K⁺ channels, inhibits Ca²⁺ influx → reduced neurotransmitter release and neuronal excitability.
Absorption
Oral bioavailability ~20–40% (high first-pass metabolism); t_max ~0.5–1 h (IR; formulation-dependent). Food effect minimal for many products; follow label.
Volume of distribution
~1–6 L/kg (widely distributed; limited BBB penetration vs more lipophilic opioids).
Protein binding
~20–35% (albumin/α₁-acid glycoprotein).
Metabolism
Predominantly UGT2B7 glucuronidation to morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G, major, inactive/aversive) and morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G, active analgesic); minor N-demethylation.
Route of elimination
Primarily renal as glucuronides; ~5–10% unchanged; minor biliary excretion/enterohepatic cycling.
Half-life
~2–4 h (IV ~2 h; prolonged in hepatic/renal impairment).
Clearance
~20–30 mL/min/kg (population-dependent). Accumulation of M6G in renal impairment.
Adverse Effects
Sedation, dizziness, nausea/vomiting, constipation, pruritus, urinary retention; serious: respiratory depression, hypotension, adrenal insufficiency, androgen deficiency, anaphylactoid reactions.
Toxicity
Overdose: miosis, coma, respiratory depression; treat with airway support and naloxone (repeat/infuse as needed due to metabolite kinetics).
Pathways
μ-receptor signaling; UGT2B7 conjugation; renal elimination of conjugates.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No required PGx. Variability in UGT2B7, ABCB1 (P-gp), and renal function influences exposure/response; caution with renal impairment (M6G accumulation).
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
CNS depressants (benzodiazepines, alcohol, sedatives): additive respiratory/CNS depression.
Mixed agonist–antagonists/partial agonists (buprenorphine, nalbuphine, pentazocine): reduced effect/precipitated withdrawal.
MAOIs: avoid within recommended washouts (serotonergic/CNS risks).
P-gp and enzyme modulators: can alter CNS penetration and exposure (clinical relevance product- and patient-specific).
Food Interactions
Product-specific; many ER products unaffected by food; follow individual labeling.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
N02AA01 (natural opium alkaloids — morphine)
Drug Categories
Opioid analgesic; μ-receptor agonist; Small molecule; Natural product
Chemical Taxonomy
Morphinan/phenanthrene alkaloid; 4,5-epoxy bridge, 3,6-diol; chiral, rigid polycyclic scaffold
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
76I7G6D29C
CAS number
57-27-2
InChI Key
BQJCRHHNABKAKU-KBQPJGBKSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C17H19NO3/c1-18-7-6-17-10-3-5-13(20)16(17)21-15-12(19)4-2-9(14(15)17)8-11(10)18/h2-5,10-11,13,16,19-20H,6-8H2,1H3/t10-,11+,13-,16-,17-/m0/s1
IUPAC Name
(5α,6α)-7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3,6-diol
SMILES
CN1CC[C@@]23C4=CC(O)=C5O[C@H]2C@@HC=CC[C@H]3[C@H]1C45
6. References
PubChem Compound Summary — Morphine (CID 5288826); formula C17H19NO3, mass ~285.34 g/mol; identifiers (SMILES/InChI/Key). PubChem
NIST Chemistry WebBook — Standard InChI and InChIKey BQJCRHHNABKAKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N; CAS 57-27-2. NIST WebBook+1
FDA GSRS/UNII — UNII 76I7G6D29C record for morphine. precisionFDA
ATC/DDD Index — N02AA01 (morphine) classification. FHI+1
IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology — ligand entry, μ-agonist class context and identifiers. guidetopharmacology.org
StatPearls (2025 update) — bioavailability ~<40%, Vd 1–6 L/kg, protein binding 20–35%, clearance ~20–30 mL/min/kg, t½ ~2 h IV, renal excretion of glucuronides with ~10% unchanged. NCBI
KEGG DRUG — morphine/morphine sulfate entries, ATC code and pathway notes. KEGG+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
