Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) indicated for major depressive disorder, obsessive–compulsive disorder, bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, and premenstrual dysphoric disorder; pediatric indications include MDD and OCD.
Brand Names
Prozac, Sarafem; multiple generics
Name
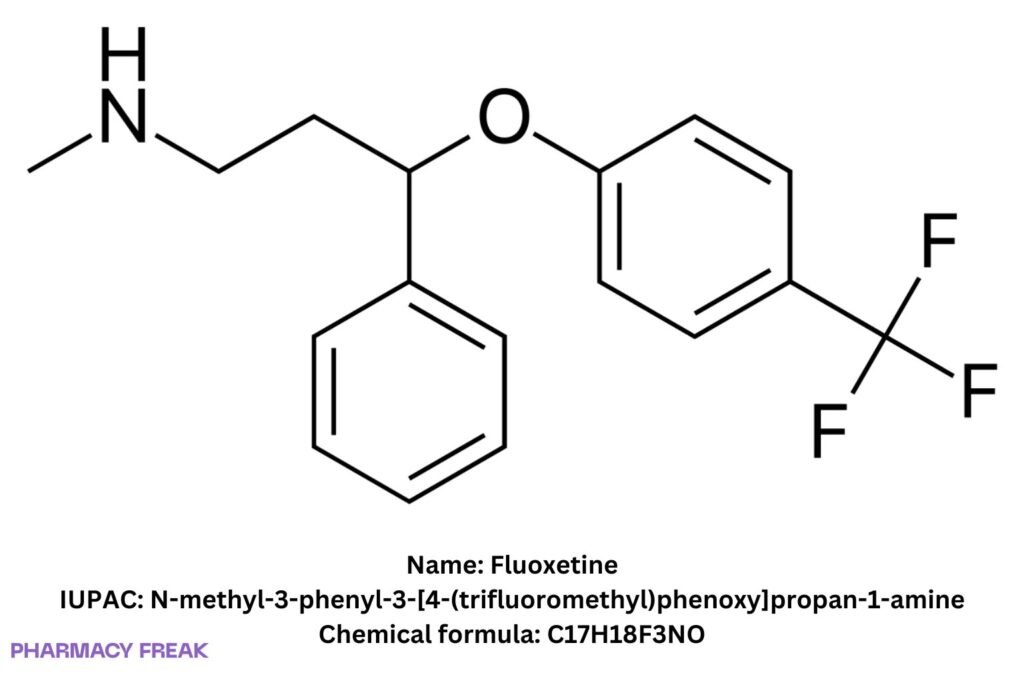
Fluoxetine
Background
Racemic SSRI introduced in the late 1980s; marketed commonly as the hydrochloride salt for oral capsules/tablets/solutions; active metabolite norfluoxetine contributes to prolonged effect.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
Weight
~309.33 g/mol (base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₇H₁₈F₃NO (base)
Synonyms
N-methyl-3-phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propan-1-amine; fluoxetine free base; fluoxetine hydrochloride (salt)
External IDs
CAS (base): 54910-89-3; CAS (HCl): 56296-78-7
PubChem CID (base): 3386
UNII (base): 01K63SUP8D; UNII (HCl): I9W7N6B1KJ
ATC: N06AB03
2. Pharmacology
Indication
MDD, OCD, bulimia nervosa, panic disorder, PMDD; pediatric MDD/OCD per labeling.
Associated Conditions
Anxiety disorders, treatment-resistant depression when used in fixed combination with olanzapine (region-specific).
Associated Therapies
Monotherapy; fixed-dose olanzapine/fluoxetine for bipolar depression or TRD (jurisdiction-dependent).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Boxed warning: antidepressants ↑ risk of suicidal thoughts/behaviors in children, adolescents, young adults.
Contraindicated with MAOIs (including linezolid and IV methylene blue), pimozide, thioridazine. Allow adequate washout intervals.
Pharmacodynamics
Potent SERT inhibition → ↑ synaptic serotonin; minimal direct NET/DAT inhibition at therapeutic exposure; active norfluoxetine maintains SERT blockade.
Mechanism of action
Reversible blockade of presynaptic serotonin transporter; downstream receptor adaptations drive clinical response.
Absorption
Oral bioavailability ~60–80%; tₘₐₓ ~6–8 h; food effect not clinically significant.
Volume of distribution
Extensive tissue distribution; crosses placenta and appears in breast milk.
Protein binding
~94–95% (albumin, α₁-acid glycoprotein).
Metabolism
Hepatic CYP2D6 (major) → norfluoxetine (active); both inhibit CYP2D6.
Route of elimination
Primarily urinary (~80%) and fecal (~15%) as metabolites/parent.
Half-life
Fluoxetine: ~1–3 days (acute), ~4–6 days (chronic).
Norfluoxetine: ~8–10 days on average; longer ranges reported.
Clearance
Hepatic clearance with auto-inhibition over time; renal function has limited effect on total exposure.
Adverse Effects
Nausea, insomnia, anxiety, headache, sexual dysfunction; hyponatremia/SIADH (elderly risk), QT prolongation (caution with risk factors), bleeding with anticoagulants/antiplatelets/NSAIDs, mania/hypomania in bipolar disorder.
Toxicity
Overdose usually benign to moderate; monitor for serotonin toxicity, QT effects, and seizures.
Pathways
SERT inhibition; CYP2D6 biotransformation; biliary/renal handling of metabolites.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
CYP2D6 poor metabolizers: ↑ exposure and longer persistence; consider interaction-driven phenoconversion (CYP2D6 inhibition of co-meds).
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Absolute: MAOIs (including linezolid/IV methylene blue), pimozide, thioridazine.
Major: other serotonergic agents (risk of serotonin syndrome); CYP2D6 substrates with narrow TI (e.g., thioridazine, pimozide, TCAs); tamoxifen (↓ endoxifen due to CYP2D6 inhibition); warfarin/antiplatelets/NSAIDs (↑ bleeding risk); QT-prolonging drugs.
Food Interactions
No clinically meaningful food effect; dose consistently.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
N06AB03 (SSRIs)
Drug Categories
Antidepressant; SSRI; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Diphenylpropylamine aryl ether with para-trifluoromethyl substituent; tertiary amine
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
01K63SUP8D (fluoxetine, base)
CAS number
54910-89-3 (base); 56296-78-7 (hydrochloride)
InChI Key
RTHCYVBBDHJXIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (base)
InChI
InChI=1S/C17H18F3NO/c1-21-12-11-16(13-5-3-2-4-6-13)22-15-9-7-14(8-10-15)17(18,19)20/h2-10,16,21H,11-12H2,1H3
IUPAC Name
N-methyl-3-phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propan-1-amine
SMILES
CNCCC(c1ccccc1)Oc2ccc(cc2)C(F)(F)F
6. References
PubChem — formula C₁₇H₁₈F₃NO, MW 309.33 g/mol, identifiers (CID 3386); IUPAC/SMILES. PubChem
NIST WebBook — Standard InChI for fluoxetine base; formula and mass. NIST WebBook
FDA GSRS/UNII — fluoxetine base 01K63SUP8D; fluoxetine HCl I9W7N6B1KJ, salt InChIKey GIYXAJPCNFJEHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N. gsrs.ncats.nih.gov+1
ATC/DDD Index — N06AB03 classification and DDD. atcddd.fhi.no
DailyMed — long half-lives of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine; persistence after discontinuation; PK ranges. DailyMed+2DailyMed+2
DrugBank/clinical PK summaries — half-life ranges (parent 1–3/4–6 days; norfluoxetine 4–16 days); interaction framework. DrugBank
Wikipedia (consolidated pharmacokinetic table with primary citations) — bioavailability 60–80%, protein binding 94–95%, urine 80%/feces 15%. Wikipedia

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
